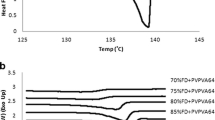
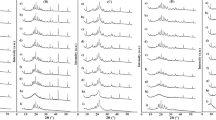
ABSTRACT
Purpose
To develop a method for drawing statistical inferences from differences between multiple experimental pair distribution function (PDF) transforms of powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) data.
Methods
The appropriate treatment of initial PXRD error estimates using traditional error propagation algorithms was tested using Monte Carlo simulations on amorphous ketoconazole. An amorphous felodipine:polyvinyl pyrrolidone:vinyl acetate (PVPva) physical mixture was prepared to define an error threshold. Co-solidified products of felodipine:PVPva and terfenadine:PVPva were prepared using a melt-quench method and subsequently analyzed using PXRD and PDF. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) was used as an additional characterization method.
Results
The appropriate manipulation of initial PXRD error estimates through the PDF transform were confirmed using the Monte Carlo simulations for amorphous ketoconazole. The felodipine:PVPva physical mixture PDF analysis determined ±3σ to be an appropriate error threshold. Using the PDF and error propagation principles, the felodipine:PVPva co-solidified product was determined to be completely miscible, and the terfenadine:PVPva co-solidified product, although having appearances of an amorphous molecular solid dispersion by DSC, was determined to be phase-separated.
Conclusions
Statistically based inferences were successfully drawn from PDF transforms of PXRD patterns obtained from composite systems. The principles applied herein may be universally adapted to many different systems and provide a fundamentally sound basis for drawing structural conclusions from PDF studies.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DSC:
-
differential scanning calorimetry
- PDF:
-
pair distribution function
- PVPva:
-
polyvinyl pyrrolidone:vinyl acetate copolymer
- PXRD:
-
powder X-ray diffraction
- G :
-
pair distribution function
- r :
-
inter-atomic radial distance
- ρ :
-
local number density
- ρ 0 :
-
average number density
- Q :
-
scattering vector magnitude
- S :
-
structure function
- σ:
-
standard error
- T g :
-
glass transition temperature
- h0 :
-
statistical null hypothesis
- hA :
-
statistical alternative hypothesis
- R :
-
sum-of-squares difference agreement factor
REFERENCES
Bates S, Kelly RC, Ivanisevic I, Schields P, Zografi G, Newman AW. Assessment of defects and amorphous structure produced in raffinose pentahydrate upon dehydration. J Pharm Sci. 2007;96:1418–33.
Atassi F, Mao C, Masadeh AS, Byrn SR. Solid-state characterization of amorphous and mesomorphous calcium ketoprofen. J Pharm Sci. 2010;99:3684–97.
Sheth AR, Bates S, Muller FX, Grant DJW. Local structure in amorphous phases of piroxicam from powder x-ray diffractometry. Cryst Growth Des. 2005;5:571–8.
Heinz A, Strachan CJ, Atassi F, Gordon KC, Rades T. Characterizing an amorphous system exhibiting trace crystallinity: a case study with saquinavir. Cryst Growth Des. 2008;8:119–27.
Moore MD, Steinbach AM, Buckner IS, Wildfong PLD. A structural investigation into the compaction behavior of pharmaceutical composites using powder X-ray diffraction and total scattering analysis. Pharm Res. 2009;26:2429–37.
Newman A, Engers D, Bates S, Ivanisevic I, Kelly RC, Zografi G. Characterization of amorphous API:Polymer mixtures using X-ray powder diffraction. J Pharm Sci. 2008;97:4840–56.
Nollenberger K, Gryczke A, Meier C, Dressman J, Schmidt MU, Bruhne S. Pair distribution function X-ray analysis explains dissolution characteristics of felodipine melt extrusion products. J Pharm Sci. 2009;98:1476–86.
Ivanisevic I, Bates S, Chen P. Novel methods for the assessment of miscibility of amorphous drug-polymer dispersions. J Pharm Sci. 2009;98:3373–86.
Peterson PF, Bozin ES, Proffen T, Billinge SJL. Improved measures of quality for the atomic pair distribution function. J Appl Crystallogr. 2003;36:53–64.
Toby BH, Billinge SJL. Determination of standard uncertainties in fits to pair distribution functions. Acta Crystallogr A. 2004;60:315–7.
Toby BH, Egami T. Accuracy of pair distribution function analysis applied to crystalline and non-crystalline materials. Acta Crystallogr A. 1992;48:336–46.
Sekiguchi K, Obi N. Studies on absorption of eutectic mixtures. I. A comparison of the behavior of eutectic mixtures of sulphathiazole and that of ordinary sulphathiazole in man. Chem Pharm Bull. 1961;9:866–72.
Couchman PR, Karasz FE. A classical thermodynamic discussion of the effect of composition on glass-transition temperatures. Macromolecules. 1978;11:117–9.
Egami T, Billinge SJL. Underneath the Bragg Peaks. Structural analysis of complex materials. Oxford: Elsevier; 2003.
Warren BE. X-ray diffraction. New York: Dover Publications, Inc; 1990.
Metropolis N, Ulam S. The Monte Carlo method. J Am Stat Assoc. 1949;44:335–41.
Prince E. Mathematical techniques in crystallography and materials science. New York: Springer; 2004.
Cullity BD, Stock SR. Elements of X-ray diffraction. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall; 2001.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
MM would like to acknowledge a pre-doctoral fellowship from the American Foundation for Pharmaceutical Education.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moore, M.D., Shi, Z. & Wildfong, P.L.D. Structural Interpretation in Composite Systems Using Powder X-ray Diffraction: Applications of Error Propagation to the Pair Distribution Function. Pharm Res 27, 2624–2632 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-010-0259-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-010-0259-7