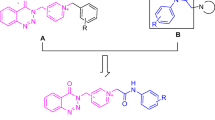
The present work summarizes the synthesis of new sulfonamides and their N-substituted derivatives as possible agents for treating Alzheimer’s disease. The synthesis was triggered by reaction of 1,4-benzodioxane-6- amine (1) with 4-bromobenzenesulfonyl chloride (2) in aqueous alkaline media to yield N-(2,3-dihydro-1,4- benzodioxin-6-yl)-4-bromobenzenesulfonamide (3), which was further treated with different alkyl/aralkyl halides (4a–4n) using N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) as reaction medium in the presence of lithium hydride (LiH) as a base to yield N-alkyl/aralkyl-N-(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-6-yl)-4-bromobenzenesulfonamides 5a–5n. The structures of all synthesized derivatives were confirmed by spectroscopic techniques including IR, 1H NMR and EI-MS. All the cholinesterase enzyme inhibitors are good agents for treating Alzheimer’s disease. The inhibition activity of synthesized molecules was studied so as to assess their possible therapeutic effect on this disease.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Shaabani, E. Soleimani and A. H. Rezayan, Tetrahedron. Lett., 48(12), 2185 – 2188 (2007).
Y. Kanda, Y. Kawanishi, K. Oda, et al, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 9(4), 897 – 907 (2001).
U. O. Ozdemir, P. Guvenc, E. Sahin, et al., Inorg.. Chim. Acta., 362(8), 2613 – 2618 (2009).
M. Irshad, M. A. Abbasi, Aziz-ur-Rehman, et al., J. Chem. Soc. Pak., 36(4), 660 – 673 (2014).
M. A. Abbasi, Aziz-ur-Rehman, T. Muhmood, et al., J. Chem. Soc. Pak., 35(2), 404 – 410 (2013).
A. Husain, Acta. Polon. Pharm., 66(5), 513 – 521 (2009).
X. Deng and N. S. Mani, Green Chem., 8(9), 835 – 838 (2006).
M. A. Abbasi, S. Najm, Aziz-ur-Rehman, et al., Trop. J. Pharm. Res., 14(1), 47 – 54 (2015).
M. Remko and C. W. V. D. Leith, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 12(20), 5395 – 5403 (2004).
M. Irshad, M. A. Abbasi, Aziz-ur-Rehman, et al., Asian J. Chem., 26(4), 1151 – 1160 (2014).
W. R. Roush, S. L. Gwaltney, and J. Cheng, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 120(42), 10994 – 10995 (1998).
W. R. Roush, J. Cheng, B. K. Reed, et al., Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 11(20), 2759 – 2762 (2001).
M. A. Abbasi, Aziz-ur-Rehman, M. Z. Qureshi, et al., Braz. J. Pharm. Sci., 49(1), 127 – 133 (2013).
M. A. Abbasi, S. Ahmad, Aziz-ur-Rehman, et al., Trop. J. Pharm. Res., 13(5), 739 – 745 (2014).
M. A. Abbasi, A. Saeed, Aziz-ur-Rehman, et al., Iran. J. Pharm. Res., 13(1), 87 – 94 (2014).
G. L. Ellman, K. D. Courtney, V. Andres Jr., et al., Biochem. Pharmacol., 7(2), 88 – 95 (1961).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abbasi, M.A., Anum, A., Aziz-ur-Rehman et al. Synthesis of Some New N-Alkyl/Aralkyl-N-(2,3-Dihydro-1,4-Benzodioxin-6-YL)-4-Bromobenzenesulfonamides as Possible Therapeutic Agents F or Alzheimer’s Disease. Pharm Chem J 56, 61–70 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-022-02598-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-022-02598-y