Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate the effect of silymarin on the pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin in systems overexpressing OATP1B1 or BCRP transporters and in healthy subjects.
Materials and Methods
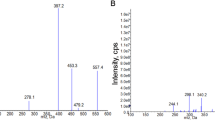
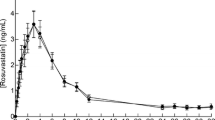
The concentration-dependent transport of rosuvastatin and the inhibitory effect of silymarin were examined in vitro in OATP1B1-expressing oocytes and MDCKII-BCRP cells. For in vivo assessment, eight healthy male volunteers, divided into two groups, were randomly assigned to receive placebo or silymarin (140 mg) three times per day for 5 days. On day 4, all subjects received rosuvastatin (10 mg, 8 am) 1 h after the placebo or silymarin administration. A series of blood samples were collected for 72 h, and the plasma concentration of rosuvastatin was determined using LC-MS/MS.
Results
Based on the concentration dependency of rosuvastatin transport in the OATP1B1 and BCRP overexpression systems, rosuvastatin is a substrate for both transporters. Silymarin inhibited both OATP1B1- and BCRP-mediated rosuvastatin transport in vitro (K i 0.93 μM and 97 μM, respectively). However, no significant changes in AUC, half-life, V d/F, or Cl/F of rosuvastatin were observed in human subjects following pretreatment with silymarin.
Conclusions
Silymarin does not appear to affect rosuvastatin pharmacokinetics in vivo, suggesting that silymarin, administered according to a recommended supplementation regimen, is not a potent modulator of OATP1B1 or BCRP in vivo.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BCRP:
-
breast cancer resistance protein
- DHEAS:
-
dehydroepiandrosterone 3-sulfate
- LC-MS/MS:
-
liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
- MRP1:
-
multidrug resistance-associated protein 1
- OATP1B1:
-
organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B1
- P-gp:
-
P-glycoprotein
- SNP:
-
single nucleotide polymorphisms
References
J. Kuhnau. The flavonoids. A class of semi-essential food components: their role in human nutrition. World Rev. Nutr. Diet. 24:117–191 (1976).
D. Lorenz, P. W. Lucker, W. H. Mennicke, and N. Wetzelsberger. Pharmacokinetic studies with silymarin in human serum and bile. Methods Find Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 6:655–661 (1984).
K. E. Mayer, R. P. Myers, and S. S. Lee. Silymarin treatment of viral hepatitis: a systematic review. J. Viral. Hepat. 12:559–567 (2005).
K. R. Ball, and K. V. Kowdley. A review of Silybum marianum (milk thistle) as a treatment for alcoholic liver disease. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 39:520–528 (2005).
X. Wang, A. W. Wolkoff, and M. E. Morris. Flavonoids as a novel class of human organic anion-transporting polypeptide OATP1B1 (OATP-C) modulators. Drug Metab. Dispos. 33:1666–1672 (2005).
H. C. Cooray, T. Janvilisri, H. W. van Veen, S. B. Hladky, and M. A. Barrand. Interaction of the breast cancer resistance protein with plant polyphenols. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 317:269–275 (2004).
S. Zhang, X. Yang, and M. E. Morris. Flavonoids are inhibitors of breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2)-mediated transport. Mol. Pharmacol. 65:1208–1216 (2004).
S. Zhang, X. Yang, and M. E. Morris. Combined effects of multiple flavonoids on breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2)-mediated transport. Pharm. Res. 21:1263–1273 (2004).
S. Zhang, X. Wang, K. Sagawa, and M. E. Morris. Flavonoids chrysin and benzoflavone, potent breast cancer resistance protein inhibitors, have no significant effect on topotecan pharmacokinetics in rats or mdr1a/1b (−/−) mice. Drug Metab. Dispos. 33:341–348 (2005).
G. Conseil, H. Baubichon-Cortay, G. Dayan, J. M. Jault, D. Barron, and A. Di Pietro. Flavonoids: a class of modulators with bifunctional interactions at vicinal ATP- and steroid-binding sites on mouse P-glycoprotein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 95:9831–9836 (1998).
E. M. Leslie, Q. Mao, C. J. Oleschuk, R. G. Deeley, and S. P. Cole. Modulation of multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1/ABCC1) transport and ATPase activities by interaction with dietary flavonoids. Mol. Pharmacol. 59:1171–1180 (2001).
S. Zhang, and M. E. Morris. Effect of the flavonoids biochanin A and silymarin on the P-glycoprotein-mediated transport of digoxin and vinblastine in human intestinal Caco-2 cells. Pharm. Res. 20:1184–1191 (2003).
M. J. Chapman, and F. McTaggart. Optimizing the pharmacology of statins: characteristics of rosuvastatin. Atheroscler. Suppl. 2:33–36 (2002)discussion 36–37.
R. Paoletti, M. Fahmy, G. Mahla, J. Mizan, and H. Southworth. Rosuvastatin demonstrates greater reduction of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol compared with pravastatin and simvastatin in hypercholesterolaemic patients: a randomized, double-blind study. J. Cardiovasc. Risk 8:383–890 (2001).
D. W. Schneck, B. K. Birmingham, J. A. Zalikowski, P. D. Mitchell, Y. Wang, P. D. Martin, K. C. Lasseter, C. D. Brown, A. S. Windass, and A. Raza. The effect of gemfibrozil on the pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 75:455–463 (2004).
R. H. Ho, R. G. Tirona, B. F. Leake, H. Glaeser, W. Lee, C. J. Lemke, Y. Wang, and R. B. Kim. Drug and bile acid transporters in rosuvastatin hepatic uptake: function, expression, and pharmacogenetics. Gastroenterology 130:1793–1806 (2006).
L. Huang, Y. Wang, and S. Grimm. ATP-dependent transport of rosuvastatin in membrane vesicles expressing breast cancer resistance protein. Drug Metab. Dispos. 34:738–742 (2006).
Y. Imai, M. Nakane, K. Kage, S. Tsukahara, E. Ishikawa, T. Tsuruo, Y. Miki, and Y. Sugimoto. C421A polymorphism in the human breast cancer resistance protein gene is associated with low expression of Q141K protein and low-level drug resistance. Mol. Cancer Ther. 1:611–616 (2002).
W. Zhang, B. N. Yu, Y. J. He, L. Fan, Q. Li, Z. Q. Liu, A. Wang, Y. L. Liu, Z. R. Tan, F. Jiang, Y. F. Huang, and H. H. Zhou. Role of BCRP 421C>A polymorphism on rosuvastatin pharmacokinetics in healthy Chinese males. Clin. Chim. Acta 373:99–103 (2006).
M. K. Pasanen, H. Fredrikson, P. J. Neuvonen, and M. Niemi. Different effects of SLCO1B1 polymorphism on the pharmacokinetics of atorvastatin and rosuvastatin. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 10.1038/sj.clpt.6100220 (2007).
J. H. Choi, M. G. Lee, J. Y. Cho, J. E. Lee, K. H. Kim, K. Park. Influence of OATP1B1 genotype on the pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin in Koreans. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 10.1038/sj.clpt.6100267 (2007).
H. Kusuhara, T. Sekine, N. Utsunomiya-Tate, M. Tsuda, R. Kojima, S. H. Cha, Y. Sugiyama, Y. Kanai, and H. Endou. Molecular cloning and characterization of a new multispecific organic anion transporter from rat brain. J. Biol. Chem. 274:13675–13680 (1999).
T. Nozawa, H. Minami, S. Sugiura, A. Tsuji, and I. Tamai. Role of organic anion transporter OATP1B1 (OATP-C) in hepatic uptake of irinotecan and its active metabolite, 7-ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin: in vitro evidence and effect of single nucleotide polymorphisms. Drug Metab. Dispos. 33:434–439 (2005).
E. L. Volk, K. M. Farley, Y. Wu, F. Li, R. W. Robey, and E. Schneider. Overexpression of wild-type breast cancer resistance protein mediates methotrexate resistance. Cancer Res. 62:5035–5040 (2002).
Y. Shitara, and Y. Sugiyama. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic alterations of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitors: drug–drug interactions and interindividual differences in transporter and metabolic enzyme functions. Pharmacol. Ther. 112:71–105 (2006).
P. J. Neuvonen, M. Niemi, and J. T. Backman. Drug interactions with lipid-lowering drugs: mechanisms and clinical relevance. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 80:565–581 (2006).
Y. C. Kim, E. J. Kim, E. D. Lee, J. H. Kim, S. W. Jang, Y. G. Kim, J. W. Kwon, W. B. Kim, and M. G. Lee. Comparative bioavailability of silibinin in healthy male volunteers. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 41:593–596 (2003).
D. Savio, P. C. Harrasser, and G. Basso. Softgel capsule technology as an enhancer device for the absorption of natural principles in humans. A bioavailability cross-over randomised study on silybin. Arzneimittelforschung 48:1104–1106 (1998).
H. U. Schulz, M. Schurer, G. Krumbiegel, W. Wachter, R. Weyhenmeyer, and G. Seidel. The solubility and bioequivalence of silymarin preparations. Arzneimittelforschung 45:61–64 (1995).
F. Q. Li, and J. H. Hu. Improvement of the dissolution rate of silymarin by means of solid dispersions. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 52:972–973 (2004).
Acknowledgment
We thank Mi-Gyung Go for her excellent technical assistance.
This work was supported by a grant from the Medical Research Center program (R13-2007-023-00000-0), KOSEF, Ministry of Science and Technology, Korea, and a grant from the Korea Health 21 R&D Project, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korea (A030001, A040155).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, J.W., Shon, JH., Shin, HJ. et al. Effect of Silymarin Supplement on the Pharmacokinetics of Rosuvastatin. Pharm Res 25, 1807–1814 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-007-9492-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-007-9492-0