Abstract
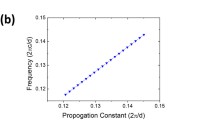
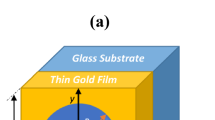
Plasmonics, often referred as “light on wire”, is an emerging nano-scale technology having the advantages of higher speed computing over the electronic devices and comparatively smaller size than the electro optical devices. With the help of plasmonics, it is possible to transmit data between chips at optical speeds and thus opening the doors towards miniaturization of devices and faster computers. Reflective codes are the self-complementing codes, which are used for communicating with computers. In this work, a novel design of plasmonic 2421 reflective code using plasmonic Mach–Zehnder interferometer has been proposed. As the designed reflective code is plasmonics based, hence it has smaller size, better processing speed, faster switching of light, better optical stability, lesser power consumption than the existing designs of codes. The footprint of the proposed device is only 190 µm × 35 µm with an extinction ratio of 18.23 dB. The performance of the device is theoretically analysed using a numerical analysis technique i.e. finite-difference-time-domain (FDTD) method and then comparing the simulation results of FDTD method with the MATLAB simulation results.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bader, M.A., Marowsky, G., Bahtiar, A., Koynov, K., Bubeck, C., Tillmann, H., Hörhold, H.H., Pereira, S.: Poly (p-phenylenevinylene) derivatives: new promising materials for nonlinear all-optical waveguideswitching. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 19(9), 2250–2262 (2002)
Barnes, W.L., Dereux, A., Ebbesen, T.W.: Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature 424, 824–830 (2003)
Boltasseva, A., Nikolajsen, T., Leosson, K., Kjaer, K., Larsen, M.S., Bozhevolnyi, S.I.: Integrated optical components utilizing long-range surface Plasmon polaritons. J. Lightw. Technol. 23, 413–422 (2005)
Bozhevolnyi, S.I., Volkov, V.S., Devaux, E., Laluet, J.Y., Ebbesen, T.W.: Channel plasmon subwavelength waveguide components including interferometers and ring resonators. Nature 440, 508–511 (2006)
Brongersma, M.L., Zia, R., Schuller, J.A.: Plasmonics—the missing link between nanoelectronics and microphotonics. Appl. Phys. B 89, 221–223 (2007)
Cheng, Q., Bahadori, M., Glick, M., Rumley, S., Bergman, K.: Recent advances in optical technologies for data centers: a review. Optica 5, 1354–1370 (2018)
Choudhary, K., Kaushik, A., Semwal, A., Mishra, S., Kumar, S.: Implementation of an optical universal one-bit arithmetic logical circuit for high-speed processing combinational circuits. Opt. Quant. Electron 52, 1–10 (2020)
Choudhary, K., Kumar, S.: Design of an optical OR gate using Mach-Zehnder interferometers. J. Opt. Commun. 39, 161–165 (2016)
Choudhary, K., Kumar, S.: Design of pseudorandom binary sequence generator using lithium-niobate-based Mach-Zehnder interferometers. Opt. Eng. 56, 1–7 (2017)
Choudhary, K., Kumar, S.: Optimized plasmonic reversible logic gate for low loss communication. Appl. Opt. 60(16), 164567–164572 (2021)
Choudhary, K., Singh, A., Singh, A., Chaudhary, D., Kumar, S.: Implementation of highly optimized optical all logic gates on a single chip using Ti-diffused lithium-niobate for high-speed processing in combinational circuits. Microelectron. J. 111, 105048 (2021)
Cotter, D., Blow, K.J., Manning, R.J., Ellis, A.D., Kelly, A.E., Nesset, D., Phillips, I.D., Poustie, A.J., Rogers, D.C.: Nonlinear optics for high-speed digital information processing. Science 286, 1523–1528 (1999)
Dionne, J.A., Sweatlock, L.A., Atwater, H.A., Polman, A.: Planar metal plasmon waveguides: frequency-dependent dispersion, propagation, localization, and loss beyond the free electron model. Phys. Rev. B 72, 1–11 (2005)
Dionne, J.A., Sweatlock, L.A., Atwater, H.A., Polman, A.: Plasmon slot waveguides: towards chip-scale propagation with subwavelength-scale localization. Phys. Rev. B 73, 1–9 (2006)
Economou, E.N.: Surface plasmons in thin films. Phys. Rev. 182, 539–554 (1969)
Gibbs, H.M.: Optical Bi-stability: Controlling Light with Light. Academic (1985)
Hosseini, A., Massoud, Y.: Nanoscale surface plasmon based resonator using rectangular geometry. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 1–3 (2007)
Hu, X., Jiang, P., Ding, C., Yang, H., Gong, Q.: Picosecond and low power all-optical switching based on an organic photonic-bandgap micro-cavity. Nat. Photon. 2, 185–189 (2008)
Jia, P., Fang, G., Wang, D.: Characterization of miniature fiber-optic Fabry-Perot interferometric sensors based on hollow silica tube. Photon. Sens. 6(3), 193–198 (2016)
Kachris, C., Tomkos, I.: A survey on optical interconnects for data centers. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor 14, 1021–1036 (2012)
Katti, R., Prince, S.: Ultrafast optical binary to gray code and gray to binary code conversion based on phase modulation in Mach-Zehnder interferometer. Opt. Eng. 56, 1–12 (2017)
Kumar, S., Bisht, A., Singh, G., Amphawan, A.: Implementation of 2-bit multiplier based on electro-optic effect in Mach-Zehnder interferometers. Opt. Quant. Electron 47, 3667–3688 (2015a)
Kumar, S., Bisht, A., Singh, G., Choudhary, K., Raina, K.K., Amphawan, A.: Design of 1-bit and 2-bit magnitude comparators using electro-optic effect in Mach-Zehnder interferometers. Opt. Commun. 357, 127–147 (2015b)
Kumar, S., Bisht, A., Singh, G., Choudhary, K., Sharma, D.: Implementation of wavelength selector based on electrooptic effect in Mach-Zehnder interferometers for high speed communications. Opt. Commun. 350, 108–118 (2015c)
Kumar, S., Raghuwanshi, S.K., Rahman, B.M.A.: Design of universal shift register based on electro-optic effect of LiNbO3 in Mach-Zehnder interferometer for high speed communication. Opt. Quant. Electron 47, 3509–3524 (2015d)
Kumar S, Singh L.: Proposed new approach to design all optical AND gate using plasmonic based Mach-Zehnder interferometer for high speed communication. Proc. SPIE 9884, Nanophotonics VI: 98842D (2016)
Lin, X.S., Huang, X.G.: Tooth-shaped plasmonic waveguide filters with nanometeric sizes. Opt. Lett. 33, 2874–2876 (2008)
Matsuzaki, Y., Okamoto, T., Haraguchi, M., Fukui, M., Nakagaki, M.: Characteristics of gap plasmon waveguide with stub structures. Opt. Express 16, 16314–16325 (2008)
Min, C., Veronis, G.: Absorption switches in metal-dielectricmetalplasmonic waveguides. Opt. Express 17, 10757–10766 (2009)
Ozbay, E.: Plasmonics: merging photonics and electronics at nanoscale dimensions. Science 311, 189–193 (2006)
Pereda, J.A., Vegas, A., Prieto, A.: An improved compact 2D fullwave FDTD method for general guided wave structures. Microw. Opt. Tech. Lett. 38, 331–336 (2003)
Roelkens, G., Liu, L., Liang, D., Jones, R., Fang, A., Koch, B., Bowers, J.: Silicon photonics for on-chip and intra-chip optical interconnects. Laser Photon. Rev. 4, 751–779 (2010)
Siokis, A., Christodoulopoulos, K., Pleros, N., Varvarigos, E.: Electro-optic switches based on space switching of multiplexed WDM signals: blocking vs non-blocking design trade-offs. Opt. Switch. Netw. 25, 40–56 (2017)
Takahara, J., Yamagishi, S., Taki, H., Morimoto, A., Kobayashi, T.: Guiding of a one-dimensional optical bema with nanometer diameter. Opt. Lett. 22, 475–477 (1997)
Veronis, G., Fan, S.: Guided subwavelength plasmonic mode supported by a slot in a thin metal film. Opt. Lett. 30, 3359–3361 (2005)
Weeber, J.C., Dereux, A., Girard, C., Krenn, J.R., Goudonnet, J.P.: Plasmon polaritons of metallic nanowires for controlling submicron propagation of light. Phys. Rev. B 60, 9061–9068 (1999)
Xiao, S., Liu, L., Qiu, M.: Resonator channel drop filters in a plasmon-polaritons metal. Opt. Express 14, 2932–2937 (2006)
Yu, H., Peng, Y., Yang, Y., Li, Z.Y.: Plasmon-enhanced light–matter interactions and applications. Npj Comput. Mater. 5(1), 1–4 (2019)
Yu, Z., Veronis, G., Fan, S., Brongersma, M.L.: Gain-induced switching in metal-dielectric-metal plasmonic waveguides. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 1–3 (2008)
Zia, R., Schuller, J.A., Chandran, A., Brongersma, M.L.: Plasmonics: the next chip scale technology. Mater Today 9, 20–27 (2006)
Zia, R., Selker, M.D., Brongersma, M.L.: Leaky and bound modes for surface plasmon waveguides. Phys. Rev. B 71, 1-9 (2005)
Funding
This research is sponsored by the DIT University, Dehradun, India project [DITU/Dean R&C/2022/003/EECE] titled, “Development of LSPR-based optical fiber sensors for bio-medical applications”. This work was supported by the Double-Hundred Talent Plan of Shandong Province, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Uniyal, S., Choudhary, K., Sachdev, S. et al. Design and performance analysis of plasmonic reflective codes in combinational circuits for high speed computing. Opt Quant Electron 54, 825 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-022-04211-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-022-04211-8