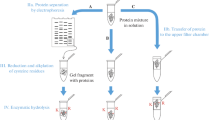
Purpose
The aim of the study is to provide a methodology for assigning unpaired cysteine residues in proteins formulated in a variety of different conditions to identify structural heterogeneity as a potential cause for protein degradation.
Methods
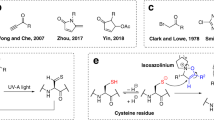
1-Cyano-4-dimethylaminopyridinium tetrafluoroborate (CDAP) was employed for cyanylating free cysteines in proteins and peptides. Subsequent basic cleavage of the peptide bond at the N-terminal side of the cyanylated cysteines provided direct information about their location.
Results
CDAP was successfully employed to a wide variety of labeling conditions. CDAP was reactive between pH 2.0 and 8.0 with a maximum labeling efficiency at pH 5.0. Its reactivity was not affected by excipients, salt or denaturant. Storing CDAP in an organic solvent increased its intrinsic stability. It was demonstrated that CDAP can be employed as a thiol-directed probe to investigate structural heterogeneity of proteins by examining the accessibility of unpaired cysteine residues.
Conclusion
CDAP is a unique cysteine-labeling reagent because it is reactive under acidic conditions. This provides an advantage over other sulfhydryl labeling reagents as it avoids potential thiol-disulfide exchange. Optimization of the cyanylation reaction allowed the utilization of CDAP as a thiol-directed probe to investigate accessibility of sulfhydryl groups in proteins under various formulation conditions to monitor structural heterogeneity.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CDAP:
-
1-Cyano-4-dimethylaminopyridinium tetrafluoroborate
- DAP:
-
4-Dimethylaminopyridinium tetrafluoroborate
- rmethG-CSF:
-
Recombinant methionyl human granulocyte-colony stimulating factor
- GdnHCl:
-
Guanidine hydrochloride
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- MALDI:
-
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization
- MS:
-
Mass spectrometry
- OPG:
-
Osteoprotegerin
- TOF:
-
Time of flight
- UV:
-
Ultraviolet
References
S. Evans P. Grassam (1986) ArticleTitleConsiderations for parenteral dosage form development of natural alpha interferon J. Parenter. Sci. Technol. 40 83–87
Z. Shahrokh G. Eberlein D. Buckley M. V. Paranandi D. W. Aswad P. Stratton R. Mischak Y. J. Wang (1994) ArticleTitleMajor degradation products of basic fibroblast growth factor: detection of succinimide and iso-aspartate in place of aspartate Pharm. Res. 11 936–944
E. R. Hoff R. C. Chloupek (1996) ArticleTitleAnalytical peptide mapping of recombinant DNA-derived proteins by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography Methods Enzymol. 271 51–68
M. W. Dong (1992) ArticleTitleTryptic mapping by reversed phase liquid chromatography Adv. Chromatogr. 32 21–51
J. T. Watson Y. Yang J. Wu (2001) ArticleTitleCapture and identification of folding intermediates of cystinyl proteins by cyanylation and mass spectrometry J. Mol. Graph. Model. 19 119–128
J. S. Weissman P. S. Kim (1991) ArticleTitleReexamination of the folding of BPTI: predominance of native intermediates Science 253 1386–1393
D. M. Rothwarf H. A. Scheraga (1993) ArticleTitleRegeneration of bovine pancreatic ribonuclease A. 1. Steady-state distribution Biochemistry 32 2671–2679
G. R. Jacobson M. H. Schaffer G. R. Stark T. C. Vanaman (1973) ArticleTitleSpecific chemical cleavage in high yield at the amino peptide bonds of cysteine and cystine residues J. Biol. Chem. 248 6583–6591
I. A. Papayannopoulos K. Biemann (1992) ArticleTitleAmino acid sequence of a protease inhibitor isolated from Sarcophaga bullata determined by mass spectrometry Protein Sci. 1 278–288
Y. Degani A. Patchornik (1974) ArticleTitleCyanylation of sulfhydryl groups by 2-nitro-5-thiocyanobenzoic acid. High-yield modification and cleavage of peptides at cysteine residues Biochemistry 13 1–11
N. D. Denslow H. P. Nguyen (1996) Tech. Protein Chem. VII 241–248
N. C. Price (1976) ArticleTitleAlternative products in the reaction of 2-nitro-5-thiocyanatobenzoic acid with thiol groups Biochem. J. 159 177–180
T. H. Liao A. Wadano (1979) ArticleTitleInactivation of DNase by 2-nitro-5-thiocyanobenzoic acid. II. Serine and threonine are the sites of reaction on the DNase molecule J. Biol. Chem. 254 9602–9607
M. Wakselman and E. Guibe-Jampel. 1-Cyano-4-dimethylamino-pyridinium salts: new water-soluble reagents for the cyanylation of protein sulfhydryl groups. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 21–22 (1976).
S. Nakagawa Y. Tamakashi T. Hamana M. Kawase S. Taketomi Y. Ishibashi O. Nishimura T. Fukuda (1994) ArticleTitleChemical cleavage of recombinant fusion proteins to yield peptide amides J. Am. Chem. Soc. 116 5513–5514
J. Wu J. T. Watson (1997) ArticleTitleA novel methodology for assignment of disulfide bond pairings in proteins Protein Sci. 6 391–398
S. Nakagawa Y. Tamakashi Y. Ishibashi M. Kawase S. Taketomi O. Nishimura T. Fukuda (1994) ArticleTitleProduction of human PTH(1-34) via a recombinant DNA technique Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 200 1735–1741
J. Wu J. T. Watson (1998) ArticleTitleOptimization of the cleavage reaction for cyanylated cysteinyl proteins for efficient and simplified mass mapping Anal. Biochem. 258 268–276
J. Wu D. A. Gage J. T. Watson (1996) ArticleTitleA strategy to locate cysteine residues in proteins by specific chemical cleavage followed by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry Anal. Biochem. 235 161–174
J. Wu Y. Yang J. T. Watson (1998) ArticleTitleTrapping of intermediates during the refolding of recombinant human epidermal growth factor (hEGF) by cyanylation, and subsequent structural elucidation by mass spectrometry Protein Sci. 7 1017–1028
S. F. Betz G. J. Pielak (1992) ArticleTitleIntroduction of a disulfide bond into cytochrome c stabilizes a compact denatured state Biochemistry 31 12337–12344
S. F. Betz (1993) ArticleTitleDisulfide bonds and the stability of globular proteins Protein Sci. 2 1551–1558
O. B. Ptitsyn (1995) ArticleTitleStructures of folding intermediates Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 5 74–78
Y. J. Li D. M. Rothwarf H. A. Scheraga (1995) ArticleTitleMechanism of reductive protein unfolding Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2 489–494
P. S. Kim R. L. Baldwin (1990) ArticleTitleIntermediates in the folding reactions of small proteins Ann. Rev. Biochem. 59 631–660
C. R. Matthews (1993) ArticleTitlePathways of protein folding Ann. Rev. Biochem. 62 653–683
Q. X. Hua W. Jia B. H. Frank N. F. Phillips M. A. Weiss (2002) ArticleTitleA protein caught in a kinetic trap: structures and stabilities of insulin disulfide isomers Biochemistry 41 14700–14715
J. Schuurman G. J. Perdok A. D. Gorter R. C. Aalberse (2001) ArticleTitleThe inter-heavy chain disulfide bonds of IgG4 are in equilibrium with intra-chain disulfide bonds Mol. Immunol. 38 1–8
D. N. Brems P. L. Brown G. W. Becker (1990) ArticleTitleEquilibrium denaturation of human growth hormone and its cysteine-modified forms J. Biol. Chem. 265 5504–5511
N. Darby T. E. Creighton (1997) ArticleTitleProbing protein folding and stability using disulfide bonds Mol. Biotechnol. 7 57–77
A. Wawrzynow J. H. Collins (1993) ArticleTitleChemical modification of the Ca(2+)-ATPase of rabbit skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum: identification of sites labeled with aryl isothiocyanates and thiol-directed conformational probes Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1203 60–70
C. P. Hill T. D. Osslund D. Eisenberg (1993) ArticleTitleThe structure of granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor and its relationship to other growth factors Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90 5167–5171
S. Krishnan E. Y. Chi J. N. Webb B. S. Chang D. Shan M. Goldenberg M. C. Manning T. W. Randolph J. F. Carpenter (2002) ArticleTitleAggregation of granulocyte colony stimulating factor under physiological conditions: characterization and thermodynamic inhibition Biochemistry 41 6422–6431
E. Y. Chi S. Krishnan B. S. Kendrick B. S. Chang J. F. Carpenter T. W. Randolph (2003) ArticleTitleRoles of conformational stability and colloidal stability in the aggregation of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor Protein Sci. 12 903–913
B. Bishop D. C. Koay A. C. Sartorelli L. Regan (2001) ArticleTitleReengineering granulocyte colony-stimulating factor for enhanced stability J. Biol. Chem. 276 33465–33470
T. Arakawa S. J. Prestrelski L. O. Narhi T. C. Boone W. C. Kenney (1993) ArticleTitleCysteine 17 of recombinant human granulocyte-colony stimulating factor is partially solvent-exposed J. Protein Chem. 12 525–531
M. S. Ricci C. A. Sarkar E. M. Fallon D. A. Lauffenburger D. N. Brems (2003) ArticleTitlepH Dependence of structural stability of interleukin-2 and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor Protein Sci. 12 1030–1038
L. O. Narhi W. C. Kenney T. Arakawa (1991) ArticleTitleConformational changes of recombinant human granulocyte-colony stimulating factor induced by pH and guanidine hydrochloride J. Protein Chem. 10 359–367
Acknowledgment
The author likes to thank David Brems of Amgen for helpful discussions and guidance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pipes, G.D., Kosky, A.A., Abel, J. et al. Optimization and Applications of CDAP Labeling for the Assignment of Cysteines. Pharm Res 22, 1059–1068 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-005-5643-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-005-5643-3