Abstract
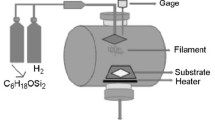
Synthesis of silicon carbide nanostructures is generally including complex chemical processes and often sophisticated technology. In this work, a new method to synthesize silicon carbide nanostructures on the surface of p-type silicon substrate is proposed by electrically-induced diffusion of carbon atoms deposited on this surface. This process was supported by magnetic field applied on the reaction volume. The electric field was applied throughout a needle-like anode that can increase the electric field intensity by two orders of magnitude. Accordingly, the reaction between carbon and silicon atoms within the surface layer is effectively possible. The structural, electrical and optoelectronics characteristics of the fabricated samples were introduced. A minimum particle size of about 19 nm was determined and reasonable purity of the synthesized nanostructures was confirmed. These nanostructures show peak photoluminescence at 435 nm when excited by a 325 nm radiation source. An anisotropic heterojunction from n-SiC/p-Si structure was formed with ideality factor of 0.53 and built-in potential of 2.20 eV. The proposed technique showed high reliability and very good reproducibility at low cost and simple requirements.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The author declares that all data and materials included in this manuscript are available.
References
Andrievski, R.A.: Nano-sized silicon carbide: synthesis, structure and properties. Russ. Chem. Rev. 78(9), 821–831 (2009)
Bluet, J.-M., Botsoa, J., Zakharko, Y., Geloen, A., Alekseev, S., Marty, O., Mognetti, B., Patskovsky, S., Rioux, D., Lysenko, V.: SiC as a biocompatible marker for cell labeling. In: Saddow, S. (ed.) Silicon Carbide Biotechnology, pp. 377–429. Elsevier, New York (2012)
Boo, J.H., Ustin, S.A., Ho, W.: Supersonic jet epitaxy of single crystalline cubic SiC thin films on Si substrates from t-butyldimethylsilane. Thin Solid Films 324, 124–128 (1998)
Chen, K., Huang, Z., Huang, J., Fang, M., Liu, Y., Ji, H., Yin, L.: Synthesis of SiC nanowires by thermal evaporation method without catalyst assistant. Ceram. Int. 39, 1957–1962 (2013)
Derevyanko, I.V., Polyakov, O.I.: Studies of polytype silicon carbide produced from recycled materials. Metall. Min. Ind. 4(4), 14–18 (2012)
Di Carlo, J.A., Yun, H.-M.: Non-oxide (silicon carbide) fibers. In: Bansal, N.P. (ed.) Handbook of Ceramic Composites, pp. 33–52. Springer, Berlin (2005)
Du, X.W., Zhao, X., Jia, S.L., Lu, Y.W., Li, J.J., Zhao, N.Q.: Direct synthesis of SiC nanowires by multiple reaction VS growth. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 136, 72–77 (2007)
Fan, J.Y., Wu, X.L., Chu, P.K.: Low-dimensional SiC nanostructures: fabrication, luminescence, and electrical properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 51, 983–1031 (2006)
Gupta, A., Paramnik, D., Varma, S., Jacob, C.: CVD growth and characterization of 3C-SiC thin films. Bull. Mater. Sci. 27(5), 445–451 (2004)
Hamadi, O.A.: Characteristics of CdO-Si heterostructure produced by plasma-induced bonding technique. Proc. Imeche Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 222, 65–71 (2008a)
Hamadi, O.A.: Effect of annealing on the electrical characteristics of CdO-Si heterostructure produced by plasma-induced bonding technique. Iraq. J. Appl. Phys. (IJAP) 4(3), 34–37 (2008b)
Hamadi, O.A.: Profiling of antimony diffusivity in silicon substrates using laser-induced diffusion technique. Iraq. J. Appl. Phys. Lett. 3(1), 23–26 (2010)
Hamadi, O.A., Yahiya, K.Z.: Optical and electrical properties of selenium-antimony heterojunction formed on silicon substrate. Sharjah Univ. J. Pure Appl. Sci. 4(2), 1–11 (2007)
Hamadi, O.A., Yahiya, K.Z., Jassim, O.N.S.: Properties of silicon carbide thin films deposited by vacuum thermal evaporation. J. Semicond. Technol. Sci. (JSTS) 5(3), 69–73 (2005)
Hammadi, O.A.: Photovoltaic properties of thermally-grown selenium-doped silicon photodiodes for infrared detection applications. Photonic Sens. 5(2), 152–158 (2015)
Hammadi, O.A., Khalaf, M.K., Kadhim, F.J.: Silicon nitride nanostructures prepared by reactive sputtering using closed-field unbalanced dual magnetrons. Proc. Imeche Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. (2015a). https://doi.org/10.1177/1464420715601151
Hammadi, O.A., Khalaf, M.K., Kadhim, F.J.: Fabrication of UV photodetector from nickel oxide nanoparticles deposited on silicon substrate by closed-field unbalanced dual magnetron sputtering technique. Opt. Quantum Electron. 47, 3805–3813 (2015b)
Hammadi, O.A., Khalaf, M.K., Kadhim, F.J.: Fabrication and characterization of UV photodetectors based on silicon nitride nanostructures prepared by magnetron sputtering. Proc. Imeche Part N J. Nanomater. Nanoeng. Nanosyst. 230(1), 32–36 (2016)
Han, W., Fan, S., Li, Q., Liang, W., Gu, B., Yu, D.: Continuous synthesis and characterization of silicon carbide nanorods. Chem. Phys. Lett. 265, 374–378 (1997)
Khamsuwan, J., Intarasiri, S., Kirkby, K., Chu, P.K., Singkarat, S., Yu, L.D.: Ion-beam synthesis and photoluminescence of SiC nanocrystals assisted by MeV-heavy-ion-beam annealing. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 282, 88–91 (2012)
Kim, Y.T., Yoon, S.G., Kim, H., Suh, S.J., Janga, G.E., Yoon, D.H.: Crystallization of a-Si:H and a-SiC:H thin films deposited by PECVD. J. Ceram. Process. Res. 6(4), 294–297 (2005)
Leal, G., Bastos Campos, T.M., da Silva Sobrinho, A.S., Pessoa, R.S., Maciel, H.S., Massi, M.: Characterization of SiC thin films deposited by HiPIMS. Mater. Res. 17(2), 472–476 (2014)
Madapura, S., Steckl, A.J., Loboda, M.: Heteroepitaxial growth of SiC on Si(100) and (111) by chemical vapor deposition using trimethylsilane. J. Electrochem. Soc. 146(3), 1197–1202 (1999)
Nagarajan, K., Kumara Raman, S.: Photoluminescence Study of SiC Nanotubes. Bulg. J. Phys. 35, 53–57 (2008)
Sarro, P.M.: Silicon carbide as a new MEMS technology. Sens. Actuators Phys. 82(1–3), 210–218 (2000)
Seong, H.K., Choi, H.J., Lee, S.K., Lee, J.I., Choi, D.J.: Optical and electrical transport properties in silicon carbide nanowires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 85(7), 1256–1258 (2004)
Stoldt, C.R., Fritz, M.C., Carraro, C., Maboudian, R.: Micromechanical properties of silicon-carbide thin films deposited using single-source chemical-vapor deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 79(3), 347–349 (2001)
Sun, G.S., Li, J.M., Luo, M.C., Zhu, S.R., Wang, L., Zhang, F.F., Lin, L.Y.: Epitaxial growth of SiC on complex substrates. J. Cryst. Growth 227–228, 811–815 (2001)
Tanner, P., Dimitrijev, S., Harrison, H.B.: Current mechanisms in n-SiC/p-Si heterojunctions. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Optoelectronic and Microelectronic Materials and Devices, COMMAD 2008 (28 July–1 August, Sydney, Australia), pp. 41–43 (2008)
Volz, K., Schreiber, S., Gerlach, J.W., Reiber, W., Rauschenbach, B., Stritzker, B., Assmann, W., Ensinger, W.: Heteroepitaxial growth of 3C-SiC on (100) silicon by C60 and Si molecular beam epitaxy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 289, 255–264 (2000)
Xi, G., Yu, S., Zhang, R., Zhang, M., Ma, D., Qian, Y.: Crystalline silicon carbide nanoparticles encapsulated in branched wavelike carbon nanotubes: synthesis and optical properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 13200–13204 (2005)
Yang, Y.T., Ekinci, K.L., Huang, X.M.H., Schiavone, L.M., Roukes, M.L., Zorman, C.A., Mehregany, M.: Monocrystalline silicon carbide nanoelectromechanical systems. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78(2), 162–164 (2001)
Yang, S., Cai, W., Zeng, H., Xu, X.: Ultra-fine β-SiC quantum dots fabricated by laser ablation in reactive liquid at room temperature and their violet emission. J. Mater. Chem. 19, 7119–7123 (2009)
Yih, P.H., Li, J.P., Steckl, A.J.: SiC/Si heterojunction diodes fabricated by self-selective and by blanket rapid thermal chemical vapour deposition. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 41(3), 281–287 (1994)
Yousif, A.K., Hamadi, O.A.: Plasma-induced etching of silicon surfaces. Bulg. J. Phys. (BJP) 35(3), 191–197 (2008)
Zhang, H., Ding, W., He, K., Li, M.: Synthesis and characterization of crystalline silicon carbide nanoribbons. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 5, 1264–1271 (2010)
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work did not any fund or financial support from any institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that he does not have any conflict of interest related to this work.
Ethics approval
The author declares that his commitment to ethics related to his work.
Consent to participate
The author declares that he has individually designed the experiment, collected and analyzed the data, and written the manuscript.
Consent of publication
The author declares his consent of publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hammadi, O.A. Magnetically-supported electrically-induced formation of silicon carbide nanostructures on silicon substrate for optoelectronics applications. Opt Quant Electron 54, 427 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-022-03824-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-022-03824-3