Abstract
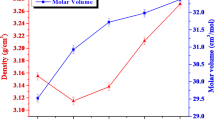
The present investigation, aimed to prepare lead silicate glasses doped with samarium ions and to study it’s structure, elastic, spectroscopic and thermoluminiscence properties with Al(10−x)Sbx composite influence. The objective of the investigation is to develop TL sustained good laser active resource by means of studying photo and thermoluminiscence properties. In this direction, we have prepared the glass series of Al(10−x)SbxSm0.1Pb30Si59.9 materials (where, 0 ≤ x ≤ 10, with steps of 0, 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10 mol%) after that planned for structural (XRD, FT-IR, DTA, EDS & SEM), Optical (UV & PL) and thermoluminescence characterization. The XRD and SEM studies reveal the glassy behavior of test samples. The EDX analysis signifies the chemical constitutes with atomic weight %. The physical properties such as density and molar volume of glasses were evaluated. The DTA studies of glasses reveal the glass transition and crystallization temperature points. The values of thermal stabilities of glasses found to be purely function of Sb3+ ions. Various structural vibrations of test glass conformed using FT-IR studies. Using ultrasonic velocities of the test glasses, the glasses' micro-hardness was evaluated. From the absorption spectra, the Judd–Ofelt intensity parameters (Ω2, Ω4, Ω6) have been calculated. The PL spectra under stimulation at 402 nm show a prominent reddish–orange emission at 602 nm. The experimental lifetimes (τr) of the 4G5/2 → 6H7/2 (602 nm) luminescence transition were measured using the decay spectral profiles of this transition. The evaluated emission cross-sections (σse), branching ratios (βr), and quantum efficiency (η) allow us to speculate that the lead silicate glasses doped with Sm3+ ions are ideally suitable as potential gain mediums for visible reddish orange lasers pumped directly by readily available 405 nm laser diodes. Quantum efficiencies of the produced glasses are obtained using a decay curve analysis. The emission spectra used to establish the developed glasses' reddish orange emission are used to compute the CIE chromaticity coordinates. It is evident from the stated fluorescent properties that the developed glasses are suited for reddish–orange laser applications, particularly in opto-electronic devices. From all of the values obtained, it can be observed that SAS6 glass code is ideally suited for reddish–orange laser applications. The TL properties are studied at 30 kGy gamma irradiation dose range. The frequency factor and A.E. of glasses were evaluated. This reveals that the TL behavior of glasses is a purely function of Sb3+ ions. Overall, the Al(10−x)SbxSm0.1Pb30Si59.9 glasses prepared are mechanical hard, TL effective, and optically useful resources.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be provided based on genuine request.
References
Abdel Wahab, E.A., Shaaban, K.S., Yousef, E.S.: Enhancement of optical and mechanical properties of sodium silicate glasses using zirconia. Opt. Quant. Electron. 52, 458 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-020-02575-3
Al-Harbi, N., Al-Hadeethi, Y., Bakry, A.S.: Mechanical and radiation shielding features of bioactive glasses: SiO2–Na2O–CaO–P2O5–B2O3 for utilization in dental applications. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 552, 120489 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2020.120489
Ali, A.S., Alrowaily, A.W., Issa, S.A.M., Rashad, M., Elsaman, R., Zakaly, H.M.H.: Unveiling the structural, optical, and electromagnetic attenuation characteristics of B2O3–SiO2–CaO–Bi2O3 glasses with varied WO3 content. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 212, 111089 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2023.111089
Annadurai, G., Kennedy, S.M.M., Sivakumar, V.: Photoluminescence properties of a novel orange–red emitting Ba2CaZn2Si6O17:Sm3+ phosphor. J. Rare Earths 34(6), 576–582 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0721(16)60064-9
Barrera, G.R., Souza, L.F., Novais, A.L.F., Caldas, L.V.E., Abreu, C.M., Machado, R., Sussuchi, E.M., Souza, D.N.: Thermoluminescence and optically stimulated luminescence of PbO–H3BO3 and PbO–H3BO3–Al2O3 glasses. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 155, 150–157 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2018.02.005
Barve, R.A., Patil, R.R., Moharil, S.V., Bhatt, B.C., Kulkarni, M.S.: Phase dependent TL–OSL studies in various phases of chemically synthesized Cu doped crystalline SiO2. J. Luminesc. 171, 72–78 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2015.10.076
Bhargavi, K., Sanyal, B., Sundara Rao, M., Kumar, V.R., Gandhi, Y., Baskaran, G.S., Veeraiah, N.: γ-Ray induced thermoluminescence characteristics of the PbO–Al2O3–SiO2:Pr3+ glass system. J. Luminesc. 161, 417–421 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2015.01.038
Biswas, J., Jana, S.: Visible luminescence and energy migration mechanism of Sm3+ in phospho-tellurite glasses by co-activating with Tb3+ ions for solid state lighting device applications. Phys. B Condens. Matter 657, 414812 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2023.414812
Dawngliana, K.M.S., Rai, S.: Linear and nonlinear and optical properties of Sm3+ co-doped alumino-silicate glass prepared by sol–gel method. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 598, 121929 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2022.121929
de Araújo, C.B., Kassab, L.R.P., da Silva, D.M.: Optical properties of glasses and glass-ceramics for optical amplifiers, photovoltaic devices, color displays, optical limiters, and random lasers. Opt. Mater. 131, 112648 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2022.112648
Deepa, A.V., Vinothkumar, P., Sathya Moorthy, K., et al.: Optical, electrical, mechanical properties of Pr3+ and Yb3+ doped phosphate glasses. Opt. Quant. Electron. 52, 483 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-020-02606-z
Devi, C.A., Swapna, K., Sk Mahamuda, M., Venkateswarlu, M.V.V.K.S.P., Rama Krishna Reddy, K.S., Deopa, N., Rao, A.S.: Spectroscopic studies and lasing potentialities of Sm3+ ions doped single alkali and mixed alkali fluoro tungstentellurite glasses. Opt. Laser Technol. 111, 176–183 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2018.09.051
Doweidar, H., El-Egili, K., Ramadan, R., Al-Zaibani, M.: Structural investigation and properties of Sb2O3–PbO–B2O3 glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 497, 93–101 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2018.01.025
El-Hagary, M., Emam-Ismail, M., Shaaban, E.R., Shaltout, I.: Optical properties of glasses (TeO2–GeO2–K2O) thin films co-doped with rare earth oxides Sm2O3/Yb2O3. J. Alloys Compd. 485(1–2), 519–523 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.06.016
Gaikwad, D.K., Sayyed, M.I., Obaid, S.S., Issa, S.A.M., Pawar, P.P.: Gamma ray shielding properties of TeO2–ZnF2–As2O3–Sm2O3 glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 765, 451–458 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.06.240
Hamlík, L., Liška, M., Slábiková, M., Hatalová, B.: DTA study of temperature chracteristics in dependance on composition for glasses in the CaO–MgO–Al2O3–SiO2–B2O3 system. Thermochim. Acta 93, 243–246 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-6031(85)85063-2
Hemalatha, S., Nagaraja, M., Madhu, A., Suresh, K., Srinatha, N.: The role of Sm2O3 on the structural, optical and spectroscopic properties of multi-component ternary borate glasses for orange–red emission applications. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 554, 120602 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2020.120602
Hivrekar, M.M., Jagannath, G., Pramod, A.G., Aloraini, D.A., Almuqrin, A.H., Sayyed, M.I., Keshavamurthy, K., Hegde, V., Sathish, K.N., Pasha, U.M., Venugopal Rao, S., Yasmin, S., Jadhav, K.M.: Third-order nonlinear optical properties of Sm2O3 activated cadmium alkali borate glasses. Opt. Mater. 127, 112313 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2022.112313
Ibrahim, M.S.S., Hamed, M.K.G., El-Okr, M.M., et al.: Highly sensitive photonic crystal gamma ray dosimeter. Opt. Quant. Electron. 53, 348 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-021-02968-y
Jiang, X., Sun, Y., Wang, X., Hu, L., Chen, S., Yang, Q.: Temperature dependence of spectroscopic properties and energy transfer in Nd3+/Yb3+ co-doped silicate glass. J. Luminesc. 251, 119146 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2022.119146
Jose, A., Krishnapriya, T., Jose, T.A., Joseph, C., Unnikrishnan, N.V., Biju, P.R.: Color tunable luminescence characteristics and energy transfer analysis of Dy3+/Sm3+ co-doped multicomponent borosilicate glasses. Scr. Mater. 203, 114088 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114088
Kang, J., Wang, J., Lou, X., Khater, G.A., Hou, Y., Tang, F., Yue, Y.: Effect of Y2O3 content on the crystallization behaviors and physical properties of glasses based on MgO–Al2O3–SiO2 system. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 497, 12–18 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2018.05.029
Karki, S., Kesavulu, C.R., Kim, H.J., Kaewkhao, J., Chanthima, N., Ruangtaweep, Y.: Physical, optical and luminescence properties of B2O3–SiO2–Y2O3–CaO glasses with Sm3+ ions for visible laser applications. J. Luminesc. 197, 76–82 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2018.01.015
Katyayan, S., Agrawal, S.: Optical behavior and TL kinetics of Eu3+ and Tb3+ doped zirconate thermoluminescent phosphors. Opt. Quant. Electron. 51, 277 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-019-1993-7
Kaur, R., Singh, S., Pandey, O.P.: Structural variation in gamma ray irradiated PbO–Na2O–B2O3–SiO2 glasses. Solid State Commun. 188, 40–44 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssc.2014.02.022
Kaur, J., Kaur, P., Mudahar, I., Singh, K.: Effect of Sm2O3 on the physical, structural and optical properties of 40SiO2–40B2O3–10V2O5-(10–x) Fe2O3 glasses. Ceram. Int. 49(9), 13610–13617 (2023a). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.12.237
Kaur, J., Mattu, N.K., Mudahar, I., Singh, K.: Role of Sm2O3 on surface to bulk crystallization and thermal properties of Fe2O3–V2O5–B2O3–SiO2 glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 610, 122304 (2023b). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2023.122304
Khan, I., Shoaib, M., Srisittipokakun, N., Ullah, I., Ahad, A., Kothan, S., Rooh, G., Kaewkhao, J.: Spectroscopic investigation of Sm2O3-activated barium calcium strontium borate glasses for laser and display-devices applications. Optik 265, 169439 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2022.169439
Kolavekar, S.B., Ayachit, N.H., Rajaramakrishna, R., Pramod, N.G., Kaewkhao, J.: Reddish–orange emission and Judd–Ofelt investigation of Sm3+ ions doped in zince–bismuth–phosphor–tellurite glasses for solid lighting application. J. Luminesc. 226, 117498 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2020.117498
Kumar, M., Rao, A.S.: Concentration-dependent reddish-orange photoluminescence studies of Sm3+ ions in borosilicate glasses. Opt. Mater. 109, 110356 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2020.110356
Lakshmi, Y.A., Swapna, K., Sk Mahamuda, M., Venkateswarlu, A.S.R.: Photoluminescence properties of Sm3+ ions doped bismuth Boro tellurite glasses. Solid State Sci. 116, 106609 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2021.106609
Le, V.V., Dinh, H.T.: Structural and mechanical properties of densified (Li2O)0.2(SiO2)0.8 glasses: a molecular dynamics simulations study. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 530, 119815 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2019.119815
Lin, H., Yang, H., Zhou, L., He, J., Liu, B., Li, N., Li, C., Li, S., Yang, W., Jiang, X., Liu, H., Zeng, F., Su, Z.: Research on the physical and optical properties of Dy3+ doped 30 mol%Tb2O3–B2O3–GeO2–PbO–SiO2 magneto-optical glass with high verdet constant. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 166, 110682 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2022.110682
Liška, M., Hamlík, L., Valášek, J.: Statistical verification of attribution viscosity values to the corresponding significant points on the DTA curves of glasses in the CaO–MgO–Al2O3–SiO2–B2O3 system (CMASB). Thermochim. Acta 93, 247–250 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-6031(85)85064-4
Mahamuda, Sk., Swapna, K., Venkateswarlu, M., Srinivasa Rao, A., Shakya, S., Prakash, G.V.: Spectral characterisation of Sm3+ ions doped Oxy-fluoroborate glasses for visible orange luminescent applications. J. Luminesc. 154, 410–424 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2014.05.017
Mansour, E.: Semi-quantitative analysis for FTIR spectra of Al2O3–PbO–B2O3–SiO2 glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 358(3), 454–460 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2011.10.037
Martinet, C., Heili, M., Martinez, V., Kermouche, G., Molnar, G., Shcheblanov, N., Barthel, E., Tanguy, A.: Highlighting the impact of shear strain on the SiO2 glass structure: from experiments to atomistic simulations. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 533, 119898 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2020.119898
Mu, N., Chen, D., Li, B.: Influence of Zn/Ba ratio on crystallization, sintering behavior and properties of CaO–Al2O3–SiO2 glass-ceramics. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 622, 122662 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2023.122662
Okada, G., Kasap, S., Yanagida, T.: Optically- and thermally-stimulated luminescence of Ce-doped SiO2 glasses prepared by spark plasma sintering. Opt. Mater. 61, 15–20 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2016.08.020
Pesina, T., Tikhonova, L., Kireenko, M., Sinani, A.: Alexandre Chmel, fine structure, mechanical characteristics and mid-range order in xZnO–yNa2O–(1–x-y)SiO2 glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 481, 17–20 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2017.10.019
Prabhu, N.S., Sharmila, K., Kumaraswamy, S., Somashekarappa, H.M., Sayyed, M.I., Al-Ghamdi, H., Almuqrin, A.H., Kamath, S.D.: An examination of the radiation-induced defects and thermoluminescence characteristics of Sm2O3 doped BaO–ZnO–LiF–B2O3 glass system for γ-dosimetry application. Opt. Mater. 118, 111252 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2021.111252
Prasad, R.N.A., Siva, B.V., Neeraja, K., Mohan, N.K., Rojas, J.I.: Effect of modifier oxides on spectroscopic and optical properties of Pr3+ doped PbO–Ro2O3–WO3–B2O3 glasses (with Ro2O = Sb2O3, Al2O3, and Bi2O3). J. Luminesc. 230, 117666 (2021a). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2020.117666
Prasad, R.N.A., Srinivasa Rao, L., Babu, T.A., Neeraja, K., Mohan, N.K.: Structural and photoluminescence characteristics of PbO–M2O3(M2O3 = Al2O3, Sb2O3 and Bi2O3)–WO3–B2O3:Sm2O3 glasses suitable for orange-red lasers. Optik 244, 167563 (2021b). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.167563
Qiao, Y.-P., Chen, P.: Luminescence, energy transfer, and colour adjustment of CaO–CaF2–Al2O3–B2O3–SiO2 glass co-doped with CeO2 and Sm2O3. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 552, 120461 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2020.120461
Rajesh, M., Kavaz, E., Deva Prasad Raju, B.: Photoluminescence, radiative shielding properties of Sm3+ ions doped fluoroborosilicate glasses for visible (reddish–orange) display and radiation shielding applications. Mater. Res. Bull. 142, 111383 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2021.111383
Rajesham, S., Chandra Sekhar, K., Shareefuddin, M., et al.: Synthesis, physical, optical and structural studies of B2O3–CdO–Al2O3–PbF2 glasses modified with MoO3 ions. Opt. Quant. Electron. 54, 470 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-022-03874-7
Rani, P.R., Venkateswarlu, M., Sk Mahamuda, K., Swapna, N.D., Rao, A.S., Prakash, G.V.: Structural, absorption and photoluminescence studies of Sm3+ ions doped barium lead alumino fluoro borate glasses for optoelectronic device applications. Mater. Res. Bull. 110, 159–168 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2018.10.033
Saddeek, Y.B., Kaid, M.A., Ebeid, M.R.: FTIR and physical features of Al2O3–La2O3–P2O5–PbO glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 387, 30–35 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2013.12.029
Sailaja, P., Sk Mahamuda, K., Swapna, M.V., Rao, A.S.: Optical properties of Sm3+ ions doped 10SrO–(10–x)Al2O3–10BaCl2–60B2O3–10TeO2 glasses for reddish orange laser applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 270, 115198 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2021.115198
Sayyed, M.I., Kurtulus, R., Kavas, T.: Impact of La2O3 reinforcement on the mechanical, and photon shielding properties of La2O3–B2O3 glass. Optik 258, 168923 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2022.168923
Šmejcký, J., Jeřábek, V., Mareš, D., Voves, J., Vařák, P., Cajzl, J., Oswald, J., Prajzler, V., Nekvindová, P.: Erbium–bismuth-doped germanium silicate active optic glass for broad-band optical amplification. Opt. Mater. 137, 113621 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2023.113621
Suebsing, N., Bootjomchai, C., Promarak, V., Laopaiboon, R.: Luminescent properties of calcium-alumino-silicate glasses (CaAlSi) doped with Sm2O3 and co-doped with Sm2O3 + Eu2O3 for LED glass applications. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 523, 119598 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2019.119598
Sun, Y., Zhang, Z., Liu, L., Wang, X.: FTIR, Raman and NMR investigation of CaO–SiO2–P2O5 and CaO–SiO2–TiO2–P2O5 glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 420, 26–33 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2015.04.017
Sundara Rao, M., Sanyal, B., Bhargavi, K., Vijay, R., IV., Kityk, N.V.: Influence of induced structural changes on thermoluminescence characteristics of γ-ray irradiated PbO–Al2O3–SiO2:Dy3+ glasses. J. Mol. Struct. 1073, 174–180 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2014.04.075
Świontek, S., Środa, M.: The effect of SiO2 on the thermal stability and thermoluminescence properties of barium–cerium borate glass and glass-ceramics. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 559, 120708 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2021.120708
Tamrakar, R.K., Upadhyay, K.: Thermoluminescence behaviour of GdAlO3:Yb3+under gamma exposure. Opt. Quant. Electron. 50, 271 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-018-1542-9
Tirupataiah, Ch., Narendrudu, T., Suresh, S., Srinivasa Rao, P., Teja, P.M.V., Sambasiva Rao, M.V., Ram, G.C., Krishna Rao, D.: Influence of valence state of copper ions on structural and spectroscopic properties of multi-component PbO–Al2O3–TeO2–GeO2–SiO2 glass ceramic system—a possible material for memory switching devices. Opt. Mater. 73, 7–15 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2017.07.040
Ullah, I., Khan, I., Shah, S.K., Khattak, S.A., Shoaib, M., Kaewkhao, J., Ahmad, T., Ahmed, E., Rooh, G., Khan, A.: Luminescence properties of Sm3+ doped Na2B4O7 glasses for lighting application. J. Luminesc. 230, 117700 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2020.117700
Zakaly, H.M.H., Alsaif, N.A.M., Shams, M.S., et al.: Synthesis, physical, optical characteristics, neutron/γ-rays shielding capacity of newly arsenic glasses: experimental, theoretical, and simulation investigations. Opt. Quant. Electron. 55, 365 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-04610-5
Acknowledgements
Authors thank to the Dr. K. T. Mahee (Chairman), Mr. K. Abijith Rao (C.E.O), and Prof. C.V.Tomy (Director) of Sreenidhi Institute of Science and Technology for needful help and moral support during overall completion of the investigation.
Funding
No funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr. P.A.: synthesis, characterization and results analysis; Dr. R.K.G.: conceptualization, methodology, results analysis and report drafting; Dr. S.S.D.: helped during optical characterization; Dr. Ch.R.: helped during TL characterization; Dr. K.R.K.C.: helped during FT-IR deconvolution Analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No competing interest.
Ethics approval statement
Yes.
Consent to participate statement
Yes.
Consent for publication
Yes.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ashok, P., Guntu, R.K., Devi, S.S. et al. Spectroscopic and TL properties of Sm2O3 doped lead silicate glasses containing alumina and antimony oxides. Opt Quant Electron 56, 446 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-06093-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-06093-w