Abstract
Purpose
Food stimulates changes to gastrointestinal secretion and motility patterns, however, the effect of smaller quantities of lipid, such as that contained in a lipid-based drug formulation, has not been detailed. This study aimed to examine the effects of small quantities of lipid on gastric emptying and biliary secretion.
Methods
The influence of oral administration of three lipid-based formulations and a negative control formulation on gastric emptying and biliary secretion was evaluated in 16 healthy male subjects using gamma scintigraphy, ultrasonography and duodenal aspiration.
Results
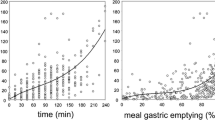
Low quantities (2 g) of long chain lipid stimulated gall bladder contraction and elevated intestinal bile salt, phospholipid and cholesterol levels. Changes in gastric emptying were also evident, although these did not reach statistical significance. Administration of a similar quantity of medium chain lipid, however, had little effect on gastric emptying and gallbladder contraction and did not stimulate appreciable increases in intestinal concentrations of biliary-derived lipids.
Conclusions
The quantities of long chain lipid that might be administered in a pharmaceutical formulation stimulate gallbladder contraction and elevate intestinal levels of bile salt and phospholipid. This effect is a likely contributor to the ability of lipid based formulations to enhance the absorption of poorly water-soluble drugs.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Borel, B. Pasquier, M. Armand, V. Tyssandier, P. Grolier, M. Alexandre-Gouabau, M. Andre, M. Senft, J. Peyrot, V. Jaussan, D. Lairon, and V. Azais-Braesco. Processing of vitamin A and E in the human gastrointestinal tract. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 280:G95–G103 (2001).
N. Aoyagi, H. Ogata, N. Kaniwa, and A. Ejima. Effect of food on the bioavailability of griseofulvin from microsize and PEG ultramicrosize (GRIS-PEG) plain tablets. J. Pharmacobio-Dyn. 5:120–124 (1982).
W. N. Charman, M. C. Rogge, A. W. Boddy, and B. M. Berger. Effect of food and a monoglyceride emulsion formulation on danazol bioavailability. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 33:381–386 (1993).
A. J. Humberstone, C. J. H. Porter, and W. N. Charman. A physicochemical basis for the effect of food on the absolute oral bioavailability of halofantrine. J. Pharm. Sci. 85:525–529 (1996).
E. Nicolaides, M. Symillides, J. B. Dressman, and C. Reppas. Biorelevant dissolution testing to predict the plasma profile of lipophilic drugs after oral administration. Pharm. Res. 18:380–388 (2001).
L. E. Schmidt and K. Dalhoff. Food–drug interactions. Drugs 62:1481–1502 (2002).
W. N. Charman, C. J. H. Porter, S. Mithani, and J. B. Dressman. Physicochemical and physiological mechanisms for the effects of food on drug absorption: the effects of lipids and pH. J. Pharm. Sci. 86:269–282 (1997).
D. Fleisher, C. Li, Y. Zhou, L. Pao, and A. Karim. Drug, meal and formulation interactions influencing drug absorption after oral administration. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 36:233–254 (1999).
K. M. Cunningham, R. J. Baker, M. Horowitz, A. F. Maddox, M. A. Edelbroek, and B. E. Chatterton. Use of technetium-99m(V)thiocyanate to measure gastric emptying of fat. J. Nucl. Med. 32:878–881 (1991).
C. Feinle, T. Rades, B. Otto, and M. Fried. Fat digestion modulates gastrointestinal sensations induced by gastric distension and duodenal lipid in humans. Gastroenterology 120:1100–1107 (2001).
M. Fried, E. A. Mayer, J. B. Jansen, C. B. Lamers, I. L. Taylor, S. R. Bloom, and J. H. Meyer. Temporal relationships of cholecystokinin release, pancreatobiliary secretion, and gastric emptying of a mixed meal. Gastroenterology 95:1344–1350 (1988).
T. Okumura, K. Fukagawa, P. Tso, I. L. Taylor, and T. N. Pappas. Apolioprotein A-IV acts in the brain to inhibit gastric emptying in the rat. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 33:G49–G53 (1996).
J. Glatzle, T. J. Kalogeris, T. T. Zittel, S. Guerrini, P. Tso, and H. E. Raybould. Chylomicron components mediate intestinal lipid-induced inhibition of gastric motor function. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 282:G86–G91 (2002).
P. Tso and M. Liu. Apolipoprotein A-IV, food intake, and obesity. Physiol. Behav. 83:631–643 (2004).
H. E. Raybould, J. H. Meyer, Y. Tabrizi, R. A. Liddle, and P. Tso. Inhibition of gastric emptying in response to intestinal lipid is dependent on chylomicron formation. Am. J. Physiol. 274:R1834–R1838 (1998).
S. M. Caliph, W. N. Charman, and C. J. H. Porter. Effect of short-, medium-, and long-chain fatty acid-based vehicles on the absolute oral bioavailability and intestinal lymphatic transport of halofantrine and assessment of mass balance in lymph-cannulated and non-cannulated rats. J. Pharm. Sci. 89:1073–1084 (2000).
B. G. Stone, H. J. Ansel, F. J. Peterson, and R. L. Gebhard. Gallbladder emptying stimuli in obese and normal-weight subjects. Hepatology 15:795–798 (1992).
F. Froehlich, J. J. Gonvers, and M. Fried. Role of nutrient fat and cholecystokinin in regulation of gallbladder emptying in man. Dig. Dis. Sci. 40:529–533 (1995).
O. Hernell, J. E. Staggers, and M. C. Carey. Physical–chemical behavior of dietary and biliary lipids during intestinal digestion and absorption. 2. Phase analysis and aggregation states of luminal lipids during duodenal fat digestion in healthy adult human beings. Biochemistry 29:2041–2056 (1990).
M. C. Carey, D. M. Small, and C. M. Bliss. Lipid digestion and absorption. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 45:651–677 (1983).
L. J. Naylor, V. Bakatselou, and J. B. Dressman. Comparison of the mechanism of dissolution of hydrocortisone in simple and mixed micelle systems. Pharm. Res. 10:865–870 (1993).
B. L. Pedersen, H. Brondsted, H. Lennernas, F. N. Christensen, A. Mullertz, and H. G. Kristensen. Dissolution of hydrocortisone in human and simulated intestinal fluids. Pharm. Res. 17:183–189 (2000).
B. L. Pedersen, A. Mullertz, H. Brondsted, and H. G. Kristensen. A comparison of the solubility of danazol in human and simulated gastrointestinal fluids. Pharm. Res. 17:891–894 (2000).
G. L. Amidon, H. Lennernas, V. P. Shah, and J. R. Crison. A theoretical basis for a biopharmaceutic drug classification: the correlation of in vitro drug product dissolution and in vivo bioavailability. Pharm. Res. 12:413–420 (1995).
J. N. Hunt and M. T. Knox. A relation between the chain length of fatty acids and the slowing of gastric emptying. J. Physiol. 194:327–336 (1968).
S. D. Ladas, P. E. T. Isaacs, G. M. Murphy, and G. E. Sladen. Comparison of the effects of medium and long chain triglyceride containing liquid meals on gall bladder and small intestinal function in normal man. Gut 25:405–411 (1984).
E. M. Persson, A.-S. Gustafsson, A. S. Carlsson, R. G. Nilsson, L. Knutson, P. Forsell, G. Hanisch, H. Lennernas, and B. Abrahamsson. The effects of food on the dissolution of poorly soluble drugs in human and in model small intestinal fluids. Pharm. Res. 22:2141–2151 (2005).
C. J. H. Porter, A. M. Kaukonen, B. J. Boyd, G. A. Edwards, and W. N. Charman. Susceptibility to lipase-mediated digestion reduces the oral bioavailability of danazol after administration as a medium-chain lipid-based microemulsion formulation. Pharm. Res. 21:1405–1412 (2004).
K. Kelly, B. O’Mahony, B. Lindsay, T. Jones, M. McDonagh, L. Martini, H. N. E. Stevens, and C. G. Wilson. The effect of long chain fatty acids on the gastric emptying of a co-administered tablet in fasted human volunteers. AAPS PharmSci. 4:T3072 (2002).
A. Rasyid and A. Lelo. The effect of curcumin and placebo on human gall-bladder function: an ultrasound study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 13:245–249 (1999).
L. Kalantzi, T. Fuerst, B. Abrahamsson, K. Goumas, V. Kalioras, J. B. Dressman, and C. Reppas. Characterization of the human upper gastrointestinal contents under conditions simulating bioavailability studies in the fasting and in the fed state AAPS PharmSci. 5: R6068 (2003).
A. Lindahl, A. Ungell, L. Knutson, and H. Lennernas. Characterisation of fluids from the stomach and proximal jejunum in men and women. Pharm. Res. 14:497–502 (1997).
H. P. Porter and D. R. Saunders. Isolation of the aqueous phase of human intestinal contents during the digestion of a fatty meal. Gastroenterology 60:997–1007 (1971).
L. Sek, C. J. H. Porter, A. M. Kaukonen, and W. N. Charman. Evaluation of the in-vitro digestion profiles of long and medium chain glycerides and the phase behaviour of their lipolytic products. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 54:29–41 (2002).
S. Ellenbogen, S. A. Jenkins, J. S. Grime, M. Critchley, C. R. Mackie, and J. N. Baxter. Preduodenal mechanisms in initiating gallbladder emptying in man. Br. J. Surg. 75:940–945 (1988).
E. M. Persson, R. G. Nilsson, G. I. Hansson, L. J. Lofgren, F. Liback, L. Knutson, B. Abrahamsson, and H. Lennernas. A clinical single-pass perfusion investigation of the dynamic in vivo secretory response to a dietary meal in human proximal small intestine. Pharm. Res. 23:742–751 (2006).
P. Holzer. Gastrointestinal afferents as targets of novel drugs for the treatment of functional bowel disorders and visceral pain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 429:177–193 (2001).
C. G. Wilson and K. Kelly. Gastrointestinal transit and drug absorption. In J. B. Dressman and J. Kramer (eds.), Pharmaceutical Dissolution Testing, Taylor and Francis, London, 2006, pp. 97–125.
C. J. H. Porter, N. L. Trevaskis, and W. N. Charman. Lipids and lipid based formulations: optimising the oral delivery of lipophilic drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 6:231–248 (2007).
M. A. Edelbroek, M. Horowitz, A. F. Maddox, and J. Bellen. Gastric emptying and intragastric distribution of oil in the presence of a liquid or a solid meal. J. Nucl. Med. 33:1283–1290 (1992).
N. Kaniwa, N. Aoyagi, H. Ogata, H. Motoyama, and H. Yasumi. Gastric emptying rates of drug preparations. II. Effects of size and density of enteric-coated drug preparations and food on gastric emptying rates in humans. J. Pharmacobio-Dyn. 11:571–575 (1988).
R. L. Oberle, T. S. Chen, C. Lloyd, J. L. Barnett, C. Owyang, J. Meyer, and G. L. Amidon. The influence of the interdigestive migrating myoelectric complex on the gastric emptying of liquids. Gastroenterology 99:1275–1282 (1990).
C. L. Dobson, S. S. Davis, S. Chauhan, R. A. Sparrow, and I. R. Wilding. The effect of oleic acid on the human ileal brake and its implications for small intestinal transit of tablet formulations. Pharm. Res. 16:92–96 (1999).
C. L. Dobson, S. S. Davis, S. Chauhan, R. A. Sparrow, and I. R. Wilding. The effect of ileal brake activators on the oral bioavailability of atenolol in man. Int. J. Pharm. 248:61–70 (2002).
K. Fujimoto, J. A. Cardelli, and P. Tso. Increased apolipoprotein A-IV in rat mesenteric lymph after lipid meal acts as a physiological signal for satiation. Am. J. Physiol. 262:G1002–G1006 (1992).
R. P. Jazrawi, P. Pazzi, M. L. Petrioni, N. Prandini, C. Paul, J. A. Adam, S. Gullini, and T. C. Northfield. Postprandial gallbladder motor function: refilling and turnover of bile in health and in cholelithiasis. Gastroenterology 109:582–591 (1995).
G. A. Kossena, B. J. Boyd, C. J. H. Porter, and W. N. Charman. Separation and characterization of the colloidal phases produced on digestion of common formulation lipids and assessment of their impact on the apparent solubility of selected poorly water-soluble drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. 92:634–648 (2003).
G. A. Kossena, W. N. Charman, B. J. Boyd, D. E. Dunstan, and C. J. H. Porter. Probing drug solubilisation patterns in the gastrointestinal tract after administration of lipid based delivery systems: a phase diagram approach. J. Pharm. Sci. 93:332–348 (2004).
C. J. H. Porter, A. M. Kaukonen, A. Taillardat-Bertschinger, B. J. Boyd, J. M. O’Connor, G. A. Edwards, and W. N. Charman. Use of in vitro lipid digestion data to explain the in vivo performance of triglyceride-based oral lipid formulations of poorly water-soluble drugs: studies with halofantrine. J. Pharm. Sci. 93:1110–1121 (2004).
G. A. Kossena, W. N. Charman, B. J. Boyd, and C. J. H. Porter. Influence of the intermediate digestion phases of common formulation lipids on the absorption of a poorly water-soluble drug. J. Pharm. Sci. 94:481–492 (2005).
A. K. Trull, K. K. C. Tan, L. Tan, G. J. M. Alexander, and N. V. Jamieson. Enhanced absorption of new oral cyclosporin microemulsion formulation, Neoral, in liver transplant recipients with external biliary diversion. Transplant Proceedings 29:2977–2978 (1994).
A. Tangerman, A. van Schaik, and E. W. van der Hock. Analysis of conjugated and unconjugated bile acids in serum and jejunal fluid of normal subjects. Clin. Chim. Acta 159:123–132 (1986).
O. Fausa. Duodenal bile acids after a test meal. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 9:567–570 (1974).
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to GSK for financial support and to Dr. Paul Ingram and Kirsteen Wilson (Bio-Images Research Ltd) for analytical assistance. The co-ordination roles of Eilis O’Driscoll and Paul Linacre at GSK are also gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kossena, G.A., Charman, W.N., Wilson, C.G. et al. Low Dose Lipid Formulations: Effects on Gastric Emptying and Biliary Secretion. Pharm Res 24, 2084–2096 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-007-9363-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-007-9363-8