Abstract
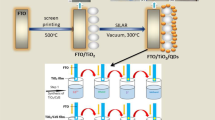
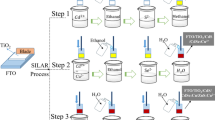
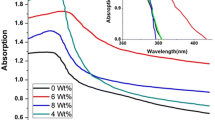
In this research, photoanodes on the basis of a CdS/CdSe multilayer film, where CdSe-doped with Cu were successfully fabricated and optimized at a 3% doping concentration. The highest performance of quantum dot solar cells is 4.24%. This result is also confirmed by studying the optical and electrical properties of quantum dot solar cells that change with the Cu doping concentration. The enhanced efficiency can be explained by electrical-optical parameters, which are determined from UV–Vis spectra, J–V curves, and EIS experiments. The optical parameters such as absorption density, the band gap, the top of the valence band, and the bottom of the conduction band are estimated based on the Tauc equation and the UV–Vis spectra experiments for optical properties. Moreover, the electrical parameters, such as the shunt resistance and Rct1 and Rct2 resistances, are also extracted from J-V curves and the electrochemical impedance spectra experiments for electrical properties. Finally, the obtained results are used to explain the enhanced performance efficiency of devices.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Bataineh, Q.M., et al.: Structural, electronic and optical characterization of ZnO thin film-seeded platforms for ZnO nanostructures: sol–gel method versus ab initio calculations. J. Electr. Mater. 48(8), 5028–5038 (2019)
Fang, B., et al.: Facile synthesis of open mesoporous carbon nanofibers with tailored nanostructure as a highly efficient counter electrode in CdSe quantum-dot-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem 21(24), 8742–8748 (2011)
Guijarro, N., et al.: CdSe quantum dot-sensitized TiO2 electrodes: effect of quantum dot coverage and mode of attachment. J. Phys. Chem. c. 113(10), 4208–4214 (2009)
Ha, T.T., et al.: Improving the performance of QDSSC s based on TiO2/CdS (Silar)/CdSe (Colloid)/Zns (Silar) photoanodes. Environ. Progr. Sustain. Energy. 34(6), 1774–1779 (2015)
Hagfeldt, A., et al.: Dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem. Rev. 110(11), 6595–6663 (2010)
Hassanien, A.S., Akl, A.A.J.J.O.A.: Compounds, Influence of composition on optical and dispersion parameters of thermally evaporated non-crystalline Cd50S50− xSex thin films. J. Alloy. Compd. 648, 280–290 (2015)
Husain, M., et al.: Optical, electrical and structural investigations on Cd1− xZnxSe sintered films for photovoltaic applications. Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cell. 76(3), 399–415 (2003)
Mondal, R., et al.: Synthesis of acenaphthyl and phenanthrene based fused-aromatic thienopyrazine co-polymers for photovoltaic and thin film transistor applications. Chem. Mater. 21(15), 3618–3628 (2009)
Muthalif, M.P.A., et al.: Enhanced photovoltaic performance of quantum dot-sensitized solar cells with a progressive reduction of recombination using Cu-doped CdS quantum dots. Appl. Surf. Sci. 396, 582–589 (2017)
Pattanaik, A., Srinivasan, A.J.S.S.: Electrical and optical studies on Pb-modified amorphous Ge–Se–Te films. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 19, 2–157 (2003)
Phuc, D.H., Tung, H.T.: Tung, Band tunable CdSe quantum dot-doped metals for quantum dot-sensitized solar cell application. Int. J. Photoenergy 2019, 9812719 (2019)
Phuong, H.N., et al.: Effect of precursors on Cu2S counter electrode on the quantum dot sensitized solar cell performance. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 80(12), 1133–1142 (2022)
Pinto, A.H., et al.: Green chemistry applied to transition metal chalcogenides through synthesis, design of experiments, life cycle assessment, and machine learning. In Green Chemistry-New Perspectives, IntechOpen (2022)
Rühle, S., Shalom, M., Zaban, A.J.C.: Quantum-dot-sensitized solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 11(11), 2290–2304 (2010)
Sanchez-Ramirez, E., et al.: Nanocrystalline CdS1− xSex alloys as thin films prepared by chemical bath deposition: effect of x on the structural and optical properties. J. Alloy. Compd 615, 511–514 (2014)
Shockley, W., Queisser, H.J.J.J.O.A.P.: Detailed balance limit of efficiency of p-n junction solar cells. J. Appl. Phys. 32(3), 510–519 (1961)
Song, L., Duan, J., Zhan, J.J.M.L.: One-pot microwave assisted synthesis of homogeneously alloyed CdSexTe1-x nanocrystals with tunable photoluminescence. Mater. Lett. 64(16), 1843–1845 (2010)
Tauc, J., Grigorovici, R., Vancu, A.J.P.S.S.: Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous germanium. Physica Status Solidi (b) 15(2), 627–637 (1966)
Tung, H.T., et al.: Ag+ ion doped on the CdSe quantum dots for quantum-dot-sensitized solar cells’ application. Appl. Phys. a. 125, 1–9 (2019)
Urbach, F.J.P.R.: The long-wavelength edge of photographic sensitivity and of the electronic absorption of solids. Phys. Rev. 92(5), 1324 (1953)
Venables, J.: Introduction to surface and thin film processes. Cambridge University Press (2000)
Vogel, R., Pohl, K., Weller, H.J.C.P.L.: Sensitization of highly porous, polycrystalline TiO2 electrodes by quantum sized CdS. Chem. Phys. Lett. 174(3–4), 241–246 (1990)
Zhao, F., et al.: Effects of Ag doping on the electronic and optical properties of CdSe quantum dots. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 21(29), 16108–16119 (2019)
Funding
This research was fully supported/funded by Tra Vinh University under grant contract number 415/2022/HĐ.HĐKH&ĐT-ĐHTV.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TTAT: Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Data curation, Conceptualization. LTNT: Writing—review & editing, Methodology, Conceptualization PTH, TTNT, NS, VCN, DHP: Writing—review & editing, Writing—original draft, Project administration, Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Confict of interest
The authors have no conficts of interest or competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tuan, T.T.A., Hung, P.T., Chinh, T.T.N. et al. Optimizing electrical-optical parameters in TiO2@CdS@CdxCu1-xSe photoanodes using UV–Vis spectra, J-V curves, and EIS experiments in quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. Opt Quant Electron 55, 1221 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-05363-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-05363-x