Abstract
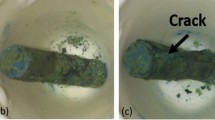
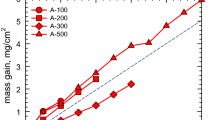
CMSX-4 is a single-crystalline Ni-base superalloy designed to be used at very high temperatures and high mechanical loadings. Its excellent corrosion resistance is due to external alumina-scale formation, which however can become less protective under thermal-cycling conditions. The metallic substrate in combination with its superficial oxide scale has to be considered as a composite suffering high stresses. Factors like different coefficients of thermal expansion between oxide and substrate during temperature changes or growing stresses affect the integrity of the oxide scale. This must also be strongly influenced by the thickness of the oxide scale and the substrate as well as the ability to relief such stresses, e.g., by creep deformation. In order to quantify these effects, thin-walled specimens of different thickness (t = 100−500 μm) were prepared. Discontinuous measurements of their mass changes were carried out under thermal-cycling conditions at a hot dwell temperature of 1100 °C up to 300 thermal cycles. Thin-walled specimens revealed a much lower oxide-spallation rate compared to thick-walled specimens, while thin-walled specimens might show a premature depletion of scale-forming elements. In order to determine which of these competetive factor is more detrimental in terms of a component’s lifetime, the degradation by internal precipitation was studied using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) in combination with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). Additionally, a recently developed statistical spallation model was applied to experimental data [D. Poquillon and D. Monceau, Oxidation of Metals, 59, 409–431 (2003)]. The model describes the overall mass change by oxide scale spallation during thermal cycling exposure and is a useful simulation tool for oxide scale spallation processes accounting for variations in the specimen geometry. The evolution of the net-mass change vs. the number of thermal cycles seems to be strongly dependent on the sample thickness.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Poquillon and D. Monceau, Oxidation of Metals 59, 409 (2003).
J. L. Smialek and G. H. Meier, in Superalloys II, High-Temperature Oxidation. C. T. Sims, N. S. Stoloff, and W. C. Hagel, eds. (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1987), Chapter 11, p. 293.
R. Orosz, U. Krupp, and H.-J. Christ, Zeitschrift für Metallkunde 96, 775 (2005).
R. Orosz, U. Krupp, and H.-J. Christ, Materials and Corrosion 57, 154 (2006).
H. E. Evans and A. T. Donaldson, Oxidation of Metals 50, 457 (1998).
G. Strehl, D. Naumenko, H. Al-Badary, L. M. Rodriguez Lobo, G. Borchardt, G. Tatlock, and W. J. Quadakkers, Materials at High Temperatures 17, 87 (2000).
S. Chang, U. Krupp, and H.-J. Christ, in Proceedings of Cyclic Oxidation of High Temperature Materials (EFC publications, 1999), p. 63.
U. Krupp, S. Y. Chang, and H.-J. Christ, Materials Science Forum 369–372, 287 (2001).
I. Gurrappa, S. Weinbruch, D. Naumenko, and W. J. Quadakkers, Materials and Corrosion 51, 224 (2000).
B. A. Pint, P. F. Tortorelli, and I. G. Wright, Oxidation of Metals 58, 73 (2002).
J. L. Smialek, Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A 9A, 309 (1978).
C. E. Lowell, C. A. Barrett, R. W. Palmer, J. V. Auping, and H. B. Probst, Oxidation of Metals 36, 81 (1991).
J. L. Smialek and J. V. Auping, Oxidation of Metals 57, 559 (2002).
P. Y. Hou, A. P. Paulikas, and B. W. Veal, Materials Science Forum 461–464, 671 (2004).
V. K. Tolpygo and D. R. Clarke, Oxidation of Metals 49, 187 (1998).
Acknowledgement
The financial support by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) under grant no. KR1999/2 is gratefully acknowledged. The authors thank Alstom Power, Baden, Switzerland for providing the material used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orosz, R., Krupp, U., Christ, HJ. et al. The Influence of Specimen Thickness on the High Temperature Corrosion Behavior of CMSX-4 during Thermal-Cycling Exposure. Oxid Met 68, 165–176 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-007-9067-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-007-9067-9