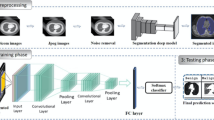
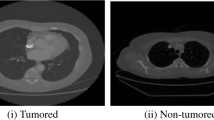
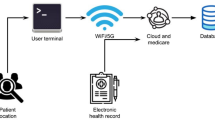
Abstract
Lung disease is one of the most common illnesses that should be treated in its early stages to improve the chances that patients will survive. Making the cancer diagnosis is the radiologist’s most difficult task. The advantages of a sophisticated computer-aided system for radiologists are enormous. Numerous studies use ML algorithms to detect lung cancer. To predict lung cancer, a multistage classification is most frequently used. The segmentation and data improvement classification scheme has been completed. This study suggests a unique method for detecting lung cancer combining machine learning and quantum music photonics. Here, trumpet players’ data has been gathered and examined for noise reduction, normalization, and smoothing. With the help of support kernel vector Gaussian learning and spatio convolutional perceptron learning, the characteristics of the processed data are retrieved and categorized. Different lung cancer datasets are subjected to experimental study in terms of accuracy, precision, recall, AUC, TPR, and FPR. The efficiency of the suggested strategy for the identification and categorization of lung cancer nodules is demonstrated by experimental data. The proposed technique attained accuracy of 97%, precision of 94%, recall of 85%, AUC of 72%, TPR of 55%, FPR of 45%.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used in this study will be made available upon reasonable request.
References
Balnis, J., Lauria, E.J., Yucel, R., Singer, H.A., Alisch, R.S., Jaitovich, A.: Peripheral blood omics and other multiplex-based systems in pulmonary and critical care medicine. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 69(4), 383–390 (2023)
Cheng, J., Pan, Y., Huang, W., Huang, K., Cui, Y., Hong, W., Tan, P.: Differentiation between immune checkpoint inhibitor-related and radiation pneumonitis in lung cancer by CT radiomics and machine learning. Med. Phys. 49(3), 1547–1558 (2022)
Gudur, A., Sivaraman, H., Vimal, V.: Deep learning-based detection of lung nodules in CT scans for cancer screening. Int. J. Intell. Syst. Appl. Eng. 11(7s), 20–28 (2023)
Shanshan Guo, Junshan Xiu, Wenqiang Chen, Te Ji, Fuli Wang, Huiqiang Liu, Precise diagnosis of lung cancer enabled by improved FTIR-based machine learning, Infrared Physics & Technology, 132, 104732 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infrared.2023.104732.
Karthika, M.S., Rajaguru, H., Nair, A.R.: Evaluation and Exploration of Machine Learning and CNN Classifiers in Detection of Lung Cancer from Microarray Gene-A Paradigm Shift (2023)
Khoirunnisa, A., Adytia, D.: Implementation of CRNN method for lung cancer detection based on microarray data. JOIV: Int. J. Inform. vis. 7(2), 600–605 (2023)
Kumar, S.: Importance of Artificial Intelligence–Machine Learning & Deep Learning Prediction in Cancer Diagnosis using Logistic Regression (2019)
Lee, S.H., Han, P., Hales, R.K., Voong, K.R., Noro, K., Sugiyama, S., Lee, J.: Multi-view radiomics and dosiomics analysis with machine learning for predicting acute-phase weight loss in lung cancer patients treated with radiotherapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 65(19), 195015 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6560/ab8531
Li Meng-Pan, Liu Wen-Cai, Sun Bo-Lin, Zhong Nan-Shan, Liu Zhi-Li, Huang Shan-Hu, Zhang Zhi-Hong, Liu Jia-Ming, Prediction of bone metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer based on machine learning, Frontiers in Oncology, 12 (2023) https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.1054300
M S, Karthika, Harikumar Rajaguru, and Ajin R. Nair. 2023. "Evaluation and Exploration of Machine Learning and Convolutional Neural Network Classifiers in Detection of Lung Cancer from Microarray Gene—A Paradigm Shift" Bioengineering 10 (8), 933. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10080933
Rani, K.M.S., Prasad, V.K.: Identification of lung cancer using ensemble methods based on gene expression data. Int. J. Intell. Syst. Appl. Eng. 11(10s), 257–266 (2023)
Sim, A.J., Kaza, E., Singer, L., Rosenberg, S.A.: A review of the role of MRI in diagnosis and treatment of early stage lung cancer. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 24, 16–22 (2020)
Wankhade, S., Vigneshwari, S.: Lung cell cancer identification mechanism using deep learning approach. Soft. Comput. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-08661-4
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to all guides for their valuable contributions and support during the course of this research.
Funding
The funders had no role in the design, execution, or interpretation of the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The Single author contributed significantly to the study and preparation of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest that could influence the research or the interpretation of results presented in this manuscript.
Ethical approval
N/A.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, J. Quantum photonics based health monitoring system using music data analysis by machine learning models. Opt Quant Electron 56, 590 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-06129-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-06129-1