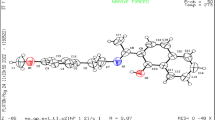
β-Sitosterol (βs) is one of important phytosterols, which is well known for its ability to lower the cholesterol level and is also useful in the treatment of various diseases. Keeping in mind its biological activities, complexation of βs with Cu(II) was performed and it was found that βs-Cu complex enhances the biological activities of βs. The pH-metric titration technique was used to control the formation of metal (M)—ligand (L) complexes βs-Cu in solutions with variable mole ratio of metal ion to ligand, 1:1, 1:2 and 1:3 (denoted as ML, ML2 and ML3 respectively). The complex formation was indicated by change in the solution color due to change in pH. Results obtained by the mole ratio variation and isomolar series method revealed the formation of ML2 complex. The synthesized βs-Cu complex was characterized by elemental analysis and various spectroscopic techniques including IR, UV/Vis, and 1H NMR. The results of analysis indicated that complexes contained Cu(II) ions coordinated via OH and C=C groups of the steroid. The data of antimicrobial activity assay showed higher activity of βs-Cu in 1:2 (ML2) form as compared to other mole ratios.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. H. Pegel, S. Afr. J. Sci., 93, 263 – 268 (1997).
K. A. Kim, I. A. Lee, W. Gu, et al., Mol. Nutr. Food Res., 58, 963 – 972 (2014).
R. Tao, C. Z. Wang, Z. W. Kong, Molecules, 18, 2166 – 2182 (2013).
K. Hac-Wydro, Colloids Surf. B: BioiInterfaces, 110, 113 – 119 (2013).
J. Quilez, P. Garcia-Lorda, J. Salas-Salvado, Clin. Nutr., 22, 343351 (2003).
Metallotherapeutic Drugs and Metal-Based Diagnostic Agents: the Use of Metals in Medicine, M. Gielen, E. R. T. Tiekink (Eds.), Wiley: Chichester (2005), pp. 145 – 208.
J. E. Weder, C. T. Dillon, T. W. Hambley, et al., Coord. Chem. Rev., 232, 95 – 126 (2002).
D. C.Ware, P. J. Brothers and G. R. Clark, J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans., 6, 925 – 932 (2000).
M. Nakai, F. Sekiguchi, M. Obata, et al., J. Inorg. Biochem., 99, 1275 – 1282 (2005).
T. H. A. Chaviara, P. C. Christidis, A. Papageorgiou, et al., J. Inorg. Biochem., 99, 2102 – 2109 (2005).
P. J. Sadler and Z. Guo, Pure Appl. Chem., 70, 863 – 871 (1998).
B. Kastenholz, Protein Pept. Lett., 13, 503 – 508 (2006).
B. Kastenholz, Protein Pept. Lett., 14, 389 – 393 (2007).
W. M. Kwiatek, T. Drewniak, M. Gajda, et al., J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol., 16, 155 – 160 (2002).
M. T. Tarafder, K. T. Jin, K. A. Crouse, et al., Polyhedron, 21, 2547 – 2554 (2002).
R. A. Sanchez-Delgado, K. Lazardi, L. Rincon, et al., J. Med. Chem., 36, 2041 – 2043 (1993).
C. Orvig, M. J. Abrams, Chem. Rev., 99, 2201 – 2204 (1999).
S. J. Lippard and J. M. Beng, Principles of Bioinorganic Chemistry, University Science Books: Mile Valley, California (1994).
A. Bagchi, P. Mukherjee, and A. Raha, Int. J. Recent Adv. Pharm. Res., 5, 171 – 180 (2015).
W. R. Walker, S. J. Beveridge, and M. W. Whitehouse, Agents Actions Suppl., 8, 359 – 367 (1981).
S. Dutta, S. Padhye, and V. Mckee, Inorg. Chem. Commun., 7, 1071 – 1074 (2004).
J. Forestier and A. Certonciny, Presse Medicale, 54, 884 – 885 (1946).
J. R. Sorenson and W. Hangarter, Inflammation, 2, 217 – 238 (1977).
S. K. Bharti and S. K. Singh, Der. Pharm. Lett., 1, 39 – 51 (2009).
C. Perez, M. Paul, and P. Bazerque, Acta Biol. Med. Exp., 15, 113 – 115 (2009).
Wuthi-udomlert, Mansuang, and O. Vallisuta, Pharmacogn. J., 3, 69 – 73 (2011).
R. Smyth, S. Bengtsson, J. Cloke, and G. Kahlmeter, Clin. Microbiol. Infect., 14, 857 (2008).
Y. Vaghasiya, H. Patel, and S. Chanda, Afr. J. Biotechnol., 10, 15788 – 15794 (2011).
A. Zirino and S. Yamamoto, Limnol. Oceanogr., 17, 661 – 671 (1972).
A. L. Sekaly, R. Mandal, N. M. Hassan, et al., Anal. Chim. Acta., 402, 211 – 221(1999).
M. I. Bulatov and I. P. Kalinkin, Practical Handbook of Photometric Analytical Methods, 5th Edn. Revised, Khimiya: Leningrad (1986).
A. Dakshinamoorthy and V. Venugopal, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 3, 425 – 429 (2005).
P. Mondal and A. Bose, BioImpacts, 9, 115 (2019).
A. S. Alturiqi, A. N. Alaghaz, R. A. Ammar, and M. E. Zayed, J. Chem., 1 – 17 (2018).
S. Chandraleka, and G. Chandramohan, Afr. J. Pure Appl. Chem., 8, 162 – 175 (2014).ý
K. Nakamoto, Infrared Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds, Wiley: New York (1970), pp. 386 – 400.
N. Nawar, and N. M. Hosny, Transit. Met. Chem., 25, 1 – 8 (2000).
R. K. Reddy, P. B. Ka Suneetha, C. S. C. Karigar, et al., J. Chil. Chem. Soc., 53, 1653 – 1657 (2008).
A.Wahab, A. Sultana, K. M. Khan, et al., Pak. J. Pharm. Sci., 5, 1984 – 1987 (2012).
Z. H. Chohan, H. Pervez, A. Rauf, et al., J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem., 19, 417 – 423 (2004).
A. A. Abou-Hussein and W. Linert, Spectrochim. Acta A: Mol. Biomol., 117, 763 – 771 (2014).
S. B. Bumrela and S. R. Naik, Int. J. Phytomed., 3, 204 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bibi, Y., Mahmood, T., Shah, S.N. et al. Formation of βs-Cu Complexes Via pH-Metric Titration for Antimicrobial Studies. Pharm Chem J 56, 1535–1543 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-023-02825-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-023-02825-0