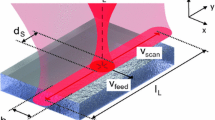
Abstract
Microfluidic systems have become part of our everyday life, with surface microfluidics occupying its niche in instant diagnostics and point-of-care testing. Implementing surface microfluidics on a large scale appears to be impossible without developing or upgrading manufacturing technologies. Our paper proposes a CO2-laser microtechnology of precise fused silica surface processing. Key microfluidic elements–microchannels, input and deposition reservoirs have been designed, fabricated and tested with picoliter volumes of fluids. Optical transmittance of the elements remains high enough to observe reactions in a microfluidic system by means of optical methods. The above research and its results would contribute to making laser microtechnologies available to a wide range of experimental and commercial users of microfluidics.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Budinski, V., Donlagic, D.: All silica micro-fluidic flow injection sensor system for colorimetric chemical sensing. Sensors (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/s21124082
Casavant, B.P., Berthier, E., Theberge, A.B., Berthier, J., Montanez-Sauri, S.I., Bischel, L.L., Beebe, D.J.: Suspended microfluidics. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1302566110
Chen, W., Sugita, K., Morikawa, Y., Yasunami, S., Hayashi, T., Uchida, T.: Application of magnetic neutral loop discharge plasma in deep silica etching. J. Vacuum Sci. Technol.: Vacuum, Surfaces, Films (2001). https://doi.org/10.1116/1.1415355
Chu, L., Li, Z., Zhu, H., Li, R., Ren, F., Chen, F.: Surface plasmon enhanced photoluminescence of monolayer WS2 on ion beam modified functional substrate. Appl. Phys. Lett. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0054333
Dadadzhanov, D.R., Gladskikh, I.A., Baranov, M.A., Vartanyan, T.A., Karabchevsky, A.: Self-organized plasmonic metasurfaces: the role of the Purcell effect in metal-enhanced chemiluminescence (MEC). Sens. Actuators, B Chem. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.129453
Hülsenberg, D., Harnisch, A., Bismarck, A.: Microstructuring glasses using lasers. Springer (2008)
Li, X., Hofmeister, W., Shen, G., Davis, L., & Daniel, C.: Fabrication and characterization of nanofluidics device using fused silica for single protein molecule detection. Medical Device Materials IV (Proceedings of Materials and Processes for Medical Devices 2007), pp 145–150, ASM International (2008).
Li, K., Myers, N., Bishop, G., Li, Y., Zhao, X.: Study of surface wettability on fused silica by ultrafast laser-induced micro/nano-surface structures. Journal of Manufacturing Processes (2022).https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.04.035
Li, X., Ballerini, D.R., Shen, W.: A: A perspective on paper-based microfluidics: current status and future trends. Biomicrofluidics (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3687398
Lin, L., Chung, C.K.: PDMS microfabrication and design for microfluidics and sustainable energy application. Micromachines (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12111350
Murray, L.P., Mace, C.R.: Usability as a guiding principle for the design of paper-based, point-of-care devices – a review. Anal. Chim. Acta (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.09.063
Olanrewaju, A., Beaugrand, M., Yafia, M., Juncker, D.: Capillary microfluidics in microchannels: from microfluidic networks to capillaric circuits. Lab Chip (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8LC00458G
Otitoju, T.A., Ahmad, A.L., Ooi, B.S.: Superhydrophilic (superwetting) surfaces: A review on fabrication and application. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2016.12.016
Pandey, C.M., Augustine, S., Kumar, S., Kumar, S., Nara, S., Srivastava, S., Malhotra, B.D.: Microfluidics based point-of-care diagnostics. Biotechnol. J. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201700047
Pattanayak, P., Singh, S.K., Gulati, M., Vishwas, S., Kapoor, B., Chellappan, D.K., Kumar, V.: Microfluidic chips: recent advances, critical strategies in design, applications and future perspectives. Microfluidics Nanofluidics. 25, 871 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-021-02502-2
Perrone, E., Cesaria, M., Zizzari, A., Bianco, M., Ferrara, F., Raia, L., Arima, V.: Potential of CO2-laser processing of quartz for fast prototyping of microfluidic reactors and templates for 3D cell assembly over large scale. Mater. Today Biol. 20, 1 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtbio.2021.100163
Smith, M. A., Berry, S., Parameswaran, L., Holtsberg, C., Siegel, N., Lockwood, R.,& Rothschild, M.: Design, simulation, and fabrication of three-dimensional microsystem components using grayscale photolithography. Journal of Micro/Nanolithography, MEMS, and MOEMS (2019). doi: https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JMM.18.4.043507
Temmler, A., Weingarten, C.B., Schober, B., Uluz, E.: Investigation on laser beam figuring of fused silica using microsecond pulsed CO2 laser radiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.149609
Vaidyanathan, R., Soon, R. H., Zhang, P., Jiang, K., & Lim, C. T.: Cancer diagnosis: from tumor to liquid biopsy and beyond. Lab on a Chip (2019). https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlehtml/2019/lc/c8lc00684a
Wlodarczyk, K.L., Carter, R.M., Jahanbakhsh, A., Lopes, A.A., Mackenzie, M.D., Maier, R.R., Maroto-Valer, M.M.: Rapid laser manufacturing of microfluidic devices from glass substrates. Micromachines (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9080409
Xiao, J., Liu, Y., Su, L., Zhao, D., Zhao, L., Zhang, X.: Microfluidic chip-based wearable colorimetric sensor for simple and facile detection of sweat glucose. Anal. Chem. 91(23), 14803–14807 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b03110
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Laser Center LLC, St. Petersburg, Russia for providing commercial laser system “C-Marker”. The authors are grateful to the Interdisciplinary Resource Center for Nanotechnology of St. Petersburg State University for the study of the surface by scanning electron microscopy.
Funding
The study is funded by RPMA grant of School of Physics and Engineering of ITMO University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by AGB. The first draft of the manuscript was written by AGB and RAZ and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. Methodology was suggested by RAZ. Visualisation was prepared by AR-V. The study of the surface by scanning electron microscopy was performed by AVS. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Supervision: RAZ.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bondarenko, A.G., Ramos-Velazquez, A., Shmalko, A.V. et al. Surface microfluidics elements fabrication by CO2-laser writing on glass: challenges and perspectives. Opt Quant Electron 55, 379 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-04675-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-04675-2