Abstract
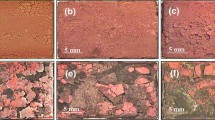
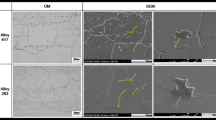
The oxidation behavior and mechanism of as-cast Inconel 740H superalloy, newly developed for advanced ultra-supercritical power plants superheater and reheater pipes, were investigated in the temperature range of 1050–1170 °C in air. Isothermal oxidation testing, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy were used in this study. The results showed that the oxidation of Inconel 740H was a diffusion-controlled process and controlled by the outward diffusion of metallic elements and inward penetration of oxygen. Owing to the complicated chemical composition of the alloy, different oxides tended to form in the oxidation process. Cross-sectional characterization investigation indicated that the oxide-scale layer consisted of three parts when the temperature was high or the oxidation time was long: an internal oxidation zone composed of Al2O3 and TiO2, a continuous and dense middle layer of Cr2O3 containing precipitates of TiO2 and an outmost layer of NiCr2O4 spinel. In the formation process of NiCr2O4, NiO was found in the early transient stage. With further oxidation, TiO2 finally could not be detected in the internal oxidation zone as a result of outwards diffusion of Ti and its limited concentration in the matrix.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Viswanathan, J. Henry, J. Tanzosh, G. Stanko, J. Shingledecker and B. Vitalis, Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance 14, 281 (2005).
S. Q. Zhao, X. S. Xie, G. D. Smith and S. J. Patel, Materials and Design 27, 1120 (2006).
C. F. Miller, G. W. Simmons and R. P. Wei, Scripta Materialia 42, 227 (2000).
M. Bensch, J. Preußner, R. Hüttner, G. Obigodi, S. Virtanen and J. Gabel, Acta Materialia 58, 1607 (2010).
W. Gao, Z. W. Li, W. Zheng, S. Li and Y. D. He, Intermetallics 10, 263 (2002).
S. Sinharoy and S.L. Narasimhan, in Proceedings of the 10th International Symposium on Superalloys, 623 (2004).
J. Xiao, N. Prud’homme, N. Li and V. Ji, Applied Surface Science 284, 446 (2013).
J. Zhu, A. Wise, T. Nuhfer, G. R. Holcomb, P. D. Jablonski and S. Sridhar, Materials Science and Engineering: A 566, 134 (2013).
Q. Jia and D. Gu, Optics and Laser Technology 62, 161 (2014).
A. Vesel, A. Drenik, K. Elersic, M. Mozetic, J. Kovac and T. Gyergyek, Applied Surface Science 305, 674 (2014).
F. J. Liu, M. C. Zhang, J. X. Dong and Y. W. Zhang, Acta Metallurgica Sinica (English Letters) 20, 102 (2007).
L. Zheng, M. C. Zhang and J. X. Dong, Applied Surface Science 256, 7510 (2010).
X.-M. Hou and K.-C. Chou, Journal of the European Ceramic Society 29, 517 (2009).
F. Pérez-González and N. Garza-Montes-de, Oxidation of Metals 82, 145 (2014).
X. X. Huang, J. S. Li, R. Hui, G. H. Bai and H. Z. Fu, Rare Metal Materials and Engineering 39, 1908 (2010).
P. Berthod, S. Michon, J. Di Martino, S. Mathieu, S. Noël and R. Podor, Calphad 27, 279 (2003).
N. Birks, G. H. Meier and F. S. Pettit, Introduction to the High Temperature Oxidation of Metals, 2nd ed, (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2006).
D. R. Clarke, Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science 6, 237 (2002).
D. Kim, C. Jang and W. Ryu, Oxidation of Metals 71, 271 (2009).
C. V. Robino, Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B 27, 65 (1996).
R. Haugsrud and T. Norby, Solid State Ionics 111, 323 (1998).
R. E. Lobnig, H. P. Schmidt, K. Hennesen and H. J. Grabke, Oxidation of Metals 37, 81 (1992).
B. Albert, R. Völkl and U. Glatzel, Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A 45, 4561 (2014).
A. Kumar, M. Nasrallah and D. L. Douglass, Oxidation of Metals 8, 227 (1974).
S. Q. Zhao, X. S. Xie and G. D. Smith, Surface and Coatings Technology 185, 178 (2004).
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate the financial support from National Basic Research Program (863 Program) of China under Grant No. 2012AA03A501.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, H., Dong, J., Zhang, M. et al. Oxidation Behavior and Mechanism of Inconel 740H Alloy for Advanced Ultra-supercritical Power Plants Between 1050 and 1170 °C. Oxid Met 84, 61–72 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-015-9543-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-015-9543-6