Abstract
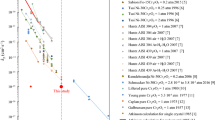
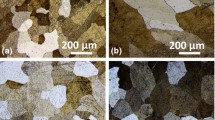
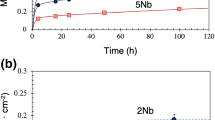
The oxidation behavior of Si- and/or Mn-Ni-25Cr alloys at 1050 °C in air was studied to provide new insights on the effect of minor additions on chromia-scale growth. Four nickel alloys with and without Si or Mn were prepared. Thermogravimetry and post-oxidation characterizations evidenced that manganese increased, whereas silicon addition decreased chromia growth rate. On the contrary, addition of both Si and Mn to the Ni-25Cr alloy led to an unchanged oxidation rate in comparison with the unalloyed Ni-25Cr material. Oxide scales were characterized by photoelectrochemistry (PEC) to evaluate the role of the additions on the point defects nature. The n and p contributions of chromia forming in air were not changed by Si. On the opposite, Mn modified the scale conducting properties since only n contributions were observed for both chromia and Mn1+xCr2−xO4 spinel oxide with Mn-containing samples. In the latter case, the PEC contribution at ~ 3.2–3.4 eV was allocated to the signature of the Mn1+xCr2−xO4 spinel oxide. These data suggested that manganese enhances and silicon limits grain boundary diffusion in chromia scale as reactive element does.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. J. Young, High Temperature Oxidation and Corrosion of Metals (Elsevier,Oxford, 2008).
J. H. Chen, P.M. Rogers and J. A. Little, Oxidation of Metals 47, 381-410 (1997).
J. J. Carey, and M. Nolan, Journal of Materials Chemistry A 5, 15613–15630 (2017 ).
T. Perez, L. Latu-Romain, R. Podor, J. Lautru, Y. Parsa, S. Mathieu, M. Vilasi and Y. Wouters, Oxidation of Metals 89, 781–795 (2018).
J. Zurek, D.J. Young, E. Essuman, M. Hansel, H.J. Penkalla, L. Niewolak and W.J. Quadakkers, Materials Science and Engineering A 477, 259–270 (2008).
D. L. Douglass, and J.S. Armijo, Oxidation of Metals 2, 207–231(1969).
B. Li and B. Gleeson, Oxidation of Metals 65, 101–122 (2006).
E. Evans, D. A. Hilton, R. A. Holm, and S. J. Webster, Oxidation of Metals 19, 1–18 (1983).
J. Robertson, and M. I. Manning, Materials Science and Technology 6, 81–92 (1990).
J. W. Hickman and E. A. Gulbransen, Transactions of the Metallurgical Society of AIME 180, 519–534 (1949).
L. Latu-Romain, Y. Parsa, S. Mathieu, M. Vilasi, A. Galerie and Y. Wouters, Corrosion Science 126, 238–246 (2017).
Y. Madi, L. Latu-Romain, S. Mathieu, V. Parry, J. P. Petit, M. Vilasi and Y. Wouters, Corrosion Science 87, 218–223 (2014).
Y. Wouters, L. Marchetti, A. Galerie and J.P. Petit, Corrosion Science 50, 1122–1131 (2008).
D. Monceau, and B. Pieraggi, Oxidation of Metals 50, 477–493 (1998).
H. F. McMurdie, M. C. Morris, E. H. Evans, B. Paretzkin, W. Wong-Ng, Y. Zhang, and C. R. Hubbard, Powder Diffraction 2, 41–52 (1987).
Z. Jirák, S. Vratislav, and P. Novák, Physica Status Solidi (a) 50, K21–K24 (1978)
W. W. Gartner, Physical Review 116, 84 (1959).
M. A. Butler, Journal of Applied Physic 48, 1914 (1977).
L. Latu-Romain, S. Mathieu, M. Vilasi, G. Renou, S. Coindeau, A. Galerie and Y. Wouters, Oxidation of Metals 88, 481–493 (2017).
M. Sugiyama and T. Nakayama, Journal of the Japan Institute of Metals 24, 196–199 (1960).
L. Mikkelsen, S. Linderoth, and J.B. Bilde-Sørensen, Materials Science Forum 461–464, 117–122 (2004).
T. D. Nguyen, J. Zhang, and D. J. Young, Corrosion Science 130, 161–176 (2018).
T. Perez, Oxydation à haute température d’alliages modèles Ni-25Cr, Influence des éléments mineurs Mn et Si sur les mécanismes de croissance des oxydes protecteurs, PhD dissertation, University of Lorraine (2019).
Y. Parsa, L. Latu-Romain, Y. Wouters, S. Mathieu, T. Perez, and M. Vilasi, Corrosion Science 141, 46–52 (2018).
F. Rhines, Transactions of the Metallurgical Society of AIME 137, 246–286 (1940).
T. Perez, S. Mathieu, L. Latu-Romain, Y. Wouters, and M. Vilasi, Photoelectrochemical and Raman features of MnCr2O4 spinel grown by the Rhines pack method, Under review (Available on demand).
X. Ledoux, S. Mathieu, M. Vilasi, Y. Wouters, P. Del-Gallo and M. Wagner, Oxidation of Metals 80, 25–35 (2013).
E. Schmucker, C. Petitjean, L. Martinelli, P-J. Panteix, S. Ben Lagha, M. Vilasi, Corrosion Science 111, 474–485 (2016)
H.V. Atkinson, Oxidation of Metals 24, 177–197 (1985)
T. Perez, J. Ghanbaja, S. Mathieu, L. Latu-Romain, M. Vilasi, and Y. Wouters, Scripta Materialia 178, 176–180 (2020).
H. Beske, W.J. Quadakkers, H. Holzbrecher, H. Schuster, H. Nickel (1990). SIMS investigations on the growth mechanisms of protective chromia and alumina surface scales. Mikrochimica Acta 101, 109–119 (1990)
G.N. Greaves, Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids 71, 203-217 (1985).
J. Zarzicki et al., Glasses and the Vitreous State (Cambridge Solid State Science Series) (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge), First Edition edition (1991).
Acknowledgements
We are pleased to acknowledge Ms. G. Medjahdi and L. Aranda for their assistance, respectively, with the XRD and the thermogravimetric experiments. Authors thank the French National Research Agency (ANR) for the support of the PSEUDO project (Grant No. ANR-15-CE08-0021).
Funding
This study was funded by the French National Research Agency (ANR) in the framework of the PSEUDO project (Grant No. ANR-15-CE08-0021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TP contributed to conceptualization, methodology, investigation, software and writing—review and editing. SM helped in supervision, conceptualization, validation and writing—original draft preparation. YP contributed to investigation and formal analysis. LLR helped in investigation, formal analysis and writing—reviewing and editing. YW contributed to supervision and writing—reviewing and editing. MV helped in supervision and writing—reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Availability of Data and Material
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time due to time limitations. Raw data of the present study will be made available on demand.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perez, T., Mathieu, S., Parsa, Y. et al. About the Synergetic Influence of Manganese and Silicon on the Oxidation Rate of Chromia Forming Nickel-Based Model Alloys at 1050 °C. Oxid Met 94, 235–249 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-020-09988-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-020-09988-1