Abstract
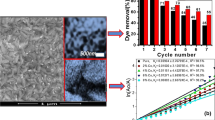
Cadmium oxide (CdO) photocatalysts have been prepared using chemically controlled co-precipitation method with the intension to serve as photocatalyst in the degradation of methylene blue dye. Photocatalytic property of CdO was improved by properly undertook calcination at various temperatures 400, 600 and 800 °C, and by doping with Al3+ to different weight percentages (0.5 and 1 wt%). The powder X-ray diffraction patterns of the synthesized CdO and Cd(1−x)AlxO samples exposed the formation of single phase polycrystalline face centered cubic (Fm\(\overline{3}\)m) CdO structure with no impurity phases even after doping with Al3+. Obtained crystallite size in the range 22 to 72 nm was well suited for photocatalytic activity. The presence of Al dopant as Al3+ ion in the CdO lattice was confirmed from the information derived from the XPS spectra. In the SEM images the revealed agglomerated spherical morphology evidenced the presence of round edges and corners that can have more active sites in the photocatalytic process so as to advance the photocatalytic activity. Direct optical band gaps measured from the UV–Vis spectra seemed to lay in the range 2.09 to 2.57 eV and were liable for the greater photocatalytic activity of the readied nanoparticles. In the photoluminescence spectra, for an excitation wavelength of 440 nm, the pure and doped CdO nanoparticles displayed bands about 485, 530 and 600 nm with poorer intensities and exposed its appropriateness to serve as superior photocatalyst. Attained good electrical conductivity of CdO and its enhancement with Al doping exposed the liableness of the samples to use as better photocatalysts. The small-sized Al doped CdO nanoparticles showed evidence of considerably high visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity for the degradation of methylene blue solution, with better degradation percentage and kinetic rate constant compared to pure CdO.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
My manuscript has associated data in a data repository.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Aksoy, S., Caglar, Y., Ilican, S., Caglar, M.: Effect of heat treatment on physical properties of CdO films deposited by sol–gel method. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 34(12), 5191–5195 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.09.057
Alamgir, Khan, W., Ahmad, S., Naqvi, A.H.: Formation of self-assembled spherical-flower like nanostructures of cobalt doped anatase TiO2 and its optical band-gap. Mater. Lett. 133, 28–31 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2014.06.121
Alias, S.S., Mohamad, A.A.: Synthesis of Zinc Oxide by Sol–Gel Method for Photoelectrochemical Cells. Springer Briefs in Materials. Springer, Berlin (2014)
Barbalace, K. Periodic table of elements. EnvironmentalChemistry.com. 1995–2020. Accessed on-line: 4/22/2020, https://EnvironmentalChemistry.com/yogi/periodic/
Bazargan, A.M., Fateminia, S.M.A., Ganji, M.E., Bahreva, M.A.: Electrospinning preparation and characterization of cadmium oxide nanofibers. Chem. Eng. J. 155(1–2), 523–527 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.08.004
Behnajady, M.A., Modirshahla, N., Shokri, M., Zeininezhad, A., Zamani, H.A.: Enhancement photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanoparticles by silver doping with optimization of photodeposition method parameters. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 44(7), 666–672 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1080/10934520902847752
Brundle, C.R., Baker, A.D.: Electron Spectroscopy: Theory, Techniques and Applications, vol. 2. Academic Press, London (1978)
Byrappa, K., Yoshimura, M.: Handbook of Hydrothermal Technology: A Technology for Crystal Growth and Materials Processing. Noyes Publications, New York (2001)
Carp, O., Huisman, C.L., Reller, A.: Photoinduced reactivity of titanium dioxide. Prog Solid State. Chem. 32(1–2), 33–177 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progsolidstchem.2004.08.001
Celebioglu, A., Vempati, S., Akgun, C.O., Biyikliab, N., Uyar, T.: Water-soluble non-polymeric electrospun cyclodextrin nanofiber template for the synthesis of metal oxide tubes by atomic layer deposition. RSC Adv. 4(106), 61698–61705 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA12073F
Dai, T.M., Lee, W.W., Lin, W.C., Chen, C.C.: Synthesis and photocatalytic properties of nano-crystalline In2O3. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 60(12), 1415–1424 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/jccs.201300202
Dakhel, A.A.: Electrical and optical investigations on tungsten-incorporated CdO thin films. J. Electron. Mater. 41(9), 2405–2410 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-012-2160-0
Dakhel, A.A.: Defect-induced ferromagnetic properties of Tb-doped CdO synthesized via Cd hydroxychloride: effect of hydrogen post treatment. Mater. Res. 19(2), 379–383 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-MR-2015-0404
Dingle, R.: Luminescent transitions associated with divalent copper impurities and the green emission from semiconducting zinc oxide. Phys. Rev. Lett. 23(11), 579–581 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.23.579
Dou, Y., Egdell, R.G., Walker, T., Law, D.S.L., Beamson, G.: N-type doping in CdO ceramics: a study by EELS and photoemission spectroscopy. Surf. Sci. 398(1–2), 241–258 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0039-6028(98)80028-9
Fan, J.C.C., Goodenough, J.B.: X-ray photoemission spectroscopy studies of Sn-doped indium-oxide films. J. Appl. Phys. 48, 3524–3531 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.324149
Fernandez, T., Jose, G., Mathew, S., Rejikumar, P.R., Unnikrishnan, N.V.: An ultra-low hydrolysis sol-gel route for titanosilicate xerogels and their characterization. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 41(2), 163–168 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-006-0522-x
Ferro, R., Rodriguez, J.A., Vigil, O., Acevado, A.M., Puente, G.C.: F-doped CdO thin films deposited by spray pyrolysis. Phys. Status Solidi A 177(2), 477–483 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1521-396X(200002)177:2%3C477::AID-PSSA477%3E3.0.CO;2-3
Ghodsi, F.E., Absalan, H.: Comparative study of ZnO thin films prepared by different sol-gel route. Acta Phys. Pol. A 118, 659–663 (2010). https://doi.org/10.12693/APhysPolA.118.659
Ghosh, M., Rao, C.N.R.: Solvothermal synthesis of CdO and CuO nanocrystals. Chem. Phys. Lett. 393(4–6), 493–497 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2004.06.092
Granqvist, C.G.: Electrochromic tungsten oxide films: Review of progress 1993–1998. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 60(3), 201–262 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-0248(99)00088-4
Gulino, A., Dapporto, P., Rossi, P., Fragala, I.: A liquid MOCVD precursor for thin films of CdO. Chem. Mater. 14(4), 1441–1444 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm0112946
Guo, Z., Li, M., Liu, J.: Highly porous CdO nanowires: preparation based on hydroxy- and carbonate-containing cadmium compound precursor nanowires, gas sensing and optical properties. Nanotechnology 19(24), 245611 (1–8) (2008). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/19/24/245611
Guo, M.L., Zhang, X.D., Liang, C.T., Jia, G.Z.: Mechanism of visible photoactivity of F-doped TiO2. Chin. Phys. Lett. 27(5), 057103 (1–4) (2010). https://doi.org/10.1088/0256-307X/27/5/057103
Hoffmann, M.R., Martin, S.T., Choi, W.Y., Bahnemann, D.W.: Environmental applications of semiconductor photocatalysis. Chem. Rev. 95(1), 69–96 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1021/cr00033a004
Hosni, M., Hinkov, I., Ricolleau, C., Pauporte, T., Farhat, S., Jouini, N.: Mass synthesis in polyol of tailored zinc oxide nanoparticles for photovoltaic applications. J. Surf. Eng. Mater. Adv. Technol. 6, 1–10 (2016). https://doi.org/10.4236/jsemat.2016.61001
Hossain, M.S., Islam, R., Khan, K.A.: Electrical conduction mechanisms of undoped and vanadium doped ZnTe thin films. Chalcogenide Lett. 5(1), 1–9 (2008)
Ibhadon, A.O., Fitzpatrick, P.: Heterogeneous photocatalysis: recent advances and applications. Catalysts 3(1), 189–218 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3390/catal3010189
Ibrahim, D.M., Abu-Ayan, Y.M.: Preparation and characterization of ultrafine alumina via sol–gel polymeric route. Mat. Chem. Phy. 111, 326–330 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2008.04.023
Karami, H.: Investigation of sol–gel synthesized CdO-ZnO nanocomposite for CO gas sensing. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 5, 720–730 (2010)
Khallaf, H., Chen, C.T., Chang, L.B., Lupan, O., Dutta, A., Heinrich, H., Shenouda, A., Chow, L.: Investigation of chemical bath deposition of CdO thin films using three different complexing agents. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257(22), 9237–9242 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.04.060
Khan, M.K.R., Rahman, M.A., Shahjahan, M., Rahman, M.M., Hakim, M.A., Saha, D.K., Khan, J.U.: Effect of Al-doping on optical and electrical properties of spray pyrolytic nano-crystalline CdO thin films. Curr. Appl. Phys. 10(3), 790–796 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2009.09.016
Kim, H., Gilmore, C.M., Pique, A., Horwitz, J.S., Mattoussi, H., Murata, H., Kafafi, Z.H., Chrisey, D.B.: Electrical, optical, and structural properties of indium–tin–oxide thin films for organic light-emitting devices. J. Appl. Phys. 86(11), 6451–6461 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.371708
Kole, C., Kumar, S.D., Khodakovskaya, M.V.: Plant Nanotechnology: Principles and Practices. Springer, Berlin (2016)
Kotani, A., Suzuki, N. (eds.): Recent Advances in Magnetism of Transition Metal Compounds. World Scientific, Singapore (1993)
Kumar, R., Khare, N.: Temperature dependence of conduction mechanism of ZnO and Co-doped ZnO thin films. Thin Solid Films 516(6), 1302–1307 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2007.06.121
Lalitha, S., Sathyamoorthy, R., Senthilarasu, S., Subbarayan, A., Natarajan, K.: Characterization of CdTe thin film - dependence of structural and optical properties on temperature and thickness. Sol. Energy. Mater. Sol. Cells 82(1–2), 187–199 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2004.01.017
Li, W., Li, M., Xie, S., Zhai, T., Yu, M., Liang, C., Ouyang, X., Lu, X., Li, H., Tong, Y.: Improving the photoelectrochemical and photocatalytic performance of CdO nanorods with CdS decoration. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 15, 4212–4216 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CE40092A
Lim, J.H., Lee, S.M., Kim, H.S., Kim, H.Y., Park, J., Jung, S.B., Park, G.C., Kim, J., Joo, J.: Synergistic effect of Indium and Gallium co-doping on growth behavior and physical properties of hydrothermally grown ZnO nanorods. Sci. Rep. 7, 41992 (1–10) (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41992
Liu, D., Lv, Y., Zhang, M., Liu, Y., Zhu, Y., Zong, R., Zhu, Y.: Defect-related photoluminescence and photocatalytic properties of porous ZnO nanosheets. J. Mater. Chem. A 2(37), 15377–15388 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TA02678K
Lv, Y., Liu, Y., Zhu, Y., Zhu, Y.: Surface oxygen vacancy induced photocatalytic performance enhancement of a BiPO4 nanorod. J. Mater. Chem. A 2(4), 1174–1182 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TA13841K
Mandal, R.K., Saha, P., Majumder, T.P.: Structural, optical characterization of the synthesized Fe doped CdO Nano particles, its application as a promising photocatalyst for degradation of the hazardous methyl violet dye. Optik 246, 167795 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.167795
Mekasuwandumrong, O., Pawinrat, P., Praserthdam, P., Panpranot, J.: Effects of synthesis conditions and annealing post-treatment on the photocatalytic activities of ZnO nanoparticles in the degradation of methylene blue dye. Chem. Eng. J. 164(1), 77–84 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.08.027
Millesi, S., Schilirò, M., Greco, F., Crupi, I., Impellizzeri, G., Priolo, F., Egdell, R.G., Gulino, A.: Nanostructured CdO thin films for water treatments. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 42(1), 85–88 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2015.08.005
Mondal, K., Bhattacharyya, S., Sharma, A.: Photocatalytic degradation of naphthalene by electrospun mesoporous carbon-doped anatase TiO2 nanofiber mats. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 53(49), 18900–18909 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/ie5025744
Moulder, J., Stickle, W., Sobol, P., Bomben, K., Chastain, J. (eds.): Handbook of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy. Perkin-Elmer Corporation, Minnesota (1992)
Nadaf, L.I., Venkatesh, K.S.: Synthesis and characterization of tin oxide nanoparticles by co-precipitation method. IOSR- JAC 9(2), 1–4 (2016). https://doi.org/10.9790/5736-09210104
Patel, A.A., Wu, F., Zhang, J.Z., Martinez, C.L.T., Mehra, R.K., Yang, Y., Risbud, S.H.: Synthesis, optical spectroscopy and ultrafast electron dynamics of PbS nanoparticles with different surface capping. J. Phys. Chem. B 104(49), 11598–11605 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp000639p
Rajput, J.K., Pathak, T.K., Kumar, V., Kumar, M., Purohit, L.P.: Annealing temperature dependent investigations on nano-cauliflower like structure of CdO thin film grown by sol–gel method. Surf. Interfaces 6, 11–17 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2016.11.005
Rane, Y.N., Shende, D.A., Raghuwanshi, M.G., Koli, R.R., Gosavi, S.R., Deshpande, N.G.: Visible-light assisted CdO nanowires photocatalyst for toxic dye degradation studies. Optik 179, 535–544 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2018.10.215
Reddy, K.T.R., Shanthini, G.M., Johnston, D., Miles, R.W.: Highly transparent and conducting CdO films grown by chemical spray pyrolysis. Thin Solid Films 427(1–2), 397–400 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-6090(02)01183-5
Reddy, C.V., Shim, J., Byon, C., Rao, L.V.K., Satish, D.V., Ravikumar, R.V.S.S.N.: Room temperature synthesis and spectral characterization of Cu2+-doped CdO powder. Indian J. Phys. 90(3), 359–364 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2014.07.004
Saha, B., Das, S., Chattopadhyay, K.K.: Electrical and optical properties of Al doped cadmium oxide thin films deposited by radio frequency magnetron sputtering. Sol Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 91(18), 1692–1697 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2007.05.025
Shad, N.A., Sajid, M.M., Haq, A.U., Amin, N., Imran, Z., Anwar, H., Ali, K., Hussain, Z., Younus, A., Javed, Y.: Photocatalytic investigation of cadmium oxide nanosheets prepared by hydrothermal method. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 44, 6669–6675 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-03897-5
Singh, A.: Characterization, electrical and sensing properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Adv. Powder Technol. 21(6), 609–613 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2010.02.002
Singh, J.P., Bansal, N.P., Bhalla, A.S., Mahmoud, M.M., Manjooran, N.J., Singh, G., Lamon, J., Choi, S.R., Pickrell, G., Lu, K., Brennecka, G., Goto, T. (eds.): Processing and Properties of Advanced Ceramics and Composites: Ceramic Transactions, vol. 249. Wiley, Hoboken (2014)
Sivalingam, G., Nagaveni, K., Hegde, M.S., Madras, G.: Photocatalytic degradation of various dyes by combustion synthesized nano anatase TiO2. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 45(1), 23–38 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-3373(03)00124-3
Suryanarayana, C., Grant Norton, M.: X-ray Diffraction: A Practical Approach. Plenum Press, New York (1998)
Suwanchawalit, C., Wongnawa, S.: Influence of calcination on the microstructures and photocatalytic activity of potassium oxalate-doped TiO2 powders. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 338(1), 87–99 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2007.12.029
Tang, W., Cameron, D.C.: Aluminum-doped zinc oxide transparent conductors deposited by the sol–gel process. Thin Solid Films 238(1), 83–87 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-6090(94)90653-X
Thennarasu, G., Sivasamy, A.: Metal ion doped semiconductor metal oxide nanosphere particles prepared by soft chemical method and its visible light photocatalytic activity in degradation of phenol. Powder Technol. 250, 1–12 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2013.08.004
Vamathevan, V., Amal, R., Beydoun, D., Low, G., Evoy, S.M.: Photocatalytic oxidation of organics in water using pure and silver-modified titanium dioxide particles. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 148(1–3), 233–245 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1010-6030(02)00049-7
Vanalakar, S.A., Mali, S.S., Suryavanshi, M.P., Patil, P.S.: Quantum size effect in chemosynthesized nanostructured CdS thin films. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostructures 5, 805–810 (2010)
Vidyasagar, C.C., Naik, A.Y., Venkatesh, T.G., Viswanatha, R.: Solid-state synthesis and effect of temperature on optical properties of Cu–ZnO, Cu–CdO and CuO nanoparticles. Powder Technol. 214(3), 337–343 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2011.08.025
Wandelt, K.: Photoemission studies of adsorbed oxygen and oxide layers. Surface Sci. Rep. 2(1), 1–121 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-5729(82)90003-6
Wang, Q., Yang, X., Liu, D., Chi, L., Hou, J.: Ag and CdS nanoparticles co-sensitized TiO2 nanotubes for enhancing visible photoelectrochemical performance. Electrochim. Acta 83, 140–145 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2012.07.092
Wang, J., Fang, T., Zhang, L., Feng, J., Li, Z., Zou, Z.: Effects of oxygen doping on optical band gap and band edge positions of Ta3N5 photocatalyst: A GGA + U calculation. J. Catal. 309, 291–299 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2013.10.014
Waren, B.E.: X-ray Diffraction. Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA (1969)
Xiang, Q., Yu, J., Jaroniec, M.: Graphene-based semiconductor photocatalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41(2), 782–796 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CS15172J
Yang, S., Gao, L.: Preparation of titanium dioxide nanocrystallite with high photocatalytic activities. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 88(4), 968–970 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2005.00151.x
Yu, J., Dai, G., Cheng, B.: Effect of crystallization methods on morphology and photocatalytic activity of anodized TiO2 nanotube array films. J. Phys. Chem. C 114(45), 19378–19385 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp106324x
Zaien, M., Ahmed, N.M., Hassan, Z.: Fabrication and characterization of an n-CdO/p-Si solar cell by thermal evaporation in a vacuum. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 8, 6988–6996 (2013)
Funding
No funding was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Photonics: Current Challenges and Emerging Applications.
Guest edited by Jelena Radovanovic, Dragan Indjin, Maja Nesic, Nikola Vukovic and Milena Milosevic.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeejamol, D.J., Jai Aultrin, K.S. & Dev Anand, M. Exploration of CdO properties favoring superior photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye by Al3+ doping. Opt Quant Electron 54, 291 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-022-03694-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-022-03694-9