Abstract
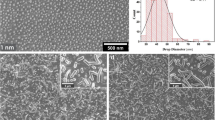
On silicon (100) surface substrates, single-crystal ZnO nanorods (NRs) were produced in a CVD (Chemical vabour deposition) home-made reactor with the help of a catalytic Au-seeds layer. Si substrates were coated with an Au- catalyst layer of 20 nm thickness using direct current sputtering (DC sputtering). Au-catalyst layer plays a pivotal role in synthesizing nanostructures by VLS (Vapour–Liquid–Solid) process. Zinc powder [0.2 g] was used as a source, and silicon (100) of 1.0 × 1.0 cm2 area was used as a substrate. We utilized a mixture of argon/oxygen gases (40/10 flow rate) with 700 °C growth temperature for 1 h to ZnO NRs formation. The Au–ZnO NRs were characterized by XRD (X-ray diffraction), AFM (Atomic force microscopy), and FESEM (Field emission scanning electron microscopy) techniques. The results demonstrate that the Au–ZnO NRs are single crystalline and have a hexagonal structure (wurtzite) with a (101) preferred orientation. The sharp and robust diffractions from ZnO NRs confirm that the CVD thermal-grown ZnO NRs have good crystallinity and high purity. The AFM pictures showed that the average particle size of Au–ZnO NRs is 45.31 nm, which is in reasonable agreement with the crystallite sizes estimated from the XRD pattern. The FESEM confirm that the grown ZnO NRs are hexagonal wurtzite NRs. As a whole, Au–ZnO NRs ranged in size from 1.6 to 1.738 μm in length and 250–300 nm in diameter on average. The Au catalyst seed layer acts as a nucleation layer that draws Zn2+ and O ions to the substrate’s surface and serves as an active site for the growth of ZnO NRs. Those results were accomplished with discussion of the mechanism and model of growth for Au–ZnO NRs.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ali, M.N., Salman, S.A., Dawood, M.O.: The growth mechanism of ZnO nanorods and the effects of growth conditions. NVEO-NAT. VOLATILES Essent. OILS J. NVEO 8(6), 1611–1620 (2021)
Alsultany, F.H., Ghazia, R.A.: Seed/catalyst-free growth of 2D and 3D ZnO nanostructures on glass substrate by thermal evaporation method: effects of carrier gas flow rate. Al-Mustansiriyah J. Sci. 29(3), 129–132 (2018)
Alwan, R.M., et al.: Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles via sol–gel route and their characterization. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 5(1), 1–6 (2015)
Aysa, N.H., Al-Maamori, M.H., Al-Maamori, N.A.A.: Preparation and surface modification of zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Babylon Univ. Appl. Sci. 25, 497–503 (2017)
Bhushan, B.: Surface roughness analysis and measurement techniques. In: Modern Tribology Handbook, Two Volume Set, pp. 79–150. CRC Press (2000)
Chen, J.-Y., Pan, C.-J., Tsao, F.-C., Kuo, C.-H., Chi, G.-C., Pong, B.-J., ... & Pearton, S.-J.: Characterization of ZnO nanowires grown on Si (100) with and without Au catalyst. Vacuum, 83(7), 1076–1079 (2009) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2009.02.001
Chou, H.-T., Hsu, H.-C.: The effect of annealing temperatures to prepare ZnO seeds layer on ZnO nanorods array/TiO2 nanoparticles photoanode. Solid-State Electron. 116, 15–21 (2016)
Chu, Y.-L., Liu, Y.-H., Chu, T.-T., Young, S.-J.: Improved UV-sensing of Au-decorated ZnO nanostructure MSM photodetectors. IEEE Sens. J. 22(6), 5644–5650 (2022)
Cruz-Vázquez, C., Bernal, R., Burruel-Ibarra, S.E., Grijalva-Monteverde, H., Barboza-Flores, M.: Thermoluminescence properties of new ZnO nanophosphors exposed to beta irradiation. Opt. Mater. (amst) 27(7), 1235–1239 (2005)
Cullity, B.D., Stock, S.R.: Elements of X-Ray Diffraction, p. 388. Prentice Hall, Up Saddle River, NJ (2001)
Daniel, G.P., Justinvictor, V.B., Nair, P.B., Joy, K., Koshy, P., Thomas, P.V.: Effect of annealing temperature on the structural and optical properties of ZnO thin films prepared by RF magnetron sputtering. Phys. B Condens. Matter 405(7), 1782–1786 (2010)
Dinesh, V.P., et al.: Plasmon-mediated, highly enhanced photocatalytic degradation of industrial textile dyes using hybrid ZnO@ Ag core–shell nanorods. RSC Adv. 4(103), 58930–58940 (2014)
Faisal, A.D.: Optimization of CVD parameters for long ZnO NWs grown on ITO/glass substrate. Bull. Mater. Sci. 39, 1635–1643 (2016)
Faisal, A.D., Dawood, M.O., Hussein, H.H., Hassoon, K.I.: Performance of ph sensor electrode based on ZnO NRs on Fto-glass substrate. Surf. Rev. Lett. 27(08), 1950198 (2020)
Gadelmawla, E.S., Koura, M.M., Maksoud, T.M.A., Elewa, I.M., Soliman, H.H.: Roughness parameters. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 123(1), 133–145 (2002)
Gupta, A.K., Kashyap, V., Gupta, B.K., Nandi, S.P., Saxena, K., Khare, N.: Synthesis of ZnO nanorods by electrochemical deposition method and its antibacterial activity. J. Nanoeng. Nanomanufacturing 3(4), 348–352 (2013)
Hahn, Y.-B.: Zinc oxide nanostructures and their applications. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 28, 1797–1813 (2011)
Han, S. K., et al.: Growth and optical properties of ZnO nanorods prepared through hydrothermal growth followed by chemical vapor deposition. In: 2010 3rd International Nanoelectronics Conference (INEC), pp. 1098–1099. IEEE (2010)
Hana, H.E.S.P.D.: Adsorption Study of the Interaction Between Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles with Albumin and Creatinine. University of Kerbala, Karbala (2019)
Hejazi, S.R., Hosseini, H.R.M.: A diffusion-controlled kinetic model for growth of Au-catalyzed ZnO nanorods: theory and experiment. J. Cryst. Growth 309(1), 70–75 (2007)
Huang, B., Zeng, W., Li, Y.: Synthesis of ZIF-8 coating on ZnO nanorods for enhanced gas-sensing performance. Chemosensors 10(8), 297–312 (2022)
Hughes, W.L., Wang, Z.L.: Formation of piezoelectric single-crystal nanorings and nanobows. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126(21), 6703–6709 (2004)
Ismail, M.A., Taha, K.K., Modwi, A., Khezami, L.: ZnO nanoparticles: Surface and X-ray profile analysis. J. Ovonic Res. 14(5), 381–393 (2018)
Kaiser, A., Ceja, E.T., Huber, F., Herr, U., Thonke, K.” Highly sensitive H2S sensing with gold and platinum surface-modified ZnO nanowire ChemFETs. In: Proceedings, p. 7. MDPI (2020)
Kar, S., Pal, B.N., Chaudhuri, S., Chakravorty, D.: One-dimensional ZnO nanostructure arrays: synthesis and characterization. J. Phys. Chem. B 110(10), 4605–4611 (2006)
Kim, H.-M., Park, J.-H., Lee, S.-K.: Fiber optic sensor based on ZnO nanowires decorated by Au nanoparticles for improved plasmonic biosensor. Sci. Rep. 9(1), 1–9 (2019)
Kołodziejczak-Radzimska, A., Jesionowski, T.: Zinc oxide—from synthesis to application: a review. Materials (basel) 7(4), 2833–2881 (2014)
Kong, Y.C., Yu, D.P., Zhang, B., Fang, W., Feng, S.Q.: Ultraviolet-emitting ZnO nanowires synthesized by a physical vapor deposition approach. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78(4), 407–409 (2001)
Kononenko, O.V., Redkin, A.N., Baranov, A.N., Panin, G.N., Kovalenko, A.A., Firsov, A.A.: ZnO nanorods: synthesis by catalyst-free CVD and thermal growth from salt composites and application to nanodevices. Nanorods Nanotechnol. Nanomater. 51–74 (2012). https://doi.org/10.5772/34936
Kumar, R.T.R., et al.: Growth of ZnO nanostructures on Au-coated Si: influence of growth temperature on growth mechanism and morphology. J. Appl. Phys. 104(8), 84309 (2008)
Kumar, S., Sahare, P.D., Kumar, S.: Optimization of the CVD parameters for ZnO nanorods growth: its photoluminescence and field emission properties. Mater. Res. Bull. 105, 237–245 (2018)
Kumbhakar, P., Singh, D., Tiwary, C.S., Mitra, A.K.: Chemical synthesis and visible photoluminescence emission from monodispersed ZnO nanoparticles. Chalcogenide Lett. 5(12), 387–394 (2008)
Levitt, A.P.: VLS Growth Mechanism of Crystal Growth in Whisker Technology. Wiley-Interscience, New York (1971)
Li, Y., et al.: Au-catalyzed growth processes and luminescence properties of ZnO nanopillars on Si. J. Appl. Phys. 99(5), 54307 (2006)
Lim, Y.S., Park, J.W., Kim, M.S., Kim, J.: Effect of carbon source on the carbothermal reduction for the fabrication of ZnO nanostructure. Appl. Surf. Sci. 253(3), 1601–1605 (2006)
Lockett, A.M., Thomas, P.J., O’Brien, P.: Influence of seeding layers on the morphology, density, and critical dimensions of ZnO nanostructures grown by chemical bath deposition. J. Phys. Chem. C 116(14), 8089–8094 (2012)
Malik, S., Muhammad, K., Waheed, Y.: Nanotechnology: a revolution in modern industry. Molecules 28(2), 661–686 (2023)
Mazhdi, M., Hossein, K.P.: Structural characterization of ZnO and ZnO: Mn nanoparticles prepared by reverse micelle method Int. J. Nano Dim. 2(4), 233–240 (2012)
Mirzaei, H., Darroudi, M.: Zinc oxide nanoparticles: biological synthesis and biomedical applications. Ceram. Int. 43(1), 907–914 (2017)
Navas, M.P., Soni, R.K., Tarasenka, N., Tarasenko, N.: Temperature and solution assisted synthesis of anisotropic ZnO nanostructures by pulsed laser ablation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 414, 413–423 (2017)
Patterson, A.L.: The Scherrer formula for X-ray particle size determination. Phys. Rev. 56(10), 978–982 (1939)
Paul, D.R., Robeson, L.M.: Polymer nanotechnology: nanocomposites. Polymer (guildf) 49(15), 3187–3204 (2008)
Purica, M., Budianu, E., Rusu, E., Danila, M., Gavrila, R.: Optical and structural investigation of ZnO thin films prepared by chemical vapor deposition (CVD). Thin Solid Films 403, 485–488 (2002)
Rosli, N., et al.: Random lasing emission of ZnO nanorods from different seeding thickness. In: Journal of Physics: Conference Series, p. 12018. IOP Publishing (2022)
Rusli, N.I., Tanikawa, M., Mahmood, M.R., Yasui, K., Hashim, A.M.: Growth of high-density zinc oxide nanorods on porous silicon by thermal evaporation. Materials (basel) 5(12), 2817–2832 (2012)
Saeed, N.M.: Preparation and properties of nanostructure zinc oxide thin films. Iraqi J. Phys. 7(8), 75–81 (2009)
Sangpour, P., Roozbehi, M., Akhavan, O., Moshfegh, A.Z.: ZnO nanowires from nanopillars: influence of growth time. Curr. Nanosci. 5(4), 479–484 (2009)
Schulz, H., Thiemann, K.H.: Structure parameters and polarity of the wurtzite type compounds Sic—2H and ZnO. Solid State Commun. 32(9), 783–785 (1979)
Shi, J., Zhang, J., Yang, L., Qu, M., Qi, D., Zhang, K.H.L.: Wide bandgap oxide semiconductors: from materials physics to optoelectronic devices. Adv. Mater. 33(50), 2006230 (2021)
Siegel, J., Lyutakov, O., Rybka, V., Kolská, Z., Švorčík, V.: Properties of gold nanostructures sputtered on glass. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 6, 1–9 (2011)
Singh, A., Vishwakarma, H.L.: Study of structural, morphological, optical and electroluminescent properties of undoped ZnO nanorods grown by a simple chemical precipitation. Mater. Sci. 33(4), 751–759 (2015)
Soleimanpour, A.M., Khare, S.V., Jayatissa, A.H.: Enhancement of hydrogen gas sensing of nanocrystalline nickel oxide by pulsed-laser irradiation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 4(9), 4651–4657 (2012)
Song, J., Lim, S.: Effect of seed layer on the growth of ZnO nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. C 111(2), 596–600 (2007)
Sun, Y., et al.: The applications of morphology controlled ZnO in catalysis. Catalysts 6(12), 188 (2016)
Tseng, Y.-K., Hsu, H.-C., Hsieh, W.-F., Liu, K.-S., Chen, I.-C.: Two-step oxygen injection process for growing ZnO nanorods. J. Mater. Res. 18(12), 2837–2844 (2003)
Wahab, R., et al.: Zinc oxide nanostructures and their applications. Intell. Nanomater. Process. Prop. Appl. 28, 183–212 (2012)
Wang, H., et al.: Selective growth of vertical-aligned ZnO nanorod arrays on Si substrate by catalyst-free thermal evaporation. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 3, 309–314 (2008)
Yi, G.-C., Wang, C., Park, W.I.: ZnO nanorods: synthesis, characterization and applications. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 20(4), S22–S34 (2005)
Young, S.-J., Chu, Y.-L.: Hydrothermal synthesis and improved CH3OH-sensing performance of ZnO nanorods with adsorbed Au NPs. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 68(4), 1886–1891 (2021)
Young, S.-J., Lai, L.T.: Investigation of a highly sensitive Au nanoparticle-modified ZnO nanorod humidity sensor. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 68(2), 775–779 (2021)
Young, S.-J., Chu, Y.-J., Chen, Y.-L.: Enhancing pH sensors performance of ZnO nanorods with Au nanoparticles adsorption. IEEE Sens. J. 21(12), 13068–13073 (2021)
Yu, X., Marks, T.J., Facchetti, A.: Metal oxides for optoelectronic applications. Nat. Mater. 15(4), 383–396 (2016)
Zak, A.K., Majid, W.H.A., Abrishami, M.E., Yousefi, R.: X-ray analysis of ZnO nanoparticles by Williamson-hall and size–strain plot methods. Solid State Sci. 13(1), 251–256 (2011)
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the current study, including a practical part, laboratory measurements, and results analysis. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were done by SJM, BBK, and MOD. The first draft of the manuscript was written by SJM and all authors have commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mezher, S.J., Kadhim, B.B. & Dawood, M.O. Synthesis and characterization of Au–ZnO nanorods growth by CVD method. Opt Quant Electron 55, 845 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-05072-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-05072-5