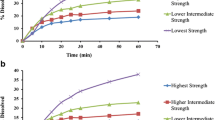
This study aims to investigate the strength-dependent dissolution pattern of two-dose strengths of valsartan: the low-dose strength of 80 mg and high-dose strength of 320 mg. For this purpose, the dissolution testing was carried out in media of buffer solutions that resemble physiological characteristics of the gastrointestinal fluid (GIF). The influence of various physiological GIF characteristics (pH, buffer capacity β, and ionic strength I) on the dissolution of a weakly acidic biopharmaceutical classification system (BCS) class II drug valsartan present in two-dose strengths was investigated. The strength-dependent and strength-independent dissolution patter was determined based on the similarity/dissimilarity of the dissolution profiles of valsartan 80 and 320 tablets using the f2 similarity test. Valsartan dissolution showed either strength-dependent or strength-independent behavior for various values of pH, buffer capacity β, ionic strength I, and sink condition S of the tested media. Results of this study shed light on the importance of studying physiological characteristics of the GIF for multiple-strength drug products for better predicting the dissolution pattern of weak acids in vivo.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Suarez-Sharp, P. R. Delvadia, A. Dorantes, et al., AAPS J., 18(3), 578 – 588 (2016).
P. Costa and J. M. S. Lobo, Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm., 13(2), 123 – 133 (2001).
U. S. Food and Drug Administration, Washington, DC (2003).
U. S. Food and Drug Administration, Rockville, MD (2014).
A. Chiolro and M. Burnier, Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs, 7(11), 1915 – 1925 (1998).
R. Pradhan, S. Y. Kim, C. S. Yong, et al., Asian J. Pharm. Sci., 11(6), 744 – 750 (2016).
B. Vladovicova, M. Lehock, V. Kormanova, et al., WO2005041941: Valsartan Containing Formulation (2005).
K. Gowthamarajan and S. K. Singh, Dissolut. Technol., 17(3), 24 – 32 (2010).
R. Hamed, A. Awadallah, S. Sunoqrot, et al., AAPS PharmSciTech, 17(2), 418 – 426 (2016).
R. Hamed, R. Al Janabi, S. Sunoqrot, et al., Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm., 43(8), 1330 – 1342 (2017).
N. Bou-Chacra, K. J. C. Melo, I. A. C. Morales, et al., AAPS J., 19(4), 989 – 1001 (2017).
D. Hörter and J. Dressman, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 25(1), 3 – 14 (1997).
A. Fuchs and J. B. Dressman, J. Pharm. Sci., 103(11), 3398 – 3411 (2014).
R. Hamed and S. H. Alnadi, AAPS PharmSciTech, 19(5), 2213 – 2225 (2018).
R. Hamed, Pharm. Dev. Technol., 23(10), 1168 – 1176 (2018).
U. S. Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER), U. S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC (1997).
S. Jamzad and R. Fassihi, AAPS PharmSciTech, 7(2), E17-E22 (2006).
S. Klein, M. F.Wempe, T. Zoeller, et al., J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 61(1), 23 – 30 (2009).
P. Liu, O. De Wulf, J. Laru, et al., AAPS PharmSciTech, 14(2), 748 – 756 (2013).
D. A. Diaz, S. T. Colgan, C. S. Langer, et al., AAPS J., 18(1), 15 – 22 (2016).
S. S. Ozturk, B. O. Palsson, and J. B. Dressman, Pharm. Res., 5(5), 272 – 82 (1988).
O. I. Corrigan, Y. Devlin, and J. Butler, Int. J. Pharm., 254(2), 147 – 154 (2003).
Y. Tsume, P. Langguth, A. Garcia-Arieta, et al., Biopharm. Drug Dispos., 33(7), 366 – 377 (2012).
J. B. Dressman, G. L. Amidon, C. Reppas, et al., Pharm. Res., 15(1), 11 – 22 (1998).
S. Klein, M. W. Rudolph, and J. B. Dressman, Dissolut. Technol., 9(4), 6 – 12 (2002).
M. R. Marques, R. Loebenberg, and M. Almukainzi, Dissolut. Technol., 18(3), 15 – 28 (2011).
Y. Lu, S. Kim, and K. Park, Int. J. Pharm., 418(1), 142 – 148 (2011).
G. L. Amidon, H. Lennernäs, V. P. Shah, et al., Pharm. Res., 12(3), 413 – 420 (1995).
R. Takano, K. Furumoto, K. Shiraki, et al., Pharm. Res., 25(10), 2334 – 2344 (2008).
J. Emami, J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci., 9(2), 169 – 189 (2006).
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the Deanship of Academic Research and Graduate Studies at Al-Zaytoonah University of Jordan. The authors would like to thank technician Jihan Al Sayyad for help in the dissolution experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamed, R., Kamal, A. Strength-Dependent and Strength-Independent Dissolution Patterns of Poorly-Soluble Drugs. Case Example: Valsartan. Pharm Chem J 54, 1227–1234 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-021-02347-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-021-02347-7