Purpose
The purpose of the article was to study melt sonocrystallization (MSC) for a drug forming a viscous melt when processed below its glass transition temperature.
Methods
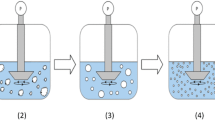
A molten mass of drug was poured in a vessel containing deionized water, maintained at 40°C using cryostatic bath, and sonicated for 1 min using probe ultrasonicator at an amplitude of 80% and a cycle of 0.8 per second. The product obtained after solidification of dispersed droplets was separated by filtration and dried at room temperature. MSC celecoxib was characterized by solubility determination, scanning electron microscopy, differential scanning calorimetry, X-ray powder diffraction, and stability study.
Results
The MSC technique was designed for celecoxib, which undergoes fast solidification. The particles obtained by MSC were porous, irregular in shape, and amorphous in nature. An increase in the apparent solubility was observed for the MSC particles. These amorphous particles also exhibited a higher stability in the amorphous state as compared with particles obtained by melt quenching.
Conclusions
The reported MSC technique for celecoxib demonstrates advantages over other approaches and can be exploited in area of particle design for the amorphization of drugs.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Amara B. Ratsimba A. Wilhelm H. Delmas (2001) ArticleTitleCrystallization of potash alum: effect of power ultrasound Ultrason. Sonochem. 8 265–270 Occurrence Handle11441609 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXltlehu7w%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1350-4177(01)00087-6
H. Li J. Wang Y. Bao Z. Guo M. Zhang (2003) ArticleTitleRapid sonocrystallization in the salting out process J. Cryst. Growth 247 192–198 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XovFelsbg%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0022-0248(02)01941-3
L. H. Thompson L. K. Doraiswamy (2000) ArticleTitleThe rate enhancing effect of ultrasound by inducing supersaturation in a solid liquid system Chem. Eng. Sci. 55 3085–3090 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXislaltr0%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0009-2509(99)00481-9
J. F. Spengler W. T. Coakley (2003) ArticleTitleMicrostreaming effects on particle concentration in an ultrasonic standing wave AIChE J. 49 2773–2782 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXpsVCisLo%3D Occurrence Handle10.1002/aic.690491110
L. C. Hagenson L. K. Doraiswamy (1998) ArticleTitleComparison of the effects of ultrasound and mechanical agitation on a reacting solid–liquid system Chem. Eng. Sci. 53 131–148 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXks1ensQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0009-2509(97)00193-0
J. Homer M. J. Howard S. C. Gooda (1995) ArticleTitleEffect of ultrasound on molecular mobility in certain crystalline compounds Ultrason. Sonochem. 2 S71–S74 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XitVKmuw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/1350-4177(95)00023-Y
R. Srinivasan I. Z. Shirgaokar A. B. Pandit (1995) ArticleTitleEffect of sonication on crystal properties Sep. Sci. Technol. 30 2239
M. Maheshwari H. Jahagirdar A. Paradkar (2005) ArticleTitleMelt sonocrystallization of ibuprofen: effect on crystal properties Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 25 41–48 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.ejps.2005.01.013
A. Paradkar M. Maheshwari A. Ketkar B. Chauhan (2003) ArticleTitlePreparation and evaluation of ibuprofen beads by melt solidification technique Int. J. Pharm. 255 33–42 Occurrence Handle12672599 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXisVGlurk%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0378-5173(03)00081-4
D. Clemett K. L. Goa (2000) ArticleTitleCelecoxib: a review of its use in osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and acute pain Drugs 59 957–980 Occurrence Handle10804043 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXjsVOmu7Y%3D Occurrence Handle10.2165/00003495-200059040-00017
S. Paulson M. Vaughn S. Jessen Y. Lawal C. Gresk B. Yan T. Maziasz C. Cook A. Karim (2001) ArticleTitlePharmacokinetics of celecoxib after oral administration in dogs and humans: effect of food and site of absorption J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 297 638–645 Occurrence Handle11303053 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXjt1Wlsbw%3D
A. Paradkar B. Chauhan S. Yamamura A. Pawar (2003) ArticleTitlePreparation and characterization of glassy celecoxib Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 29 739–744 Occurrence Handle12906331 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXltlGmtbg%3D Occurrence Handle10.1081/DDC-120021773
M. K. Srinivasu C. L. Narayana D. S. Rao O. M. Reddy (2000) ArticleTitleA validated LC method for the quantitative determination of celecoxib in pharmaceutical dosage forms and purity evaluation in bulk drugs J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 22 949–956 Occurrence Handle10857564 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXjt1eisLc%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0731-7085(00)00303-4
G. Chawla P. Gupta R. Thilagavathi A. Chakraborti A. Bansal (2003) ArticleTitleCharacterization of solid state forms of celecoxib Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 20 305–317 Occurrence Handle14592696 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXosVyltrc%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0928-0987(03)00201-X
Acknowledgments
AP is thankful to DST and Royal Society for providing a grant under the India–UK Science Network Scheme. AP is also thankful to Mr. Paul Thorning, director of the Institute of Pharmaceutical Innovations, University of Bradford, Bradford, for providing the facilities and Bharati Vidyapeeth Deemed University, Pune, India, for the sabbatical leave. The authors are grateful to Lupin Laboratories (Pune, India) for the sample of celecoxib.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paradkar, A., Maheshwari, M., Kamble, R. et al. Design and Evaluation of Celecoxib Porous Particles using Melt Sonocrystallization. Pharm Res 23, 1395–1400 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-006-0020-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-006-0020-4