Abstract
Purpose
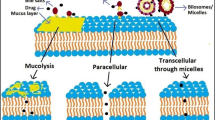
Traditionally, the oral route cannot be employed for the delivery of macromolecular drugs such as proteins and peptides due, in large part, to limited transport across the epithelial membrane. This particular challenge can potentially be addressed through the use of chemical permeation enhancers, which affect transcellular and/or paracellular transport routes. Although certain permeation enhancers have been proposed for use in oral delivery, potential for application is often unclear when the route of enhancer action is unknown.
Methods
A combination of theory and experiments was developed for determining mechanism of enhancer action. The effect of 51 enhancers on Caco-2 cells was studied using TEER, MTT, and LDH assays.
Results
The mechanistic details of intestinal permeability enhancement were uncovered for a broad set of enhancers in vitro. Understanding gained from enhancer mechanisms enabled the deduction of structure–function relationships for hydrophilic and hydrophobic permeation enhancers as well as the identification of a transcellular enhancer, 0.01% (w/v) palmityldimethyl ammonio propane sulfonate, which enabled the non-cytotoxic intracellular delivery of a model drug.
Conclusions
The results presented here emphasize the importance of understanding enhancer mechanism and uncover a zwitterionic surfactant capable of safely and effectively achieving intraepithelial drug delivery in vitro.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EP:
-
Enhancement potential
- K:
-
Mechanistic parameter
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- Log P:
-
Water-octanol partion coefficient
- LP:
-
LDH potential
- MTT:
-
Methyl thiazole tetrazolium
- PPS:
-
Palmityldimethyl ammonio propane sulfonate
- TEER:
-
Transepithelial electrical resistance
- TP:
-
Toxicity potential
References
S. K. Kim, D. Y. Lee, E. Lee, Y.-k. Lee, C. Y. Kim, H. T. Moon, and Y. Byun. Absorption study of deoxycholic acid–heparin conjugate as a new form of oral anti-coagulant. J. Control. Rel. 120:4–10 (2007).
K. M. Wood, G. Stone, and N. A. Peppas. Lectin functionalized complexation hydrogels for oral protein delivery. J. Control. Rel. 116:e66–e68 (2006).
M. Goldberg, and I. Gomez-Orellana. Challenges for the oral delivery of macromolecules. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2:289–295 (2003).
B. J. Aungst. Intestinal permeation enhancers. J. Pharm. Sci 89:429–442 (2000).
N. N. Salama, N. D. Eddington, and A. Fasano. Tight junction modulation and its relationship to drug delivery. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 58:15–28 (2006).
D. Bourdet, G. Pollack, and D. Thakker. Intestinal absorptive transport of the hydrophilic cation ranitidine: A kinetic modeling approach to elucidate the role of uptake and efflux transporters and paracellular vs. transcellular transport in Caco-2 cells. Pharm. Res. 23:1178–1187 (2006).
S. Maher, L. Feighery, D. Brayden, and S. McClean. Melittin as an epithelial permeability enhancer I: Investigation of its mechanism of action in Caco-2 monolayers. Pharm. Res. 24:1336–1345 (2007).
C. M. Meaney, and C. M. O’Driscoll. A comparison of the permeation enhancement potential of simple bile salt and mixed bile salt: Fatty acid micellar systems using the Caco-2 cell culture model. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 207:21–30 (2000).
T. Shimazaki, M. Tomita, S. Sadahiro, M. Hayashi, and S. Awazu. Absorption-enhancing effects of sodium caprate and palmitoyl carnitine in rat and human colons. Dig. Dis. Sci. 43:641–645 (1998).
S. M. van der Merwe, J. C. Verhoef, J. H. M. Verheijden, A. F. Kotze, and H. E. Junginger. Trimethylated chitosan as polymeric absorption enhancer for improved peroral delivery of peptide drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 58:225–235 (2004).
A. C. Chao, J. V. Nguyen, M. Broughall, J. Recchia, C. R. Kensil, P. E. Daddona, and J. A. Fix. Enhancement of intestinal model compound transport by DS-1, a modified Quillaja saponin. J. Pharm. Sci. 87:1395–1399 (1998).
T. Suzuki, and H. Hara. Difructose anhydride III and sodium caprate activate paracellular transport via different intracellular events in Caco-2 cells. Life Sciences 79:401–410 (2006).
E. Duizer, C. Van Der Wulp, C. H. M. Versantvoort, and J. P. Groten. Absorption enhancement, structural changes in tight junctions and cytotoxicity caused by palmitoyl carnitine in Caco-2 and IEC-18 cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 287:395–402 (1998).
S. Hess, V. Rotshild, and A. Hoffman. Investigation of the enhancing mechanism of sodium n-[8-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)amino]caprylate effect on the intestinal permeability of polar molecules utilizing a voltage clamp method. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 25:307–312 (2005).
T. Uchiyama, T. Sugiyama, Y. S. Quan, A. Kotani, N. Okada, T. Fujita, S. Muranishi, and A. Yamamoto. Enhanced permeability of insulin across the rat intestinal membrane by various absorption enhancers: Their intestinal mucosal toxicity and absorption-enhancing mechanism of n-lauryl-beta-D-maltopyranoside. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 51:1241–1250 (1999).
P. Sharma, M. V. S. Varma, H. P. S. Chawla, and R. Panchagnula. Relationship between lipophilicity of BCS class III and IV drugs and the functional activity of peroral absorption enhancers. Il Farmaco. 60:870–873 (2005).
A. A. Raoof, Z. Ramtoola, B. McKenna, R. Z. Yu, G. Hardee, and R. S. Geary. Effect of sodium caprate on the intestinal absorption of two modified antisense oligonucleotides in pigs. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 17:131–138 (2002).
T. W. Leonard, J. Lynch, M. J. McKenna, and D. J. Brayden. Promoting absorption of drugs in humans using medium-chain fatty acid-based solid dosage forms: GIPET. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 3:685–692 (2006).
E. K. Anderberg, T. Lindmark, and P. Artursson. Sodium caprate elicits dilatations in human intestinal tight junctions and enhances drug absorption by the paracellular route. Pharm. Res. 10:857–864 (1993).
J. D. Soderholm, H. Oman, L. Blomquist, J. Veen, T. Lindmark, and G. Olaison. Reversible increase in tight junction permeability to macromolecules in rat ileal mucosa in vitro by sodium caprate, a constituent of milk fat. Dig. Dis. Sci. 43:1547–1552 (1998).
M. Tomita, M. Hayashi, T. Horie, T. Ishizawa, and S. Awazu. Enhancement of colonic drug absorption by the transcellular permeation route. Pharm. Res. 5:786–789 (1988).
P. Sharma, M. V. S. Varma, H. P. S. Chawla, and R. Panchagnula. In situ and in vivo efficacy of peroral absorption enhancers in rats and correlation to in vitro mechanistic studies. Il Farmaco. 60:874–883 (2005).
M. Sakai, T. Imai, H. Ohtake, H. Azuma, and M. Otagiri. Effects of absorption enhancers on the transport of model compounds in Caco-2 cell monolayers: Assessment by confocal laser scanning microscopy. J. Pharm. Sci. 86:779–785 (1997).
M. Tomita, M. Hayashi, and S. Awazu. Absorption-enhancing mechanism of EDTA, caprate, and decanoylcarnitine in Caco-2 cells. J. Pharm. Sci. 85:608–611 (1996).
E. Fuller, C. Duckham, and E. Wood. Disruption of epithelial tight junctions by yeast enhances the paracellular delivery of a model protein. Pharm. Res. 24:37–47 (2007).
K. Whitehead, N. Karr, and S. Mitragotri. Safe and effective enhancers for oral drug delivery. Pharm Res. in press. DOI 10.1007/s11095-007-9488-9.
N. A. Motlekar, K. S. Srivenugopal, M. S. Wachtel, and B.-B. C. Youan. Oral delivery of low-molecular-weight heparin using sodium caprate as absorption enhancer reaches therapeutic levels. J. Drug Target 13:573–583 (2005).
B. Aspenstrom-Fagerlund, L. Ring, P. Aspenstrom, J. Tallkvist, N.-G. Ilback, and A. W. Glynn. Oleic acid and docosahexaenoic acid cause an increase in the paracellular absorption of hydrophilic compounds in an experimental model of human absorptive enterocytes. Toxicology 237:12–23 (2007).
G. Fotakis, and J. A. Timbrell. in vitro cytotoxicity assays: Comparison of LDH, neutral red, MTT and protein assay in hepatoma cell lines following exposure to cadmium chloride. Toxicol. Let. 160:171–177 (2006).
E. S. Swenson, and W. Curatolo. Intestinal permeability enhancement for proteins, peptides, and other polar drugs: Mechanisms and potential toxicity. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 8:39–92 (1992).
W. P. Soutter, P. Sasieni, and T. Panoskaltsis. Long-term risk of invasive cervical cancer after treatment of squamous cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Int. J. Cancer 118:2048–2055 (2006).
C. Pilette, B. Colinet, R. Kiss, S. Andre, H. Kaltner, H. J. Gabius, M. Delos, J. P. Vaerman, M. Decramer, and Y. Sibille. Increased galectin-3 expression and intraepithelial neutrophils in small airways in severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur. Respir. J. 29:914-922 (2007). DOI 09031936.00073005.
K. Ishida, M. Takaai, and Y. Hashimoto. Pharmacokinetic analysis of transcellular transport of quinidine across monolayers of human intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 29:522–526 (2006).
A. Fasano, and J. P. Nataro. Intestinal epithelial tight junctions as targets for enteric bacteria-derived toxins. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 56:795–807 (2004).
T. Lindmark, T. Nikkila, and P. Artursson. Absorption enhancement through intracellular regulation of tight junction permeability by medium chain fatty acids in Caco-2 cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 284:362–369 (1998).
A. Marin, H. Sun, G. A. Husseini, W. G. Pitt, D. A. Christensen, and N. Y. Rapoport. Drug delivery in pluronic micelles: Effect of high-frequency ultrasound on drug release from micelles and intracellular uptake. J. Control. Rel. 84:39–47 (2002).
D. M. Hallow, A. D. Mahajan, and M. R. Prausnitz. Ultrasonically targeted delivery into endothelial and smooth muscle cells in ex vivo arteries. J. Control. Rel. 118:285–293 (2007).
E. B. Ghartey-Tagoe, J. S. Morgan, K. Ahmed, A. S. Neish, and M. R. Prausnitz. Electroporation-mediated delivery of molecules to model intestinal epithelia. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 270:127–138 (2004).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a fellowship to KW from the Graduate Research and Education in Adaptive bio-Technology (GREAT) Training Program by the University of California Biotechnology Research and Education Program and by the American Diabetes Association. The authors would also like to thank Natalie Karr for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material
(DOC 360 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Whitehead, K., Mitragotri, S. Mechanistic Analysis of Chemical Permeation Enhancers for Oral Drug Delivery. Pharm Res 25, 1412–1419 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-008-9542-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-008-9542-2