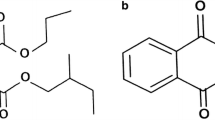
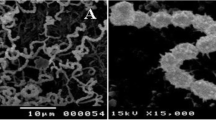
Many valuable therapeutic substances can be found in the marine environment and Actinomycetes are a goldmine for many pharmaceutical compounds among the different marine biota, which may have unique characteristics with novel structural elements which were not found in terrestrial actinomycetes. Antibiotics produced by these microorganisms, their bioactivities, and how their chemical structures have inspired generations of scientists working in the synthesis of new drugs are described thoroughly. In the present research the Streptomyces sp. NLKPB45 strain isolated from marine sediments were chosen for further investigation based on its bioactive potential availability. The structure of the extracted compound was characterized by 1H NMR and 13C NMR.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Hong, A. H. Gao, Q. Y. Xie, et al., Mar. Drugs, 7, 24– 44 (2009).
A. T. Bull, J. E. Stach, Trends Microbiol., 15, 491 – 499 (2007).
R. Subramani, W. Aalbersberg, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 97(21), 9291 – 9321 (2013).
M. Goodfellow, J. E. Stach, R. Brown, et al., Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 101(1), 185 – 193 (2012).
W. Fenical, P. R. Jensen, Nat. Chem. Biol., 2, 666 – 673 (2006).
W. Pathom-Aree, Y. Nogi, I. C. Sutcliffe, et al., Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 56, 1233 – 1237 (2006).
H. Bredholdt, O. A. Galatenko, K. Engelhardt, et al., Environ. Microbiol., 9(11), 2756 – 2764 (2007).
L. T. Wei, S. Y. Kazuo, N. Makoto, K. Tomohisa, ACS Chem. Biol., 13(9), 2615 – 2622 (2018).
B. Sudha Kalyani, P. S. Krishna, K. Sreenivasulu,. Saudi J. Biol. Sci., 26(7), 1655 – 1660 (2019).
V. Vimal, Rajan Benita Mercy, K. Kannabiran, Asian J. Med. Sci., 1(2), 57 – 63 (2009).
Ingle K. P., Deshmukh A. G., Padole D. A., et al., JPP, 6(1), 32 – 36 (2017).
R. Tian, Y. Li, M. Gao, Biosci. Rep., 35(2), e00189 (2015).
Z. Charlop-Powers, J. G. Owen, B. V. Reddy, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 111(10), 3757 – 3762 (2014).
Z. Charlop-Powers, J. G. Owen, B. V. Reddy, eLife, 4, e05048 (2015).
W. Hualin, L. Huan, C.Chu., et al., Food and Bioprocess Technol., 1657 – 1667 (2015).
J. Liu, K. W. Bowman, D. S. Schimel, Science, 358, eaam5690 (2017).
V. Singh, V. Praveen, J. Banga, et al., Ind. J. Exp. Biol., 47, 298 – 303 (2009).
P. Palanisamy, D. Dharmadurai, J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci., 54 – 60 (2015).
S. Peter, S. Alven, et al., Molecules, 27(14), 4478 (2022).
A. Becerril-Espinosa, G. Guerra-Rivas, N. E. Ayala-Sánchez, Mexico Rev. Biol. Mar. Oceanogr., 47, 317 – 325 (2012).
S. A. El-Shatoury, N. S. El-Shenawy, I. M. A. El-Salam, World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 25, 1547 – 1555 (2009).
S. Ravikumar, M. Gnanadesigan, N. Thajuddin, J. Pharm. Res., 3, 2415 – 2417 (2010).
K. Suthindhiran, K. Kannabiran, Am. J. Infect. Dis., 5, 90– 98 (2009).
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank Department of Biotechnology KLEF University and IKP-LSI management for providing facilities to carry out research work
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kalyani, B.S., Krishna, P.S., Laxminarayana, E. et al. Novel Bioactive Compounds from Streptomyces sp. NLKPB45 Isolated from Marine Soil Sediment. Pharm Chem J 57, 834–841 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-023-02957-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-023-02957-3