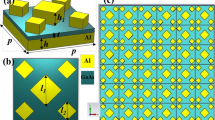
Abstract
Promising application prospects and excellent characteristics of metamaterials are currently under intensive research work all over the world. In this paper, novel wavelength selective metamaterial absorber based on 2D split rhombus grating is numerically proposed and analyzed. The suggested metamaterial absorber is made of molybdenum metals with dielectric spacer of Magnetic Florid (MgF2). The effects of the design parameters are studied to improve the absorption of the reported metamaterial absorber. Additionally, the inductor and capacitor (LC) model is investigated to understand the physics beyond the absorption of the studied design. The finite difference time domain method is used to obtain the modal analysis and absorption characteristics of the metamaterial structure. Perfect absorption is achieved through studied wavelength range from 300 to 20,000 nm with high photon-to-heat efficiency of 81.71% at 1000 K. The absorption enhancement is due to the coupling between the surface plasmon polariton, Fabry–Perot resonance, and magnetic polariton. It is also found that the achieved absorption is insensitive to the oblique incidence from θ = 0° to 60° for the transverse magnetic (TM) and transverse electric (TE) waves. Therefore, the suggested absorber has a good potential for using in solar energy harvesting and conversion systems.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelatif, G.Y., et al.: Ultrabroadband absorber based on a funnel-shaped anisotropic metamaterial. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 36(10), 2889–2895 (2019)
Abdel-Latif, G.Y., et al.: Characteristics of thermophotovoltaic emitter based on 2D cylindrical gear grating. Opt. Quant. Electron. 53(3), 1–14 (2021)
ASTM: Reference solar spectral irradiance: air mass 1.5 spectra. http://rredc.nrel.gov/solar/spectra/am1.5/ (2011)
Aydin, K., et al.: Broadband polarization-independent resonant light absorption using ultrathin plasmonic super absorbers. Nat. Commun. 2(1), 1–7 (2011)
Baxter, J., et al.: Nanoscale design to enable the revolution in renewable energy. Energy Environ. Sci. 2(6), 559–588 (2009)
Bhattarai, K., et al.: Metamaterial perfect absorber analyzed by a meta-cavity model consisting of multilayer metasurfaces. Scientific reports 7.1, 1–9 (2017)
Bossard, J.A., Werner, D.H.: Metamaterials with custom emissivity polarization in the near-infrared. Opt. Express 21(3), 3872–3884 (2013)
Cai, H., et al.: Genetic algorithm optimization for highly efficiency solar thermal absorber based on optical metamaterials. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 271, 107712 (2021)
Cao, S., et al.: Two-dimensional subwavelength meta-nanopillar array for efficient visible light absorption. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102(16), 161109 (2013)
Cao, T., et al.: Broadband polarization-independent perfect absorber using a phase-change metamaterial at visible frequencies. Sci. Rep. 4, 1–8 (2014)
Chen, H.-T., et al.: Active terahertz metamaterial devices. Nature 444(7119), 597–600 (2006)
Chen, L., et al.: Near-field imaging of the multi-resonant mode induced broadband tunable metamaterial absorber. RSC Adv. 10(9), 5146–5151 (2020)
Cui, Y., et al.: Ultrabroadband light absorption by a sawtooth anisotropic metamaterial slab. Nano Lett. 12(3), 1443–1447 (2012)
Dolling, G., et al.: Negative-index metamaterial at 780 nm wavelength. Opt. Lett. 32(1), 53–55 (2007)
Fowles, G.R.: Introduction to Modern Optics. Courier Corporation, New York (1989)
Ghobadi, A., et al.: Tuning the metal filling fraction in metal-insulator-metal ultra-broadband perfect absorbers to maximize the absorption bandwidth. Photonics Res. 6(3), 168–176 (2018)
Glybovski, S.B., et al.: Metasurfaces: from microwaves to visible. Phys. Rep. 634, 1–72 (2016)
Green, M.A.: Solar Cells: Operating Principles, Technology, and System Applications. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1982)
Guler, U., et al.: Refractory plasmonics. Science 344(6181), 263–264 (2014)
Hao, J., et al.: High performance optical absorber based on a plasmonic metamaterial. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96(25), 251104 (2010)
Haque, A., et al.: Damage analysis of a perfect broadband absorber by a femtosecond laser. Sci. Rep. 9(1), 1–8 (2019)
Hedayati, M.K., et al.: Design of a perfect black absorber at visible frequencies using plasmonic metamaterials. Adv. Mater. 23(45), 5410–5414 (2011)
Holloway, C.L., et al.: An overview of the theory and applications of metasurfaces: the two-dimensional equivalents of metamaterials. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 54(2), 10–35 (2012)
Incropera, F.P., et al.: Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer. Wiley, Hoboken (2007)
Khodasevych, I.E., et al.: Micro-and nanostructured surfaces for selective solar absorption. Adv. Opt. Mater. 3(7), 852–881 (2015)
Landy, N.I., et al.: Perfect metamaterial absorber. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100(20), 207402 (2008)
Lee, B.J., et al.: Coherent thermal emission by excitation of magnetic polaritons between periodic strips and a metallic film. Opt. Express 16(15), 11328–11336 (2008)
Lei, L., et al.: Ultra-broadband absorber from visible to near-infrared using plasmonic metamaterial. Opt. Express 26(5), 5686–5693 (2018)
Li, L., et al.: A wide-angle polarization-insensitive ultra-thin metamaterial absorber with three resonant modes. J. Appl. Phys. 110(6), 063702 (2011)
Liu, X., Padilla, W.J.: Thermochromic infrared metamaterials. Adv. Mater. 28(5), 871–875 (2016)
Liu, X., et al.: Infrared spatial and frequency selective metamaterial with near-unity absorbance. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104(20), 207403 (2010)
Liu, X., et al.: Taming the blackbody with infrared metamaterials as selective thermal emitters. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107(4), 045901 (2011)
Lu, L., et al.: Cooperative plasmonic effect of Ag and Au nanoparticles on enhancing performance of polymer solar cells. Nano Lett. 13(1), 59–64 (2012)
Lumerical Solution, I., Inc. https://www.lumerical.com
Maier, S.A.: Plasmonics: Fundamentals and Applications. Springer, Berlin (2007)
Ni, Q., et al.: Plasmonic light trapping for enhanced light absorption in film-coupled ultrathin metamaterial thermophotovoltaic cells. Front. Energy 12(1), 185–194 (2018)
Park, J.W., et al.: Multi-band metamaterial absorber based on the arrangement of donut-type resonators. Opt. Express 21(8), 9691–9702 (2013)
Pryce, I.M., et al.: Highly strained compliant optical metamaterials with large frequency tunability. Nano Lett. 10(10), 4222–4227 (2010)
Solymar, L., Shamonina, E.: Waves in Metamaterials. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2009)
Spanggaard, H., Krebs, F.C.: A brief history of the development of organic and polymeric photovoltaics. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 83(2–3), 125–146 (2004)
Sun, J., et al.: An extremely broad band metamaterial absorber based on destructive interference. Opt. Express 19(22), 21155–21162 (2011)
Walia, S., et al.: Flexible metasurfaces and metamaterials: a review of materials and fabrication processes at micro-and nano-scales. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2(1), 011303 (2015)
Wang, H., Wang, L.: Perfect selective metamaterial solar absorbers. Opt. Express 21(106), A1078–A1093 (2013)
Wang, L., Zhang, Z.M.: Effect of magnetic polaritons on the radiative properties of double-layer nanoslit arrays. JOSA B 27(12), 2595–2604 (2010)
Wang, L., Zhang, Z.J.: Wavelength-selective and diffuse emitter enhanced by magnetic polaritons for thermophotovoltaics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100(6), 063902 (2012)
Wang, B., et al.: Wide-angle and polarization-independent chiral metamaterial absorber. Phys. Rev. 80(3), 033108 (2009)
Wang, H., et al.: Tailoring thermal radiative properties with film-coupled concave grating metamaterials. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 158, 127–135 (2015)
Watts, C.M., et al.: Metamaterial electromagnetic wave absorbers. Adv. Mater. 24(23), OP98–OP120 (2012)
Wilt, D., et al. Thermophotovoltaics for space power applications. In: AIP Conference Proceedings. American Institute of Physics (2007)
Wu, C., et al.: Large-area wide-angle spectrally selective plasmonic absorber. Phys. Rev. B 84(7), 075102 (2011)
Xu, H., et al.: Dual-band metamaterial absorbers in the visible and near-infrared regions. J. Phys. Chem. C 123(15), 10028–10033 (2019)
Yen, T.-J., et al.: Terahertz magnetic response from artificial materials. Science 303(5663), 1494–1496 (2004)
Yokoyama, T., et al.: Spectrally selective mid-infrared thermal emission from molybdenum plasmonic metamaterial operated up to 1000° C. Adv. Opt. Mater. 4(12), 1987–1992 (2016)
Zhang, Z.M.: Nano/Microscale Heat Transfer. McGraw-Hill, New York (2007)
Zhao, B., et al.: Thermophotovoltaic emitters based on a two-dimensional grating/thin-film nanostructure. J. Heat Mass Transf. 67, 637–645 (2013)
Zheludev, N.I., Kivshar, Y.S.: From metamaterials to metadevices. Nat. Mater. 11(11), 917–924 (2012)
Zhou, J., et al.: Unifying approach to left-handed material design. Opt. Lett. 31(24), 3620–3622 (2006)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Solar Energy project sponsored by the Academy of Scientific Research and Technology (ASRT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest related to this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamdy, H., Abdel-Latif, G.Y., El-Agamy, M. et al. Wavelength-selective metamaterial absorber based on 2D split rhombus grating for thermophotovoltic solar cell. Opt Quant Electron 54, 117 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-021-03459-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-021-03459-w