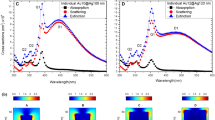
Abstract
In the field of plasmonics, the nanogap effect is often related to one aspect like the far-field resonance shift or near-field enhancement. In this study, we present a details analysis of the nanogap effect on plasmonic behaviours of the magneto-plasmonic dimer Ni–Ag and Ni–Au nanoparticles by taking the full advantages of DDA simulation. The sets of non-spherical dimer nanostructure viz. edge-to-edge (EE) and face-to-face (FF) and spherical dimer nanoparticles for plasmonic properties like LSPR peak position’s tunability as well as peak intensity at the maximum wavelength (λmax.) and near-field enhancement in Ni–Ag and Ni–Au heterodimer nanoparticles is studied. It is observed that the emerging spectra are found between the UV–visible regions (357–586 nm) for spherical dimer nanostructure while prolate dimers are in the UV–visible-Near Infrared region (345–817 nm) under both EE and FF configurations. The emergent wavelength-dependent spectra with varying nanogap between the dimer are red-shifted. The maximum plasmonic field enhancement is observed for Ni–Ag as compared to Ni–Au dimer nanoparticles under spherical and prolate geometry. It is found that the FF configuration of Ni–Ag and Ni–Au dimers nanoparticles has maximum field enhancement in comparison to the EE configuration. These results could have a big impact on how surface-enhanced spectroscopies and related plasmonic instruments based on E-field hot spots or intensity are being utilized.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the manuscript.
References
Bansal, A., Verma, S.S.: Simulated study of plasmonic coupling in noble bimetallic alloy nanosphere arrays. AIP Adv. 4, 057104 (2014)
Bansal, A., Verma, S.S.: Optical properties of bimetallic (Ag-Cu) core-noble metal shell nanoparticles. J. Opt. 45, 7–10 (2016)
Bansal, A., Sekhon, J.S., Verma, S.S.: Scattering efficiency and LSPR tunability of bimetallic Ag, Au, and Cu nanoparticles. Plasmonics 9, 143–150 (2014)
Barbillon, G.: Nanoplasmonics: fundamentals and applications. InTech (2017)
Bhatia, P., Verma, S.S., Sinha, M.M.: Tunable optical properties of Ni-Ag and Ni-Au nanoparticles in magneto-plasmonic nanostructures, Optical and Quantum. Electronics 52, 1–12 (2020)
Bhatia, P., Verma, S.S., Sinha, M.M.: Optical absorption analysis of core-shell type Ni@ Ag/Au & NiFe@ Ag/Au magneto-plasmonic nanostructures. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer 268, 107646 (2021)
Catchpole, K.A., Polman, A.: Plasmonic solar cells. Opt. Express 16, 21793–21800 (2008)
Ciraci, C., Urzhumov, Y., Smith, D.R.: Effects of classical nonlocality on the optical response of three-dimensional plasmonic nanodimers. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 30, 2731–2736 (2013)
Demchuk, A., Bolesta, I., Kushnir, O., Kolych, I.: The computational studies of plasmon interaction. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 12, 1–7 (2017)
Devaraj, V., Choi, J., Kim, C.S., Oh, J.W., Hwang, Y.H.: Numerical analysis of nanogap effects in metallic nano-disk and nano-sphere dimers: high near-field enhancement with large gap sizes. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 72, 599–603 (2018)
Draine B., T., Flatau P., J.: User guide for the discrete dipole approximation code DDSCAT 7.3, "arXiv preprint arXiv. (2013) 1305.6497.
Draine, B.T., Flatau, P.J.: Discrete-dipole approximation for scattering calculations. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 11(4), 1491 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAA.11.001491
Draine, B.T., Flatau, P.J.: Discrete-dipole approximation for periodic targets: theory and tests. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 25, 2693–2703 (2008)
Flatau, P.J., Draine, B.T.: Fast near field calculations in the discrete dipole approximation for regular rectilinear grids. Opt. Express 20, 1247–1252 (2012)
Gao, Y., Zhang, R., Cheng, J.C., Liaw, J.W., Ma, C.: Optical properties of plasmonic dimer, trimer, tetramer and pentamer assemblies of gold nanoboxes. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer 125(2013), 23–32 (2013)
Hooshmand, N., El-Sayed, M.A.: Collective multipole oscillations direct the plasmonic coupling at the nanojunction interfaces. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 116, 19299–19304 (2019)
Hooshmand, N., Jain, P.K., El-Sayed, M.A.: Plasmonic spheroidal metal nanoshells showing larger tunability and stronger near fields than their spherical counterparts: an effect of enhanced plasmon coupling. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2, 374–378 (2011)
Hooshmand, N., Bordley, J.A., El-Sayed, M.A.: The sensitivity of the distance dependent plasmonic coupling between two nanocubes to their orientation: edge-to-edge versus face-to-face. J. Phys. Chem. C 120, 4564–4570 (2016)
Hossain, M.K., Kitahama, Y., Huang, G.G., Han, X., Ozaki, Y.: Surface-enhanced Raman scattering: realization of localized surface plasmon resonance using unique substrates and methods. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 394, 1747–1760 (2009)
Hulst, H.C., van de Hulst, H.C.: Light scattering by small particles. Courier Corporation (1981)
Jain, P.K., Lee, K.S., El-Sayed, I.H., El-Sayed, M.A.: Calculated absorption and scattering properties of gold nanoparticles of different size, shape, and composition: applications in biological imaging and biomedicine. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 7238–7248 (2006)
Jain, P.K., Huang, X., El-Sayed, I.H., El-Sayed, M.A.: Noble metals on the nanoscale: optical and photothermal properties and some applications in imaging, sensing, biology, and medicine. Acc. Chem. Res. 41, 1578–1586 (2008)
Ji, X., Yang, W.: High-purity gold nanocrystal dimers: scalable synthesis and size-dependent plasmonic and Raman enhancement. Chem. Sci. 5, 311–323 (2014)
Jiang, M.M., Chen, H.Y., Li, B.H., Liu, K.W., Shan, C.X., Shen, D.Z.: Hybrid quadrupolar resonances stimulated at short wavelengths using coupled plasmonic silver nanoparticle aggregation. J. Mater. Chem. C 2, 56–63 (2013)
Johnson, P.B., Christy, R.W.: Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys. Rev. B 6, 4370–4379 (1972)
Johnson, P.B., Christy, R.W.: Optical constants of transition metals: Ti, v, cr, mn, fe, co, ni, and pd. Phys. Rev. B 9, 5056–5070 (1974)
Katyal, J.: Al-Au Heterogeneous dimer-trimer nanostructure for SERS. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 10, 21–28 (2020)
Kelly, K.L., Coronado, E., Zhao, L.L., Schatz, G.C.: The optical properties of metal nanoparticles: the influence of size, shape, and dielectric environment. J. Phys. Chem. B 107, 668–677 (2003)
Khlebtsov, B., Melnikov, A., Zharov, V., Khlebtsov, N.: Absorption and scattering of light by a dimer of metal nanospheres: comparison of dipole and multipole approaches. Nanotechnology 17, 1437 (2006)
Li, W.: Physics models of plasmonics: single nanoparticle, complex single nanoparticle, nanodimer, and single nanoparticle over metallic thin film. Plasmonics 13, 997–1014 (2018)
Link, S., Wang, Z.L., El-Sayed, M.A.: Alloy formation of gold-silver nanoparticles and the dependence of the plasmon absorption on their composition. J. Phys. Chem. B 103, 3529–3533 (1999)
Luo, D., Shi, B., Zhu, Q., Qian, L., Qin, Y., Xie, J.: Optical properties of Au-Ag nanosphere dimer: influence of interparticle spacing. Opt. Commun. 458, 124746 (2020a)
Luo, D., Shi, B., Zhu, Q., Qian, L., Qin, Y., Xie, J.: Optical properties of Au–Ag nanosphere dimer: influence of interparticle spacing. Opt. Commun. 458, 124746 (2020b)
Moores, A., Goettmann, F.: The Plasmon band in noble metal nanoparticles: an introduction to theory and applications. New J Chem 30, 1121–1132 (2006)
Noguez, C.: Surface plasmons on metal nanoparticles: the influence of shape and physical environment. J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 3806–3819 (2007)
Ross, M.B., Mirkin, C.A., Schatz, G.C.: Optical properties of one-, two-, and three-dimensional arrays of plasmonic nanostructures. J. Phys. Chem. C 120, 816–830 (2016)
Sekhon, J.S., Verma, S.S.: Rational selection of nanorod plasmons: material, size, and shape dependence mechanism for optical sensors. Plasmonics 7, 453–459 (2012)
Toroghi, S., Kik, P.G.: Cascaded plasmon resonant field enhancement in nanoparticle dimers in the point dipole limit. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 183105 (2012)
Ventra, M., Evoy, S., Heflin, J.R.: Introduction to nanoscale science and technology. Springer (2006)
Verbruggen, S.W., Keulemans, M., Martens, J.A., Lenaerts, S.: Predicting the surface plasmon resonance wavelength of gold-silver alloy nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 117, 19142–19145 (2013)
Yan, Y., Deng, C., Yan, L., Tang, Z., Tang, S., Xu, X.: Composition dependence of magneto-optical response in Ag/Co dimer nanodot arrays. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 419, 553–558 (2016)
Acknowledgements
The author (P. Bhatia) thanks B. T. Draine and P. J. Flatau for using their DDA code DDSCAT 7.3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing for financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bhatia, P., Verma, S.S. & Sinha, M.M. Nanogap effects on plasmonic properties of dimer. Opt Quant Electron 54, 663 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-022-04052-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-022-04052-5