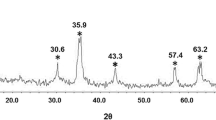
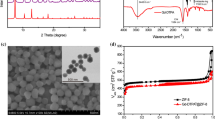
Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) are widely applied as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents and drug carriers in drug delivery systems (DDSs) for diagnostics and treatment of diseases. Observation of drug delivery, drug release, and monitoring of the treatment can be performed by MRI. Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) can be used as dual-mode agents for simultaneous MRI contrast and drug delivery. Application of dual-mode MRI-contrast and drug-carrier agent is especially useful in targeted DDS. In this study, we report on the preparation of captopril-coated MNPs as a new dual-mode agent for simultaneous MRI contrast and DDS. The influence of contrast agent on the longitudinal (T1) and transverse (T2, T2*) relaxation times was studied and it was found that the effect on T2 and T2* exceeds the effect on T1, which leads to darkening of the MR image. Release of captopril from γ-Fe2O3@SiO2@captopril system was studied at three pH values and it was established that the drug release at pH 1.2 was greater than that at pH 4.8 and 7.4. The obtained results show that MNPs loaded with captopril can be used as dual-mode MRI contrast agent and DDS system.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Swedberg, J. Kjekshus, CTS Group, Am. J. Cardiol., 62, 60A – 66A (1988).
SOLVD Investigators, New Engl. J. Med., 325, 293 – 302 (1991).
M. Ehlers, E. A. Fox, D. J. Strydom, and J. F. Riordan, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 86, 7741 – 7745 (1989).
J. Pourahmad, M.-J. Hosseini, S. Bakan, and M. Ghazi-Khansari, Pest. Biochem. Physiol., 99, 105 – 110 (2011).
M. Prabhu, S. Palaian, A. Malhotra, et al., Kathmandu Univ. Med. J. (KUMJ), 3, 296 – 304 (2004).
H. Kubinyi, J. Taylor, and C. Ramdsen, Compr. Med. Chem., 4, 589 (1990).
H.-P. Li, J.-J. Zhang, L. Qin, and M.-D. Zhao, Res. Chem. Intermed., 39, 621 – 629 (2013).
J. Zeng, P. Du, L. Liu, et al., Mol. Pharm., 12, 4188 – 4199 (2015).
H.-Y. Park, M. J. Schadt, L. Wang, et al., Langmuir, 23, 9050 – 9056 (2007).
Z. Luo, K. Cai, Y. Hu, et al., Adv. Mater., 24, 431 – 435 (2012).
L. Wang, J. Bao, L. Wang, et al., Eur. J. Chem., 12, 6341 – 6347 (2006).
H. Qiu, B. Cui, G. Li, et al., J. Phys. Chem. C, 118, 14929 – 14937 (2014).
L. Zhang, W.-F. Dong, and H.-B. Sun, Nanoscale, 5, 7664 – 7684 (2013).
X. Zhang, L. Clime, H. Roberge, et al., J. Phys. Chem. C, 115, 1436 – 1443 (2010).
H. B. Na, I. C. Song, and T. Hyeon, Adv. Mater., 21, 2133 – 2148 (2009).
S. Shen, F. Kong, X. Guo, et al., Nanoscale, 5, 8056 – 8066 (2013).
S. Laurent, D. Forge, M. Port, et al., Chem. Rev., 108, 2064 – 2110 (2008).
G. Wang, X. Zhang, A. Skallberg, et al., Nanoscale, 6, 2953 – 2963 (2014).
E. Terreno and S. Aime, Front. Pharmacol., 6, 290 (2015).
B. H. McDonagh, G. Singh, S. Hak, et al., Small, 12, 301 – 306 (2016).
Z. Bao, J. A. Rogers, and H. E. Katz, J. Mater. Chem. 9, 1895 – 1904 (1999).
B. Z. Tang, Y. Geng, J. W. Y. Lam, et al., Chem. Mater., 11, 1581 – 1589 (1999).
K. M. Ho and P. Li, Langmuir, 24, 1801 – 1807 (2008).
S. Sobhani,, Z. M. Falatooni, and M. Honarmand, RSC Adv., 4, 15797 – 15806 (2014).
K. Azizi and A. Heydari, RSC Adv., 4, 8812 – 8816 (2014).
Y. Zhang, M. Yang, N. G. Portney, et al., Biomed. Microdev., 10, 321 – 328 (2008).
M. Khalkhali, S. Sadighian, K. Rostamizadeh, et al., Nanomed. J., 2, 223 – 230 (2015).
N. Arsalani, H. Fattahi, and M. Nazarpoor, Express Polym. Lett., 4, 329 – 338 (2010).
N. Lee and T. Hyeon, Chem. Soc. Rev., 41, 2575 – 2589 (2012).
N. Sattarahmady, T. Zare, A. Mehdizadeh, et al., Coll. Surf. B: Biointerfaces, 129, 15 – 20 (2015).
T. He, P. D. Gatehouse, G. C. Smith, Magn. Reson. Med., 60, 1082 – 1089 (2008).
T. He, P. D. Gatehouse, P. Kirk, et al., Magn. Reson. Med., 60, 350 – 356 (2008).
X. Yang, J. J. Grailer, I. J. Rowland, et. al., ACS Nano, 4, 6805 – 6817 (2010).
Y. W. Jun, J. H. Lee, and J. Cheon, Angew. Chem. Intern. Ed., 47, 5122 – 5135 (2008).
S. Sitthichai, C. Pilapong, T. Thongtem, and S. Thongtem, App. Surf. Sci., 356, 972 – 977 (2015).
S. Tong, S. Hou, Z. Zheng, et al., Nano Lett., 10, 4607 – 4613 (2010).
R. Van Roosbroeck, W. Van Roy, T. Stakenborg, et al., ACS Nano, 8, 2269 – 2278 (2014).
G. Fu, L. Zhu, K. Yang, et al., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 8, 5137 – 5147 (2016).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Sistan and Baluchestan University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pour, S.A., Shaterian, H.R. Captopril-Loaded Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles as a New Dual-Mode Contrast Agent for Simultaneous In Vitro/In Vivo MR Imaging and Drug Delivery System. Pharm Chem J 51, 852–862 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-018-1704-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-018-1704-x