Abstract
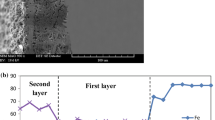
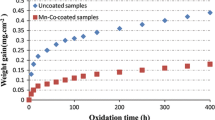
Alloy K41X has been proposed as interconnect material for high temperature vapor electrolysis (HTVE) devices. This chromia forming alloy (alloy K41X) was oxidized at 800 °C in a thermobalance in oxidizing (synthetic air) and reducing (Ar–1 %H2–9 %H2O) environments for 250 h. The evolution of the contact resistance was evaluated using a dedicated device under the same conditions. There were higher oxidation kinetics rate in air than in Ar–1 %H2–9 %H2O but surprisingly, the corresponding area specific resistance (ASR) values were 20 times higher in Ar–1 %H2–9 %H2O mixture than in air. Additional tests and analyses (exposure in Ar–D2–H2O environment, GD-OES and SIMS analyses) clearly showed that the higher ASR value can be attributed to the presence of hydrogen in the oxide scale when exposed in Ar–H2–H2O mixture. In situ changes of atmosphere during ASR measurement showed the rapid kinetics for hydrogen desorption.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Monceau and B. Pieraggi, Oxidation of metals 50, 477 (1998).
S. Chevalier, Shreir’s Corrosion Vol. 1: Basic concepts, High Temperature Corrosion, (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2010), pp. 132–152.
N. Bertrand, C. Desgranges, D. Poquillon, M. C. Lafont and D. Monceau, Oxidation of Metals 73, 139 (2010).
Y. Gong, C. Wang, Q. Shen and l. Zhang, Materials Chemistry and Physics 116, 573 (2009).
S. Fontana, R. Amendola, S. Chevalier, P. Piccardo, G. Caboche, M. Viviani, R. Molins and M. Sennour, Journal of Power Sources 171, 652 (2007).
M.R. Ardigo, I. Popa, S. Chevalier, C. Desgranges, and R. Bousquet, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 37, 8177 (2012).
X. Montero, F. Tietz, D. Stöver, M. Cassir and I. Villarreal, Corrosion Science 51, 110 (2009).
C. Piaget and C. Desgranges, Etude de l’oxydation à haute température de matériaux d’interconnecteur pour l’Electrolyse à Haute Température (EHT), Technical Report No CEA/DEN/DANS/DPC/SCCME 09-793-A (CEA, 2009).
S. Guillou, C. Cabet, C. Desgranges, L. Marchetti and Y. Wouters, Oxidation of Metals 76, 193 (2011).
D. M. England and A. V. Virkar, Journal of the Electrochemical Society 146, 3196 (1999).
D. M. England and A. V. Virkar, Journal of the Electrochemical Society 148, A330 (2001).
A. Galerie, Y. Wouters and M. Caillet, Materials Science Forum 369–372, 231 (2001).
S. R. J. Saunders, M. Monteiro and F. Rizzo, Progress in Materials Science 53, 775 (2008).
W. J. Quadakkers and J. Zurek, Shreir’s Corrosion Vol. 1: Basic concepts, High Temperature Corrosion, (Amsterdam, Elsevier, 2010), pp. 407–456.
T. Norby, Journal de Physique IV 3, 99 (1993).
P. Kofstad, Oxydation of Metals 44, 3 (1995).
K. Huang, P. Y. Hou and J. B. Goodenough, Solid State Ionics 129, 237 (2000).
S. Guillou, Study of a chromia-forming alloy behavior as interconnect material for High Température Vapor Electrolysis, PhD Thesis, Université de Bourgogne, 2011.
B. Tveten, G. Hultquist and T. Norby, Oxidation of Metals 51, 221 (1999).
T. Norby, Selected Topics in High Temperature Chemistry, (Elsevier, London, 1989), pp. 101–142.
M. P. Brady, M. Fayek, J. R. Keiser, H. M. Meyer, K. L. More, L. M. Anovitz, D. J. Wesolowski and D. R. Cole, Corrosion Science 53, (5), 1633 (2011).
A. Holt and P. Kofstad, Solid State Ionics 100, 201 (1997).
A. Holt and P. Kofstad, Solid State Ionics 69, 137 (1994).
H. Liu, S. B. Lyon and M. M. Stack, Oxidation of Metals 56, 147 (2001).
P. Kofstad, Oxidation of Metals 44, (1–2), 3 (1995).
Acknowledgments
The authors are very thankful to M. Tabarant (CEA, DEN, DPC, SCP, Laboratoire de Réactivité des Surfaces et Interfaces F-91191 Gif-sur-Yvette, France), Y. Wouters (Science et Ingénierie des Matériaux et Procédés, CNRS UMR5266/Grenoble-INP/UJF, 38402 Saint Martin d’Hères Cedex, France) and F. Jomard (CNRS de Meudon-Bellevue, Laboratoire de Physique des Solides et de Cristallogenèse CNRS UMR 8635) for their precious help for analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guillou, S., Desgranges, C. & Chevalier, S. Study of Conductivity of K41X Chromia Forming Alloy in High Temperature Electrolysis Environment. Oxid Met 79, 507–516 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-013-9361-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-013-9361-7