Purpose
This work investigates the effect of various salts on the rate of a reaction involving a neutral species (benzocaine alkaline hydrolysis).
Methods
Benzocaine hydrolysis kinetics in NaOH solutions in the presence of different salts were studied at 25°C. Benzocaine solubility in salt solutions was also determined. Solubility data were used to estimate salt effects on benzocaine activity coefficients, and pH was used to estimate salt effects on hydroxide activity coefficients.
Results
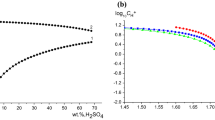
Salts either increased or decreased benzocaine solubility. For example, solubility increased with 1.0 M tetraethylammonium chloride (TEAC) ∼3-fold, whereas solubility decreased ∼35% with 0.33 M Na2SO4. Salt effects on hydrolysis rates were more complex and depended on the relative magnitudes of the salt effects on the activity coefficients of benzocaine, hydroxide ion, and the transition state. As a result, some salts increased the hydrolysis rate constant, whereas others decreased it. For example, the pseudo-first-order rate constant decreased ∼45% (to 0.0584 h−1) with 1 M TEAC, whereas it increased ∼8% (to 0.116 h−1) with 0.33 M Na2SO4.
Conclusions
Different salt effects on degradation kinetics can be demonstrated for a neutral compound reacting with an ion. These salt effects depend on varying effects on activity coefficients of reacting and intermediate species.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. T. Carstensen (1970) ArticleTitleKinetic salt effect in pharmaceutical investigations J. Pharm. Sci. 59 1140–1143 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE3cXkvVSns7g%3D Occurrence Handle4248077
J. E. Gordon (1975) The Organic Chemistry of Electrolyte Solutions John Wiley & Sons New York
K. Connors (1990) Chemical Kinetics, the Study of Reaction Rates in Solution VCH Publishers Inc. New York
L. Hammett (1970) Physical Organic Chemistry: Reaction Rates, Equilibria, and Mechanisms EditionNumber2 McGraw-Hill New York
K. Laidler (1965) Chemical Kinetics EditionNumber2 McGraw-Hill New York
C. Bunton L. Robinson (1968) ArticleTitleElectrolyte effects on bimolecular nucleophilic displacements J. Am. Chem. Soc. 90 5965–5971 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF1cXltFSmsLw%3D
F. A. Long F. B. Dunkle W. F. McDevit (1951) ArticleTitleSalt effects on the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of gamma-butyrolactone. II J. Phys. Chem. 55 829–842 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaG3MXlsVOgsQ%3D%3D
F. Q. Long W. F. McDevit (1952) ArticleTitleActivity coefficients of nonelectrolyte solutes in aqueous salt solutions Chem. Rev. 51 119–169 Occurrence Handle10.1021/cr60158a004 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaG38Xls1Cisg%3D%3D
A. Al-Maaieh D. R. Flanagan (2002) ArticleTitleSalt effects on caffeine solubility, distribution, and self-association J. Pharm. Sci. 91 1000–1008 Occurrence Handle10.1002/jps.10046 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XjtFKhuro%3D Occurrence Handle11948539
K. Connors G. Amidon V. Stella (1986) Chemical Stability of Pharmaceuticals Wiley and Sons New York
A. Moffat J. Jackson M. Moss B. Widdop (1986) Clarke's Isolation and Identification of Drugs EditionNumber2 The Pharmaceutical Press London
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Maaieh, A., Flanagan, D.R. Salt Effects on an Ion–Molecule Reaction—Hydroxide-Catalyzed Hydrolysis of Benzocaine. Pharm Res 23, 589–594 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-005-9434-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-005-9434-7