Abstract
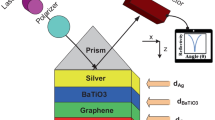
Biomolecular variations can be accounted for by changes in the intrinsic properties of the surrounding medium, such as the refractive index. This work employs such an arrangement using a modified attenuated total internal reflection configuration for telecommunication wavelength (1550 nm). The phenomenon of surface plasmon resonance is initiated by Aluminum (Al) metal due to its low cost and better compatibility with CMOS devices. To achieve improved plasmonic response in terms of the sensor’s resolution, we have explored metal-dielectric-metal configuration under angle interrogation. Barium titanate and Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) have been employed as the high dielectric constant material and the binding media respectively to enhance the sensing performance. After a series of optimizations, the proposed device configuration leads to a maximum Figure of Merit (FOM) of 540.9 RIU− 1, thus enhancing the resolution. The proposed plasmonic device can be used for chikungunya virus detection by considering different blood components in normal and infected stages. This Al-based multi-layered plasmonic device can serve many applications for resolution enhancement in the near-infrared region.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset generated or analysed during the current study is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Arora, P., Krishnan, A.: Analysis of transmission characteristics and multiple resonances in plasmonic gratings coated with homogeneous dielectrics. In: Progress in Electromagnetics Research Symposium. pp. 927–931 (2013)
Arora, P., Shukla, S.: Self-referenced integrated plasmonic device based on engineered periodic nanostructures for sensing application. In: SPIE proceedings. SPIE (2020)
Brighton, S.W.: Chikungunya Virus Infections. South Afr. Med J. 59, 552 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc1505501
Cardona, M.: Optical properties and band structure of SrTiO3 and BaTiO3. Phys. Rev. 140 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.140.A651
Gade, A., Sharma, A., Srivastava, N., Flora, S.J.S.: Surface plasmon resonance: a promising approach for label-free early cancer diagnosis. Clin. Chim. Acta. 527, 79–88 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2022.01.023
Karki, B., Pal, A., Singh, Y., Sharma, S.: Sensitivity enhancement of surface plasmon resonance sensor using 2D material barium titanate and black phosphorus over the bimetallic layer of Au, Ag, and Cu. Opt. Commun. 508, 127616 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2021.127616
Khansili, N., Rattu, G., Krishna, P.M.: Label-free optical biosensors for food and biological sensor applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 265, 35–49 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.03.004
Liang, Z., Wen, Y., Zhang, Z., Liang, Z., Xu, Z., Lin, Y.S.: Plasmonic metamaterial using metal-insulator-metal nanogratings for high-sensitive refraction index sensor. Results Phys. 15, 102602 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2019.102602
Mostufa, S., Akib, T.B.A., Rana, M.M., Mehedi, I.M., Al-Saggaf, U.M., Alsaggaf, A.U., Alsaggaf, M.U., Alam, M.S.: Numerical approach to design the graphene-based multilayered surface plasmon resonance biosensor for the rapid detection of the novel coronavirus. Opt. Contin. 1, 494 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1364/optcon.445255
Moznuzzaman, M., Khan, I., Islam, M.R.: Nano-layered surface plasmon resonance-based highly sensitive biosensor for virus detection: a theoretical approach to detect SARS-CoV-2. AIP Adv. 11(1–), 065023 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0046574
Pal, A., Jha, A.: A theoretical analysis on sensitivity improvement of an SPR refractive index sensor with graphene and barium titanate nanosheets. Optik (Stuttg). 231, 166378 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.166378
Prabowo, B.A., Hermida, I.D.P., Manurung, R.V., Purwidyantri, A., Liu, K.C.: Nano-film aluminum-gold for ultra-high dynamic-range surface plasmon resonance chemical sensor. Front. Optoelectron. 12, 286–295 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12200-019-0864-y
Pumera, M.: Graphene in biosensing. Mater. Today. 14, 308–315 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-7021(11)70160-2
Ramesh, S., Shutzberg, B.A., Huang, C.C., Gao, J., Giannelis, E.P.: Dielectric Nanocomposites for Integral Thin Film Capacitors: materials design, fabrication and integration issues. IEEE Trans. Adv. Packag. 26, 17–24 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1109/TADVP.2003.811365
Refki, S., Hayashi, S., Ishitobi, H., Nesterenko, D.V., Rahmouni, A., Inouye, Y., Sekkat, Z.: Resolution Enhancement of Plasmonic sensors by metal-insulator-metal structures. Ann. Phys. 530, 1–7 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/andp.201700411
Setareh, M., Kaatuzian, H.: Sensitivity enhancement of a surface plasmon resonance sensor using blue Phosphorene/MoS2 hetero-structure and barium titanate. Superlattices Microstruct. 153, 106867 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2021.106867
Sharma, S., Kumar, A., Singh, K.S., Tyagi, H.K.: 2D photonic crystal based biosensor for the detection of chikungunya virus. Optik (Stuttg). 237, 166575 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.166575
Shukla, S., Arora, P.: Design and comparative analysis of aluminum-MoS2 based plasmonic devices with enhanced sensitivity and figure of Merit for biosensing applications in the near-infrared region. Optik (Stuttg). 228 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.166196
Srivastava, A., Das, R., Prajapati, Y.K.: Effect of Perovskite material on performance of surface plasmon resonance biosensor. IET Optoelectron. 14, 256–265 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-opt.2019.0122
Sun, P., Wang, M., Liu, L., Jiao, L., Du, W., Xia, F., Liu, M., Kong, W., Dong, L., Yun, M.: Sensitivity enhancement of surface plasmon resonance biosensor based on graphene and barium titanate layers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 475, 342–347 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.12.283
Vasimalla, Y., Pradhan, H.S., Pandya, R.J.: Sensitivity enhancement of the SPR biosensor for Pseudomonas bacterial detection employing a silicon-barium titanate structure. Appl. Opt. 60 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1364/ao.427499
Zekriti, M., Nesterenko, D.V., Sekkat, Z.: Long-range surface plasmons supported by a bilayer metallic structure for sensing applications. Appl. Opt. 54, 2151–2157 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1364/ao.54.002151
Ziblat, R., Lirtsman, V., Davidov, D., Aroeti, B.: Infrared surface Plasmon Resonance: a Novel Tool for Real Time sensing of variations in living cells. Biophys. J. 90, 2592–2599 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1529/biophysj.105.072090
Acknowledgements
S.S. and P.A. would like to thank the Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani (Rajasthan), India for providing an Additional Competitive Research Grant (ACRG). The authors would also like to thank Nihal Singh and Vishnu Venkatesh for the fruitful discussions.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.S. and P.A. contributed equally. N.G. and P.A. supervised the work and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All the authors have their full consent for the work submitted in this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shukla, S., Grover, N. & Arora, P. Resolution enhancement using a multi-layered aluminum-based plasmonic device for chikungunya virus detection. Opt Quant Electron 55, 274 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-022-04485-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-022-04485-y