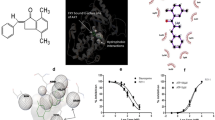
The main problems experienced in treatment with anticancer drugs are undesirable side effects, and toxicity. Minimal side effects for new anticancer compounds may be met due to enhanced efforts to clarify the compound’s mechanisms of action. Therefore, we aimed to investigate whether or the cytotoxic effect and apoptosis mechanism of a series Ag(I)NHC complexes on non-small cell lung cancer cell line (A549) and normal lung fibroblast cell line (CCD-19Lu) in this study. The cytotoxicity was determined by using the MTT method, and apoptotic effects were detected by cell cycle, annexin-V/propidium iodide (PI) staining and cell cycle, caspase-3, mitochondrial membrane potential analysis. Molecular docking studies were performed using in silico ADMET analysis, and molecular docking information on the compounds was gained using the DS 3.5 software subprotocol. All the time, the cytotoxic effect of silver compounds was monitored for 24 h in comparison to cisplatin. The apoptotic effect of these compounds increased in cancer cells as compared to normal cells. Complex 3b exhibited the highest cytotoxic activity on cancer cell in 24 and 72 h, but complex 3a exhibited the highest cytotoxic activity on cancer cell s in 48 h. Moreover, all Ag(I)NHC complexes exhibited significant statistical difference depending on the increase in concentration on cancer cells, and all compounds induced apoptosis associated with distributing of membrane polarization and stopping the cell cycle in phase G1 and the caspase-3 activity. Caspase-3 activity of the new Ag(I)NHC compounds showed 8.3 to 17.6-fold increase compared the untreated cells. The loss of mitochondrial membrane potential indicated that JC-1 assay results were 16.9 to17.2-fold higher than normal cells in Ag(I)NHC compounds and 11.3-fold higher her in cisplatin. In addition, molecular docking studies were executed on the Ag(I)NHC complexes, and cisplatin estimate that the binding modes towards the EGFR kinase. Because epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is expressed highly in a great number of epithelial tumors. These findings suggested that Ag(I)NHC complexes exhibited anticancer activity and may be considered to have a new therapeutic potential for human non-small cell lung cancer cell treatment.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Biersack, A. Ahmad, F. H. Sarkar, et al., Curr. Med. Chem., 19, 3949 – 3956 (2012).
G. Zhu, M. Myint, W. H. Ang, et al., Curr Med Chem., 72, 790 – 800 (2012).
S. Ray, R. Mohan, J. K. Singh, et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 129(48), 15042 – 15053 (2007).
A. Aktaş, Ü. Keleştemur, Y. Gök, et al., J. Iran Chem. Soc., 15(1), 131 – 139 (2018).
K. A. Ali, M. M Abd-Elzaher, and K Mahmoud, Int. J. Med. Chem., 2013, 1 – 7 (2013).
N. S. Gaud, P. Kumar, and R. D. Bharath, Heterocycles, (2020).
A. Kaplan, G. Akalın-Çifçi, and H. M. Kutlu. Tumor Biol., 2017, 1 – 12 (2017).
T. Kutlu, I. Yıdırım, H. Karabıyık, et al., J. Mol. Struct., 1228, 129462 (2021).
T. J. Siciliano, M. C. Deblock, K. M. Hindi, et al., J. Organomet. Chem., 696, 1066 – 1071 (2011).
W. J. Young, A. R. Knapp, P. O. Wagers, et al., Dalton Trans., 41, 327 – 336 (2007).
G. Davidson, E. A. V. Ebsworth, and J. S. Ogden, Spectrosc. Prop. Inorg. Organomet. Compd., 19, 251 – 286 (1985).
P. H. Stah and G. C. Wermuth. Chem. Int., 24, 21 (2002).
X. Zhang, Y. Zhang, J. Ying, et al., J. Solid State Chem., 295, 121888 (2021).
S. Sangthong, K. Krusong, N. Nagmrojanavanich, et al., Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2, 4813–4818 (2011).
L. Yurttaş, Ş. Demirayak, G. A. Çifçi, et al., Arch. Pharm.., 346(5), 403 – 414 (2013).
I. Yıldırım, A. Aktas, D. Barut-Celepci, et al., Res. Chem. Intermed., 43(17),1– 15 (2007).
M. V. Berridge, P. M. Herst, and A. S. Tan. Biotechnol. Ann. Rev., 11, 127 – 152 (2005).
M. V. Berridge and A. S. Tan, Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 303, 474 – 82 (1993).
M. Dikmen, Z. Canturk, Y. Oztürk, et al., Cancer Biother Radiopharm., 25, 749 – 755 (2010).
Y. J. Hwang and D. Y. Kim, J. Embryo Transfer, 28, 63 – 71 (2013).
H. Yan, Y. C. Wang, D. Li, et al., Leukemia, 21, 1488 – 1495 (2007).
G. M. Morris, R. Huey, W. Lindstrom, et al., J. Comput. Chem., 30(16), 2785 – 2791 (2009).
D. Irmer, J. O. Funk, and A. Blaukat, Oncogene, 26(39), 5693 – 5701 (2007).
M. J. Frisch, G. W. Trucks, H. B. Schlegel, et. al. Gaussian 09, Revision D. 01” (2009).
C. A. Lipinski, F. Lombardo, B. W. Dominy, et al., Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 46,3– 26 (2001).
D. F. Veber, S. R. Johnson, H. Y. Cheng, et al., J. Med. Chem., 45, 2615 – 2623 (2002).
J. H. Stegehuis, L. H. de Wilt, E. G de Vries, et al., Drug Resist. Updat., 13, 2 – 15 (2010).
A. Aouidate, A. Galeb, M. Ghamali, Comput. Biol. Chem., 74, 201 – 211 (2018).
A. Halim, I. S. B. Larsen, P. Neubert, et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 112(51), 15648 – 15653 (2015).
T. J. Siciliano, M. C. Deblock, K. M. Hindi, et al., J. Organomet. Chem., 696, 1066 – 1071 (2011).
K. A. Ali, M. M. Abd-Elzaher, and K. Mahmoud. Int. J. Med. Chem., 2013,1–7 (2013).
M. Baron, S. Bellemin-Laponnaz, C. Tubaro, et al., J. Inorg. Biochem., 141, 94 – 102 (2014).
M. Miharano, M. H. Fernaz, P. G. Jones, et al., Appl. Organomet. Chem., 30, 581 – 589 (2016).
A. Kaplan, G. Akalın-Çifçi, and H. M. Kutlu. Tumor Biol., 2017, 1 – 12 (2017).
M. Marinelli, M. Pellei, C. Cimarelli, et al., J. Organomet. Chem., 806, 45 – 53 (2016).
R. D. Lima, A. B. Seabra, and N. Duran. J. Appl. Toxicol., 32, 867–879 (2012).
Y. He, D. Zhiyun, S. Ma, et al., Int. J. Nanomed., 11,1879 – 1887 (2016).
J. H. Stegehuis, L. H. de Wilt, E. G. de Vries, et al., Drug Resist. Update, 13,2– 15 (2010).
S. Li, X. Jin, X. Tan, et al., Eur. J. Med. Chem., 86, 1 – 11 (2014).
J. Parker and M. D. Waterfield, Nature, 311(5985), 83 – 485 (1984).
K. Oda, Y. Matsuoka, H. Funahashi, et al., Mol. Syst. Biol., 1(1), E1 – E17 (2005).
Acknowledgments
Işıl Yıldırım would like to thank all co-authors for their contributions. This work is part of Işıl Yıldırım’s Doctoral Dissertation. Therefore, she is the main author. Studies were carried out in the Anadolu University Plant Drug and Scientific Research Center (AUBIBAM), Cell Culture Laboratory.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Inonu University Research Project Unit (Project No. the I. U. BAP 2016/166).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information
Table S1. Interaction Types and Distances of for Erlotonib, Cisplatin, and Complexes 3a-, 3b- and 3c-EGFR
Interaction | Distance Å | Bonding | Bonding Types | Binding site of target | Binding site of ligand |
A:MET769:N - A:erlotinib:N2 | 2.6991 | Hydrogen Bond | Conventional Hydrogen Bond | A:MET769:N | A:erlotinib:N2 |
A:erlotinib:H16 - A:PRO770:O | 2.4901 | Hydrogen Bond | Carbon Hydrogen Bond | A:PRO770:O | A:erlotinib:H16 |
A:erlotinib:H20 - A:GLN767:O | 2.0581 | Hydrogen Bond | Carbon Hydrogen Bond | A:GLN767:O | A:erlotinib:H20 |
A:THR830:OG1 - A:erlotinib | 4.0726 | Hydrogen Bond | Pi-Donor Hydrogen Bond | A:THR830:OG1 | A:erlotinib |
A:LEU694:CD1 - A:erlotinib | 3.6847 | Hydrophobic | Pi-Sigma | A:LEU694:CD1 | A:erlotinib |
Interaction | Distance Å | Bonding | Bonding Types | Binding site of target | Binding site of ligand |
A:LEU820:CD1 - A:erlotinib | 3.8573 | Hydrophobic | Pi-Sigma | A:LEU820:CD1 | A:erlotinib |
A:erlotinib - A:LYS721 | 4.8072 | Hydrophobic | Pi-Alkyl | A:LYS721 | A:erlotinib |
A:erlotinib - A:ALA719 | 3.7388 | Hydrophobic | Pi-Alkyl | A:ALA719 | A:erlotinib |
A:erlotinib - A:MET769 | 5.4440 | Hydrophobic | Pi-Alkyl | A:MET769 | A:erlotinib |
A:erlotinib - A:ALA719 | 5.3493 | Hydrophobic | Pi-Alkyl | A:ALA719 | A:erlotinib |
A:erlotinib - A:LEU820 | 5.3122 | Hydrophobic | Pi-Alkyl | A:LEU820 | A:erlotinib |
Interactions | Distance Å | Bonding | Bonding Types | Binding site of target | Binding site of ligand |
A:LYS721:NZ - :cisplatin:CL | 4.3661 | Electrostatic | Attractive Charge | A:LYS721:NZ | :cisplatin:CL |
A:THR766:HG1 - :cisplatin:CL | 1.8943 | Hydrogen Bond; Halogen | Conventional Hydrogen Bond; Halogen (Cl, Br, I) | A:THR766:HG1 | :cisplatin:CL |
Interactions | Distance Å | Bonding | Bonding Types | Binding site of target | Binding site of ligand |
A:LYS721:NZ - :3a:BR22 | 5.4602 | Electrostatic | Attractive Charge | A:LYS721:NZ | :3a:BR22 |
A:LYS721:HZ3 - :3a:O18 | 1.9185 | Hydrogen Bond | Conventional Hydrogen Bond | A:LYS721:HZ3 | :3a:O18 |
:3a:H8 - A:GLN767:O | 2.5549 | Hydrogen Bond | Carbon Hydrogen Bond | A:GLN767:O | :3a:H8 |
:3a:H18 - A:ASP831:OD2 | 2.1550 | Hydrogen Bond | Carbon Hydrogen Bond | A:ASP831:OD2 | :3a:H18 |
:3a:H25 - A:ASP831:OD2 | 1.9605 | Hydrogen Bond | Carbon Hydrogen Bond | A:ASP831:OD2 | :3a:H25 |
A:VAL702 - :3a | 5.1318 | Hydrophobic | Alkyl | A:VAL702 | :3a |
A:LYS721 - :3a | 5.2499 | Hydrophobic | Alkyl | A:LYS721 | :3a |
:3a:C15 - A:CYS751 | 4.0161 | Hydrophobic | Alkyl | A:CYS751 | :3a:C15 |
:3a:C15 - A:MET769 | 4.5944 | Hydrophobic | Alkyl | A:MET769 | :3a:C15 |
:3a:C15 - A:LEU820 | 5.0114 | Hydrophobic | Alkyl | A:LEU820 | :3a:C15 |
:3a - A:LEU694 | 4.4650 | Hydrophobic | Pi-Alkyl | A:LEU694 | :3a |
Interactions | Distance Å | Bonding | Bonding Types | Binding site of target | Binding site of ligand |
A:LYS721:NZ - :3b:BR22 | 3.4169 | Electrostatic | Attractive Charge | A:LYS721:NZ | :3b:BR22 |
A:LYS721:HE2 - :3b:BR22 | 2.4022 | Hydrogen Bond | Carbon Hydrogen Bond | A:LYS721:HE2 | :3b:BR22 |
A:MET742:SD - :3b | 5.4820 | Other | Pi-Sulfur | A:MET742:SD | :3b |
A:THR766:OG1 - :3b | 2.9356 | Other | Pi-Lone Pair | A:THR766:OG1 | :3b |
A:LEU694 - :3b | 5.4635 | Hydrophobic | Alkyl | A:LEU694 | :3b |
A:ALA719 - :3b | 4.6323 | Hydrophobic | Alkyl | A:ALA719 | :3b |
A:LEU820 - :3b | 4.5608 | Hydrophobic | Alkyl | A:LEU820 | :3b |
:3b:C14 - A:MET742 | 4.0514 | Hydrophobic | Alkyl | A:MET742 | :3b:C14 |
:3b:C20 - A:LYS721 | 5.0173 | Hydrophobic | Alkyl | A:LYS721 | :3b:C20 |
:3b - A:ALA719 | 4.5899 | Hydrophobic | Pi-Alkyl | A:ALA719 | :3b |
:3b - A:LYS721 | 4.1508 | Hydrophobic | Pi-Alkyl | A:LYS721 | :3b |
:3b - A:LEU764 | 5.4473 | Hydrophobic | Pi-Alkyl | A:LEU764 | :3b |
Interactions | Distance Å | Bonding | Bonding Types | Binding site of target | Binding site of ligand |
Interaction | Distance Å | Bonding | Bonding Types | Binding site of target | Binding site of ligand |
A:THR766:HG1 - :3c:O21 | 1.6837 | Hydrogen Bond | Conventional Hydrogen Bond | A:THR766:HG1 | :3c:O21 |
A:MET769:HN - :3c:O18 | 1.6885 | Hydrogen Bond | Conventional Hydrogen Bond | A:MET769:HN | :3c:O18 |
:3c:H46 - A:ALA719:O | 2.3530 | Hydrogen Bond | Conventional Hydrogen Bond | A:ALA719:O | :3c:H46 |
:3c:H46 - A:LEU764:O | 2.1519 | Hydrogen Bond | Conventional Hydrogen Bond | A:LEU764:O | :3c:H46 |
A:LEU768:HA - :3c:O18 | 2.7141 | Hydrogen Bond | Carbon Hydrogen Bond | A:LEU768:HA | :3c:O18 |
:3c:H17 - A:MET769:O | 2.8565 | Hydrogen Bond | Carbon Hydrogen Bond | A:MET769:O | :3c:H17 |
:3c:H24 - A:MET769:O | 2.4493 | Hydrogen Bond | Carbon Hydrogen Bond | A:MET769:O | :3c:H24 |
A:LEU694 - :3c | 5.3888 | Hydrophobic | Alkyl | A:LEU694 | :3c |
A:ALA719 - :3c | 4.4772 | Hydrophobic | Alkyl | A:ALA719 | :3c |
A:LEU768 - :3c | 5.3355 | Hydrophobic | Alkyl | A:LEU768 | :3c |
A:LEU820 - :3c | 4.8223 | Hydrophobic | Alkyl | A:LEU820 | :3c |
:3c - A:VAL702 | 4.4625 | Hydrophobic | Pi-Alkyl | A:VAL702 | :3c |
:3c - A:LYS721 | 5.1781 | Hydrophobic | Pi-Alkyl | A:LYS721 | :3c |
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kutlu, T., Yıldırım, I., Dikmen, M. et al. The Cytotoxicity Profile, Apoptosis Mechanism, and Molecular Docking Studies of a Series of Benzimidazolium Derivative Morpholine-Substituted Ag(I) Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes. Pharm Chem J 57, 10–28 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-023-02846-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-023-02846-9