Abstract
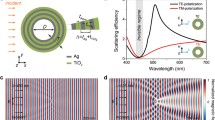
We investigated an electromagnetically induced transparency metamaterial and provided a comprehensive demonstration of its tunable electromagnetic characteristics in the terahertz region. Within a unit cell, a pair of horizontally aligned metal wires induces electric resonance, functioning as bright mode resonators. Additionally, a hybrid structure composed of metal and vanadium dioxide is employed to generate toroidal resonance, serving as dark mode resonators. Analysis of the scattered power reveals an enhancement of the energy associated with toroidal resonance within the transparent window. Simulation results illustrate a gradual reduction in the coupling strength of the electromagnetically induced transparency effect, and the transparency peak shifts toward the lower frequency range with decreasing conductivity of vanadium dioxide. Ultimately, the electromagnetically induced transparency phenomenon dissipates, resulting in a transmission spectrum characterized by a resonance curve. Theoretical analysis based on a two-coupled oscillator model unveils that the tunable effect of the electromagnetically induced transparency metamaterial is attributed to the modulation of damping rate and intrinsic resonant frequency of the dark mode resonator, achieved through adjustments in the conductivity of vanadium dioxide. This proposed approach holds promise for enhancing electromagnetically induced transparency implementations and expanding the application domains of toroidal metamaterials.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data underlying the results presented in this paper are not publicly available at this time but may be obtained from the authors upon reasonable request.
References
Boller, K.J., Imamoğlu, A., Harris, S.E.: Observation of electromagnetically induced transparency. Phys. Rev. Lett. 66(20), 2593–2596 (1991)
Cai, W., Fan, Y., Huang, X., Fu, Q., Yang, R., Zhu, W., Zhang, F.: Electromagnetically induced transparency in all-dielectric metamaterials: coupling between magnetic Mie resonance and substrate resonance. Phys. Rev. A 100(5), 053804 (2019)
Chen, M.M., Yang, X.X.: Tunable and three-dimensional dual-band metamaterial absorber based on electromagnetically induced transparency with vanadium dioxide. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 25(23), 13393–13398 (2023)
Chen, H.T., Yang, H., Singh, R., O’Hara, J.F., Azad, A.K., Trugman, S.A., Jia, Q.X., Taylor, A.J.: Tuning the resonance in high-temperature superconducting terahertz metamaterials. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105(24), 247402 (2010)
Chen, M., Xiao, Z., Lv, F., Cui, Z., Xu, Q.: Dynamically tunable dual-band electromagnetically induced transparency-like in terahertz metamaterial. Opt. Mater. 107, 110060 (2020)
Chen, M.M., Yang, X.X., Gao, S.: Tunable electromagnetically induced transparency in a metal-perovskite hybrid metamaterial and its sensing performance. IEEE Sens. J. 23, 4802–4808 (2023)
Engheta, N.: Antenna-guided light. Science 334(6054), 317–318 (2011)
Gao, E.D., Li, H.J., Liu, Z.M., Xiong, C.X., Liu, C., BX Ruan: Terahertz multifunction switch and optical storage based on triple plasmon-induced transparency on a single-layer patterned graphene metasurface. Opt. Express 28(26), 40013–23 (2020)
Gao, F., Yuan, P.C., Ma, H.F., Xu, T., Zhu, J.W., Li, K.X., Yang, F., Yan, B.: Tunable chiral-selective electromagnetically induced transparency-like effect in VO2-based metamaterial for slow light applications. EPL 132(1), 15001 (2020b)
Guo, B., Wan, D., Ishaq, A., Luo, H., Gao, Y.: Direct synthesis of high-performance thermal sensitive VO2(B) thin film by chemical vapor deposition for using in uncooled infrared detectors. J. Alloys Compd. 715, 129–136 (2017)
Ham, B.S., Hemmer, P.R., Shahriar, M.S.: Efficient electromagnetically induced transparency in a rare-earth doped crystal. Opt. Commun. 144(4), 227–230 (1997)
Han, B., Li, X., Sui, C., Diao, J., Jing, X., Hong, Z.: Analog of electromagnetically induced transparency in an E-shaped all-dielectric metasurface based on toroidal dipolar response. Opt. Mater. Express 8(8), 2197–2207 (2018)
Hau, L.V., Harris, S.E., Dutton, Z.: Light speed reduction to 17 meters per second in an ultracold atomic gas. Nature 397(6720), 594–598 (1999)
Hinamoto, T., Fujii, M.: MENP: an open-source MATLAB implementation of multipole expansion for nanophotonics. OSA Continuum 4, 1640–1648 (2021)
Jepsen, P.U., Fischer, B.M., Thoman, A., Helm, H., Suh, J.Y., Lopez, R., Haglund, R.F., Jr.: Metal-insulator phase transition in a VO2 thin film observed with terahertz spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. B 74(20), 205103 (2006)
Jiang, X., Chen, D., Zhang, Z.: Dual-channel optical switch, refractive index sensor and slow light device based on a graphene metasurface. Opt. Express 28(23), 34079–34092 (2020)
Landy, N.I., Sajuyigbe, S., Mock, J.J.: Perfect metamaterial absorber. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100(20), 207402 (2008)
Li, H., Liu, S.: Electromagnetically induced transparency with large group index induced by simultaneously exciting the electric and the magnetic resonance. Appl. Phys. Lett. 13, 133514 (2014)
Li, J., Yu, P., Cheng, H.: Optical polarization encoding using graphene-loaded plasmonic metasurfaces. Adv. Opt. Mater. 4, 91–98 (2016)
Liu, G.D., Zhai, X., Xia, S.X., Lin, Q., Zhao, C.J., Wang, L.L.: Toroidal resonance based optical modulator employing hybrid graphene-dielectric metasurface. Opt. Express 25, 26045 (2017)
Luo, C., Ibanescu, M., Johnson, S.G.: Cerenkov radiation in photonic crystals. Science 299(5605), 368–371 (2003)
Ma, J., Wang, Z.H., Liu, H., Fan, Y.X., Tao, Z.Y.: Active switching of extremely high-Q fano resonances using vanadium oxide-implanted terahertz metamaterials. Appl. Sci. 10(1), 330 (2020)
Marcinkevicius, S., Gushterov, A., Reithmaier, J.P.: Transient electromagnetically induced transparency in self-assembled quantum dots. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92(4), 041113 (2008)
Meng, F.Y., Wu, Q., Erni, D., Wu, K., Lee, J.C.: Polarization independent metamaterial analog of electromagnetically induced transparency for a refractive-index-based sensor. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 60(10), 3013–3022 (2012)
Pan, G.M., Shu, F.Z., Wang, L., Shi, L.P., Evlyukhin, A.B.: Plasmonic anapole states of active metamolecules. Photon. Res. 9, 822–828 (2021)
Pendry, J.B.: Negative refraction makes a perfect lens. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85(18), 3966–3969 (2000)
Phillips, D.F., Fleischhauer, A., Mair, A., Walsworth, R.L., Lukin, M.D.: Storage of light in atomic vapor. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86(4), 783 (2001)
Saadabad, R.M., Huang, L.J., Evlyukhin, A.B., Miroshnichenko, A.E.: Multifaceted anapole: from physics to applications. Opt. Mater. Express 12(5), 1817–1837 (2022)
Seddon, N., Bearpark, T.: Observation of the inverse doppler effect. Science 302(5650), 1537–1540 (2003)
Serapiglia, G.B., Paspalakis, E., Sirtori, C.: Laser-induced quantum coherence in a semiconductor quantum well. Phys. Rev. Lett. 84(5), 1019–1022 (2000)
Shen, Z., Yang, H., Huang, X., Xiang, T., Wu, J., Zhou, Y., Yu, Z.: Electromagnetically induced transparency metamaterial with strong toroidal dipole response. Mater. Res. Express 7(3), 035802 (2020)
Shu, C., Zhang, C., Ye, Y.L., Lin, T.Q.: Active manipulation of toroidal resonance in hybrid metal-vanadium dioxide metamaterial. Results Phys 33, 105146 (2022)
Sun, G., Peng, S., Zhang, X., Zhu, Y.: Switchable electromagnetically induced transparency with toroidal mode in a graphene-loaded all-dielectric Metasurface. Nanomaterials 10, 1064 (2020)
Wang, H., Zhang, Y.T., Hu, F.R., Jiang, M.Z., Zhang, L.H., Zhang, W.T., Han, J.G.: Active dual-control terahertz electromagnetically induced transparency analog in VO2 metasurface. Appl. Phys. Lett. 7(6), 061701 (2023)
Wu, Y., Xu, W., Zhou, H., Qiu, X., He, Y., Gao, Y., Wang, B.X.: Tunableness of single-band and dual-band absorption and filtering using vanadium-dioxide-based metamaterial. Appl. Phys. A 128(10), 930 (2020)
Wu, G.Z., Jiao, X.F., Wang, Y.D., Zhao, Z.P., Wang, Y.B., Liu, J.G.: Ultra-wideband tunable metamaterial perfect absorber based on vanadium dioxide. Opt. Express 29(2), 2703–2711 (2021)
Xiao, S., Wang, T., Liu, T., Yan, X., Li, Z., Xu, C.: Active modulation of electromagnetically induced transparency analogue in terahertz hybrid metal-graphene metamaterials. Carbon 126, 271 (2018)
Xu, X., Zhang, C., Lv, G., Jiang, J., He, X.: Actively tunable and switchable electromagnetically induced transparency in hybrid metal-graphene metamaterials. Mater. Res. Express 8(2), 025802 (2021)
Yan, C., Cui, Y., Wang, Q.: Superwide-band negative refraction of a symmetrical E-shaped metamaterial with two electromagnetic resonances. Phys. Rev. E 77(5), 056604 (2008)
Yang, R., Fu, Q., Fan, Y.: Active control of EIT-like response in a symmetry-broken metasurface with orthogonal electric dipolar resonators. Photonics Res 7, 955 (2019)
Yang, T., Liu, X.M., Zhou, J.: Terahertz polarization conversion in an electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT)-like metamaterial. Ann. Phys. 533, 2000528 (2021)
Zhang, M., Song, Z.Y.: Switchable terahertz metamaterial absorber with broadband absorption and multiband absorption. Opt. Express 29(14), 21551–21561 (2021)
Zhang, S., Genov, D.A., Wang, Y., Liu, M., Zhang, X.: Plasmon-induced transparency in metamaterials. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101(4), 047401 (2008)
Zhu, L., Dong, L., Guo, J., Meng, F.Y., He, X.J., Wu, T.H.: Polarization-independent transparent effect in windmill-like metasurface. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 51(26), 265101 (2018)
Zhu, L., Zhao, X., Miao, F., Ghosh, B.K., Dong, L., Tao, B., Meng, F., Li, W.: Dual-band polarization convertor based on electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT) effect in all-dielectric metamaterial. Opt. Express 27(9), 12163–12170 (2019)
Zhu, L., Li, H., Dong, L., Zhou, W., Rong, M., Zhang, X., Guo, J.: Dual-band electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT) terahertz metamaterial sensor. Opt. Mater. Express 11(8), 2109–2121 (2021)
Zhu, L., He, R.M., Dong, L., He, X., Meng, F.: Tunable terahertz metamaterial based on vanadium dioxide for electromagnetically induced transparency and reflection. Opt. Eng. 62(6), 067102 (2023)
Funding
The work was financially supported by Heilongjiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (grant NO. LH2022F040) and Harbin University Doctor Found (grant NO. HUDF2020108).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors reviewed the manuscript. The main manuscript and the graphic drawing were performed by CS. The revision work is carried out by JM and HS. The references were made by LC and YS.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shu, C., Mei, J., Sun, H. et al. Tunable electromagnetically induced transparency metamaterial utilizing bright-dark mode coupling between electric and toroidal resonances. Opt Quant Electron 56, 43 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-05647-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-05647-2