Abstract
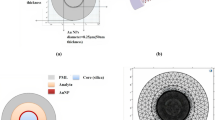
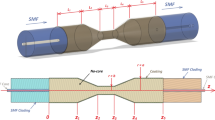
The present manuscript describes the theoretical understanding of nanoporous alumina based fiber optic sensing structures. The Cavity Maxwell Garnett theory is used to calculate the dielectric functions of the proposed layer. The performance of the proposed sensing structure is evaluated in terms of its sensitivity towards change in the refractive index of the nearby medium. The sharpness of the resonance has also been calculated as an estimation of the performance parameters. It has been observed that the proposed structure is approximately 13 times more sensitive than the conventional fiber optic sensors. The study has further been extended by replacing the nanolayer of aluminum with the nanolayer of the gold. A comparative study has been provided in terms of the efficiency of the fiber optic probe. The effects of change in pore radius, thickness of the adsorbed medium and shell radius have also been studied.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergman, D.J.: Exactly solvable microscopic geometries and rigorous bounds for the complex dielectric constant of a two-component composite material. Phys. Rev. Lett. 45, 148 (1980)
Bruggeman, D.A.G.: Calculation of various physical constants of heterogeneous substances III. The elastic constants of quasiisotropic mixtures of isotropic substances. Ann Phys (leipzig) 24, 636 (1935a)
Bruggeman, D.A.G.: Calculation of various physical constants of heterogeneous substances I. Dielectric constants and conductive capabilities of the mixing bodies of isotropic substances. Ann. Phys. (leipzig) 24, 636–791 (1935b)
Chen, Y., Yu, Y., Li, X., Tan, Z., Geng, Y.: Experimental comparison of fiber optic surface plasmon resonance sensors with multi metal and single silver or gold layer. Plasmonics 10, 1801–1808 (2015)
Chu, S.Z., Wada, K., Inoue, S., Isogai, M., Katsuta, Y., Yasumori, A.: Large-scale fabrication of ordered nanoporous alumina films with arbitrary pore intervals by critical-potential anodization. J. Electrochem. Soc. 153, 384 (2006)
Evans, P., Hendren, W.R., Atkinson, R., Wurtz, G.A., Dickson, W., Zayats, A.V., Pollard, R.J.: Growth and properties of gold and nickel nanorods in thin film alumina. Nanotechnology 17, 5746 (2006)
Fontana, E.: Thickness optimization of metal films for the development of surface-plasmon-based sensors for nonabsorbing media. Appl. Opt. 45, 7632–7642 (2006)
Friedman, A.L., Brittain, D., Menon, L.: Roles of pH and acid type in the anodic growth of porous alumina. J. Chem. Phys. 127, 154717 (2007)
Ghatak, A.K., Thyagarajan, K.: Introduction to Fiber Optics. Cambridge University Press, England (1998)
Ghicov, A., Schmuki, P.: Self-ordering electrochemistry: a review on growth and functionality of TiO2 nanotubes and other self-aligned MOx structures. Chem. Commun. 2009, 2791–2802 (2009)
Gyurcsanyi, R.E.: Chemically-modified nanopores for sensing. Trends Anal. Chem. 27, 627–639 (2008)
Homola, J.: On the sensitivity of surface plasmon resonance sensors with spectral interrogation. Sens. Actuators B 41, 207–211 (1997)
Homola, J.: Surface plasmon resonance sensors for detection of chemical and biological species. Chem. Rev. 108, 462–493 (2008)
Hotta, K., Yamaguchi, A., Teramae, N.: Nanoporous waveguide sensor with optimized nanoarchitectures for highly sensitive label free biosensing. ACS Nano 6, 1541–1547 (2012)
Jani, A.M.M., Losic, D., Voelcker, N.H.: Nanoporous anodic aluminium oxide: advances in surface engineering and emerging applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 58, 636–704 (2013)
Jha, R., Verma, R.K., Gupta, B.D.: Surface plasmon resonance-based tapered fiber optic sensor: sensitivity enhancement by introducing a teflon layer between core and metal layer. Plasmonics 3, 151–156 (2008)
Koutsioubas, A.G., Spiliopoulos, N., Anastassopoulos, D., Vradis, A.A., Priftis, G.D.: Nanoporous alumina enhanced surface plasmon resonance sensors. J. Appl. Phys. 103, 094521 (2008)
Kretschmann, E.: Determination of the optical constants of metals by excitation of surface plasmons. Z. Phys. 241, 313 (1971)
Kumeria, T., Santos, A., Losic, D.: Nanoporous anodic alumina platforms: engineered surface chemistry and structure for optical sensing applications. Sensors 14, 11878–11918 (2014)
Landau, L.D., Lifshitz, E.M.: Electrodynamcis of continuous media. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 16, 359 (1961)
Lau, K.H.A., Duran, H., Knoll, W.: In situ characterization of N-carboxy anhydride polymerization in nanoporous anodic alumina. J. Phys. Chem. B 113, 3179–3189 (2009)
Lee, W., Ji, R., Gösele, U., Nielsch, K.: Fast fabrication of long-range ordered porous alumina membranes by hard anodization. Nat. Mater. 5, 741–747 (2006)
Lee, W., Schwirn, K., Steinhart, M., Pippel, E., Scholz, R., Gösele, U.: Structural engineering of nanoporous anodic aluminium oxide by pulse anodization of aluminium. Nat. Nanotechnol. 3, 234–239 (2008a)
Lee, K., Tang, Y., Ouyang, M.: Self-ordered controlled structure nanoporous membranes using constant current anodization. Nano Lett. 8, 4624–4629 (2008b)
Lee, W., Kim, J.C., Gösele, U.: Spontaneous current oscillations during hard anodization of aluminum under potentiostatic conditions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 20, 21–27 (2010)
Looyenga, H.: Dielectric constants of heterogeneous mixtures. Physica (amsterdam) 31, 401–406 (1965)
Losic, D.: Preparation of porous anodic alumina with periodically perforated pores. Langmuir 25, 5426–5431 (2009)
Losic, D., Lillo, M.: Porous alumina with shaped pore geometries and complex pore architectures fabricated by cyclic anodization. Small 5, 1392–1397 (2009)
Ma, Y., Farrell, G., Semenova, Y., Chan, H.P., Zhang, H., Wu, Q.: Sensitivity enhancement for a multimode fiber sensor with an axisymmetric metal grating layer. Photon. Nanostruct. Fundam. Appl. 12, 69–74 (2014)
Maharana, P.K., Bharadwaj, S., Jha, R.: Electric field enhancement in surface plasmon resonance bimetallic configuration based on chalcogenide prism. J. Appl. Phys. 114, 014304 (2013)
Marsal, L.F., Vojkuvka, L., Formentin, P., Pallarés, J., Ferre-Borrull, J.: Fabrication and optical characterization of nanoporous alumina films annealed at different temperatures. Opt. Mater. 31, 860–864 (2009)
Maxwell Garnett, J.C.: Colours in metal glasses and in metallic films. Philos. Trans. r. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 203, 385–420 (1904a)
Meng, G., Jung, Y.J., Cao, A., Vajtai, R., Ajayan, P.M.: Controlled fabrication of hierarchically branched nanopores, nanotubes, and nanowires. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 7074–7078 (2005)
Mishra, A.K., Mishra, S.K., Verma, R.K.: Graphene and beyond graphene MoS2: a new window in surface-plasmon-resonance-based fiber optic sensing. J. Phys. Chem. C 120, 2893–2900 (2016)
Monecke, J.: Bergman spectral representation of a simple expression for the dielectric response of a symmetric two-component composite. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 6, 907 (1994)
Ono, S., Saito, M., Asoh, H.: Self-ordering of anodic porous alumina formed in organic acid electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 51, 827–833 (2005)
Piliarik, M., Parova, L., Homola, J.: High-throughput SPR sensor for food safety. Biosens. Bioelectron 24, 1399–1404 (2009)
Ren, Y., Ma, Z., Bruce, P.G.: Ordered mesoporous metal oxides: synthesis and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 4909–4927 (2012)
Santos, A., Formentín, P., Pallarès, J., Ferré-Borrull, J., Marsal, L.F.: Structural engineering of nanoporous anodic alumina funnels with high aspect ratio. J. Electroanal. Chem. 655, 73–78 (2011)
Santos, A., Kumeria, T., Losic, D.: Nanoporous anodic aluminum oxide for chemical sensing and biosensors. Trends Anal. Chem. 44, 25–38 (2013)
Sasaki, Y., Nishina, Y., Sato, M., Okamura, K.: Optical-phonon states of SiC small particles studied by Raman scattering and infrared absorption. Phys. Rev. B 40, 1762 (1989)
Sharma, A.K., Mohr, G.J.: Theoretical understanding of an alternating dielectric multilayer-based fiber optic SPR sensor and its application to gas sensing. New J. Phys. 10, 023039 (2008)
Sharma, A.K., Jha, R., Gupta, B.D.: Fiber-optic sensors based on surface plasmon resonance: a comprehensive review. Sens. J. IEEE 7, 1118–1129 (2007)
Sipova, H., Homola, J.: Surface plasmon resonance sensing of nucleic acids: a review. Anal. Chim. Acta 773, 9–23 (2013)
Spanier, J.E., Herman, I.P.: Use of hybrid phenomenological and statistical effective-medium theories of dielectric functions to model the infrared reflectance of porous SiC films. Phys. Rev. B 61, 10437 (2000)
Srivastava, S.K., Gupta, B.D.: Fiber optic plasmonic sensors: past present and future. Open Opt. J. 7, 58 (2013)
Sulka, G.D., Stepniowski, W.J.: Structural features of self-organized nanopore arrays formed by anodization of aluminum in oxalic acid at relatively high temperatures. Electrochim. Acta 54, 3683–3691 (2009)
Tabassum, R., Gupta, B.D.: Influence of oxide overlayer on the performance of a fiber optic SPR sensor with Al/Cu layers. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 23, 81–88 (2017)
Tripathi, S.M., Kumar, A., Marin, E., Meunier, J.P.: Side-polished optical fiber grating-based refractive index sensors utilizing the pure surface plasmon polariton. Lightwave Technol. 26, 1980–1985 (2008)
Verma, R.K., Gupta, B.D.: Surface plasmon resonance-based fiber optic sensor for the IR region using a conducting metal oxide film. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 27, 846–851 (2010)
Vikas and Verma, R.K.: Sensitivity enhancement of a lossy mode resonance based tapered fiber optic sensor with an optimum taper profile. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 51, 415302 (2018)
Vojkuvka, L., Santos, A., Pallarès, J., Ferré-Borrull, J., Marsal, L.F., Celis, J.-P.: On the mechanical properties of nanoporous anodized alumina by nanoindentation and sliding tests. Surf. Coat. Technol. 206, 2115–2124 (2012)
Weaver, J.H., Alexander, R.W., Teng, L., Mann, R.A., Bell, R.J.: Infrared absorption of small silicon particles with oxide overlayers. Phys. Status Solidi A 20, 321–329 (1973)
Wehrspohn, R.B.: Ordered porous nanostructures and applications. Nanostruct. Sci. Technol. Springer 1, 207 (2005)
Woo, L., Jae-Cheon, K.: Highly ordered porous alumina with tailor-made pore structures fabricated by pulse anodization. Nanotechnology 21, 485304 (2010)
Yi, L., Zhiyuan, L., Shuoshuo, C., Xing, H., Xinhua, H.: Novel AAO films and hollow nanostructures fabricated by ultra-high voltage hard anodization. Chem. Commun. 46, 309–311 (2009)
Zhang, F., Liu, X., Pan, C., Zhu, J.: Nano-porous anodic aluminium oxide membranes with 6–19 nm pore diameters formed by a low-potential anodizing process. Nanotechnology 18, 345302 (2007)
Acknowledgements
Ms. Jyoti would like to acknowledge Central University of Rajasthan for providing university fellowship. Also, this work is partially supported by DST SERB CRG/2020/005593, India.
Funding
Science and Engineering Research Board, CRG/2020/005593, R. K. Verma
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors do not have any conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jyoti, Verma, R.K. Application of cavity Maxwell Garnett theory in SPR based fiber optic sensor with porous alumina structure. Opt Quant Electron 54, 223 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-022-03591-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-022-03591-1