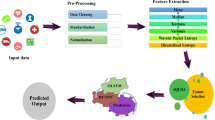
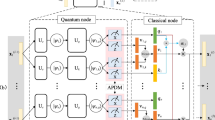
Abstract
Managing expanding urbanisation, energy use, environmental preservation, citizen economic and living standards, and people's ability to effectively use and adopt modern information and communication technology (ICT) are all objectives of smart cities. A branch of machine intelligence engineering known as explaining artificial intelligence (XAI) makes complex techniques approachable and adaptable for efficient decision-making in the sciences and technologies. The quantum uncertainty problem may be applied to the network state, which consists of several states and dimensions and requires real-time information. Specifically pertinent are the linkages between the emerging paradigms of machine learning (ML), quantum computing (QC), and quantum machine learning (QML), and traditional communication networks. This study provides a new method in explainable deep learning for analysing healthcare data in multimedia for long-term quantum photonic applications. Input has been collected from multimedia healthcare data and processed for noise removal and normalization. Processed data features have been extracted using a gradient quantum neural network, and classification is carried out using an attention-based graph neural network (GNN). The experimental analysis is carried out in terms of accuracy, precision, recall, F-1 score, NSE (normalized square error), MAP (mean average precision),and Jaccard index.The proposed technique attained an accuracy of 93%, precision of 81%, recall of 79%, F-1 score of 71%, NSE of 65%, MAP of 58%, and Jaccard index of 53%.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data’s available in the manuscript.
References
Alanazi, S.A., Kamruzzaman, M.M., Alruwaili, M., Alshammari, N., Alqahtani, S.A., Karime, A.: Measuring and preventing COVID-19 using the SIR model and machine learning in smart health care. J. Healthcare Eng. (2020)
Bharati, S., Podder, P., Mondal, M., Prasath, V.B.S.: CO-ResNet: optimized ResNet model for COVID-19 diagnosis from X-ray images. Int. J. Hybrid Intell. Syst. 17(1–2), 71–85 (2021)
Casiraghi, E., Malchiodi, D., Trucco, G., Frasca, M., Cappelletti, L., Fontana, T., et al.: Explainable machine learning for early assessment of COVID-19 risk prediction in emergency departments. IEEE Access 8, 196299–196325 (2020)
Choudhury, S., Dutta, A., Ray, D.: Chaos and complexity from quantum neural network. A study with diffusion metric in machine learning. J. High Energy Phys. 2021(4), 1–33 (2021)
Couliably, S., Kamsu-Foguem, B., Kamissoko, D., Traore, D.: Explainable deep convolutional neural networks for insect pest recognition. J. Clean. Product. 133–638 (2022)
Faust, O., Hagiwara, Y., Hong, T.J., Lih, O.S., Acharya, U.R.: Deep learning for healthcare applications based on physiological signals: a review. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 161, 1–13 (2018)
Gyongyosi, L., Imre, S.: Training optimization for gate-model quantum neural networks. Sci. Rep. 9(1), 1–19 (2019)
Hossain, M.S., Muhammad, G., Guizani, N.: Explainable AI and mass surveillance system-based healthcare framework to combat COVID-I9 like pandemics. IEEE Netw. 34(4), 126–132 (2020)
Kamruzzaman, M.M.: Architecture of smart health care system using artificial intelligence. In IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & Expo Workshops (ICMEW), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2020).
Lv, Z., Yu, Z., Xie, S., Alamri, A.: Deep learning-based smart predictive evaluation for interactive multimedia-enabled smart healthcare. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 18(1), 1–20 (2022)
Mondal, M.R.H., Bharati, S., Podder, P.: CO-IRv2: Optimized InceptionResNetV2 for COVID-19 detection from chest CT images. PLoS ONE 16(10), e0259179 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0259179
Muhammad, K., Khan, S., Del Ser, J., De Albuquerque, V.H.C.: Deep learning for multigrade brain tumor classification in smart healthcare systems: a prospective survey. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 32(2), 507–522 (2020)
Nigri, E., Ziviani, N., Cappabianco, F., Antunes, A., Veloso, A.: Explainable deep CNNs for MRI-based diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. In: International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 1–8. IEEE (2020a).
Nigri, E., Ziviani, N., Cappabianco, F., Antunes, A., Veloso, A.: Explainable deep CNNs for MRI-based diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. In: International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 1–8. IEEE. (2020b)
Patrício, C., Neves, J.C., Teixeira, L.F.: Explainable Deep Learning Methods in Medical Diagnosis: A Survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.04766 (2022).
Peddi, S.V.B., Kuhad, P., Yassine, A., Pouladzadeh, P., Shirmohammadi, S., Shirehjini, A.A.N.: An intelligent cloud-based data processing broker for mobile e-health multimedia applications. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 66, 71–86 (2017)
Rahman, A., Hossain, M.S., Alrajeh, N.A., Alsolami, F.: Adversarial examples—security threats to COVID-19 deep learning systems in medical IoT devices. IEEE Internet Things J. 8(12), 9603–9610 (2020)
Rahman, M.A., Hossain, M.S., Alrajeh, N.A., Gupta, B.B.: A multimodal, multimedia point-of-care deep learning framework for COVID-19 diagnosis. ACM Trans. Multimidia Comput. Commun. Appl. 17(1), 1–24 (2021)
Sasubilli, G., Kumar, A.: Machine learning and big data implementation on health care data. In: 4th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS), pp. 859–864. IEEE (2020).
Tobón, D.P., Hossain, M.S., Muhammad, G., Bilbao, J., Saddik, AE.: Deep learning in multimedia healthcare applications: a review. Multimed. Syst. pp. 1–15 (2022)
Waring, J., Lindvall, C., Umeton, R.: Automated machine learning: review of the state-of-the-art and opportunities for healthcare. Artif. Intell. Med. 104, 101822 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2020.101822. Epub 2020 Feb 21. PMID: 32499001.
Wei, K., Chen, B., Zhang, J., Fan, S., Wu, K., Liu, G., Chen, D.: Explainable deep learning study for leaf disease classification. Agronomy 12(5), 1035 (2022)
Yang, Y., Tresp, V., Wunderle, M., Fasching, P.A.: Explaining therapy predictions with layer-wise relevance propagation in neural networks. In: IEEE International Conference on Healthcare Informatics (ICHI), pp. 152–162. IEEE (2018).
Funding
This research not received any fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SS: Conceived and design the analysis. NBT: Writing–Original draft preparation. FA: Collecting the Data. SKB: Contributed data and analysis stools, SB: Performed and analysis, MSU: Performed and analysis, Wrote the Paper, Editing and Figure Design.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Suhasini, S., Tatini, N.B., Arslan, F. et al. Smart explainable artificial intelligence for sustainable secure healthcare application based on quantum optical neural network. Opt Quant Electron 55, 887 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-05155-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-05155-3