Abstract
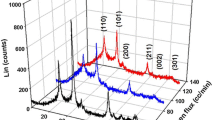
InGaN films in the non-flow and a small flow of nitrogen cases were fabricated by the RFMS (Radio Frequency Magnetron Sputter) method to compare crucial physical characteristics of its material. From the XRD analysis, application of small nitrogen flow in the InGaN thin film growth has been observed to result in changes in the crystal size, texture coefficient, and crystal structure parameters of the film. AFM results showed both films obtained have tightly packed granular, and almost homogeneous, and Nano-structural properties, but they are different in roughness, as increased by applying small nitrogen flow. Optical conductance peaks of the material in non-flow and small flow case were \(1.3957\times {10}^{10}\mathrm{ and }1.1496\times {10}^{10}(\mathrm{S}/\mathrm{m})\), showed a decrement in optical conductance by small nitrogen flow. In the same manner, electrical conductance peaks of the material in non-flow and small flow case were \(5.2512\times {10}^{12}\mathrm{ and }5.2236\times {10}^{12} (\mathrm{S})\), showed a decrement in electrical conductance by small nitrogen flow. In addition, the electrical conductivity of the InGaN material has been obtained at higher than the optical conductivity value of the InGaN material in both cases. Also, it was noticed that direct allowed optical band gap energy non-flow and small flow cases were 2.65 and 2.69 eV, displayed increased by applied small nitrogen flow. Essentially, many noteworthy physical properties such as crystalline size, texture coefficient, optical/electrical conductivity, the surface roughness of the films have been compared and studied for the non-flow and a small flow of nitrogen cases. Therefore; a better understanding of the structural/crystal and electrical characteristics of the InGaN film by applying/optimizing different growth conditions will be able to pave the way for InGaN device studies.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Supplementary file is available for this study.
References
Alizadeh, M., Tong, G.B., Qadir, K.W., Mehmood, M.S., Rasuli, R.: Cu2O/InGaN heterojunction thin films with enhanced photoelectrochemical activity for solar water splitting. Renew. Energy 156, 602–609 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.04.107
Berrah, S., Boukortt, A., Abid, H.: Optical properties of the cubic alloy (In, Ga)N. Phys. e: Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 41(4), 701–704 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2008.11.009
Bilgili, A.K., Akpınar, Ö., Öztürk, M.K., Başköse, C., Özçelik, S., Özbay, E.: Investigation of structural, optical and morphological properties of InGaN/GaN structure. Appl. Phys. A 125(1), 36 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2338-2
Bragg, W.H., Bragg, W.L.: The reflection of X-rays by crystals. Proc. r. Soc. Lond. Ser. a, Contain. Pap. Math. Phys. Character 88(605), 428–438 (1913). https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1913.0040
Chen, F., Ji, X., Lau, S.P.: Recent progress in group III-nitride nanostructures: from materials to applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. r. Rep. 142, 100578 (2020a). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mser.2020.100578
Chen, L., Zhang, K., Dong, J., Wang, B., He, L., Wang, Q., He, M., Wang, X.: The piezotronic effect in InGaN/GaN quantum-well based microwire for ultrasensitive strain sensor. Nano Energy 72, 104660 (2020b). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.104660
Cheriton, R., Sadaf, S.M., Robichaud, L., Krich, J.J., Mi, Z., Hinzer, K.: Two-photon photocurrent in InGaN/GaN nanowire intermediate band solar cells. Commun. Mater. 1(1), 63 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43246-020-00054-6
Dalapati, P., Manik, N.B., Basu, A.N.: Temperature dependence of current–voltage and carrier lifetime characteristics in InGaN blue light-emitting diode. Opt. Quant. Electron. 52(2), 54 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-019-2182-4
Dammers, A.J., Radelaar, S.: A grain growth model for evolution of polycrystalline surfaces. Mater. Sci. Forum 94–96, 345–350 (1992)
Evropeitsev, E.A., Kazanov, D.R., Robin, Y., Smirnov, A.N., Eliseyev, I.A., Davydov, V.Y., Toropov, A.A., Nitta, S., Shubina, T.V., Amano, H.: State-of-the-art and prospects for intense red radiation from core–shell InGaN/GaN nanorods. Sci. Rep. 10(1), 19048 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-76042-0
Gökden, S., Tülek, R., Teke, A., Leach, J.H., Fan, Q., Xie, J., Özgür, Ü., Morkoç, H., Lisesivdin, S.B., Özbay, E.: Mobility limiting scattering mechanisms in nitride-based two-dimensional heterostructures with the InGaN channel. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 25(4), 045024 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1088/0268-1242/25/4/045024
Harris, G.B.: X. Quantitative measurement of preferred orientation in rolled uranium bars. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 43(336), 113–123 (1952). https://doi.org/10.1080/14786440108520972
Hervé, P., Vandamme, L.K.J.: General relation between refractive index and energy gap in semiconductors. Infrared Phys. Technol. 35(4), 609–615 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1016/1350-4495(94)90026-4
Hu, H., Tang, B., Wan, H., Sun, H., Zhou, S., Dai, J., Chen, C., Liu, S., Guo, L.J.: Boosted ultraviolet electroluminescence of InGaN/AlGaN quantum structures grown on high-index contrast patterned sapphire with silica array. Nano Energy 69, 104427 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.104427
Hu, Y.-J., Huang, Y.-W., Fang, C.-H., Wang, J.-C., Chen, Y.-F., Nee, T.-E.: Anomalous disorder-related phenomena in InGaN/GaN multiple quantum well heterosystems. J. Lumin. 130(6), 1000–1004 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2010.01.014
Iyer, P.P., DeCrescent, R.A., Mohtashami, Y., Lheureux, G., Butakov, N.A., Alhassan, A., Weisbuch, C., Nakamura, S., DenBaars, S.P., Schuller, J.A.: Unidirectional luminescence from InGaN/GaN quantum-well metasurfaces. Nat. Photonics 14(9), 543–548 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-020-0641-x
Kumar, V., Singh, J.: Model for calculating the refractive index of different materials. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 48, 571–574 (2010)
Liu, W.H., Qu, Y., Ban, S.L.: Electron mobility limited by optical phonons in wurtzite InGaN/GaN core-shell nanowires. J. Appl. Phys. 122(11), 115104 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5003261
Mantarcı, A., Kundakçi, M.: Physical properties of RF magnetron sputtered GaN/n-Si thin film: impacts of RF power. Opt. Quant. Electron. 51(3), 81 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-019-1795-y
Mantarcı, A., Kundakçi, M.: Production of GaN/n–Si thin films using RF magnetron sputtering and determination of some physical properties: argon flow impacts. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 56(3), 905–914 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-019-00420-9
Mantarcı, A.: Investigation of changes in structural properties of polycrystalline ln0.6628Ga0.3372N thin film. Appl. Phys. A 127, 469 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04631-5
Moses, P.G., Miao, M., Yan, Q., Walle, C.G.V.D.: Hybrid functional investigations of band gaps and band alignments for AlN, GaN, InN, and InGaN. J. Chem. Phys. 134(8), 8470 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3548872
Moss, T.S.: Relations between the refractive index and energy gap of semiconductors. Physica Status Solidi (b) 131(2), 415–427 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.2221310202
Özen, S., Şenay, V., Pat, S., Korkmaz, Ş: The influence of voltage applied between the electrodes on optical and morphological properties of the InGaN thin films grown by thermionic vacuum arc. Scanning 38(1), 14–20 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/sca.21237
Pasayat, S.S., Gupta, C., Wong, M.S., Wang, Y., Nakamura, S., Denbaars, S.P., Keller, S., Mishra, U.K.: Growth of strain-relaxed InGaN on micrometer-sized patterned compliant GaN pseudo-substrates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 116(11), 111101 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0001480
Patterson, A.L.: The Scherrer formula for X-ray particle size determination. Phys. Rev. 56(10), 978–982 (1939). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.56.978
Qashou, S.I., El-Zaidia, E.F.M., Darwish, A.A.A., Hanafy, T.A.: Methylsilicon phthalocyanine hydroxide doped PVA films for optoelectronic applications: FTIR spectroscopy, electrical conductivity, linear and nonlinear optical studies. Phys. B 571, 93–100 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2019.06.063
Ravindra, N.M., Ganapathy, P., Choi, J.: Energy gap–refractive index relations in semiconductors – an overview. Infrared Phys. Technol. 50(1), 21–29 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infrared.2006.04.001
Roknuzzaman, M., Ostrikov, K., Wang, H., Du, A., Tesfamichael, T.: Towards lead-free perovskite photovoltaics and optoelectronics by ab-initio simulations. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 14025 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13172-y
Schenk, H.P.D., Leroux, M., Mierry, P.D.: Luminescence and absorption in InGaN epitaxial layers and the van Roosbroeck-Shockley relation. J. Appl. Phys. 88(3), 1525–1534 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.373850
Smith, J.M., Ley, R., Wong, M.S., Baek, Y.H., Kang, J.H., Kim, C.H., Gordon, M.J., Nakamura, S., Speck, J.S., DenBaars, S.P.: Comparison of size-dependent characteristics of blue and green InGaN microLEDs down to 1 μm in diameter. Appl. Phys. Lett. 116(7), 071102 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5144819
Smith, L.L., King, S.W., Nemanich, R.J., Davis, R.F.: Cleaning of GaN surfaces. J. Electron. Mater. 25(5), 805–810 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02666640
Thompson, C.V.: Grain growth in thin films. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 20(1), 245–268 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ms.20.080190.001333
Thompson, C.V., Carel, R.: Texture development in polycrystalline thin films. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 32(3), 211–219 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1016/0921-5107(95)03011-5
Vegard, L.: Die Konstitution der Mischkristalle und die Raumfüllung der Atome. Z. Phys. 5(1), 17–26 (1921). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01349680
Xue, S.W., Zu, X.T., Zhou, W.L., Deng, H.X., Xiang, X., Zhang, L., Deng, H.: Effects of post-thermal annealing on the optical constants of ZnO thin film. J. Alloy. Compd. 448(1), 21–26 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2006.10.076
Yang, H., Ma, Z., Jiang, Y., Wu, H., Zuo, P., Zhao, B., Jia, H., Chen, H.: The enhanced photo absorption and carrier transportation of InGaN/GaN quantum wells for photodiode detector applications. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 43357 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep43357
Yarar, Z.: Electron mobility in modulation doped AlGaN/GaN and InGaN/GaN quantum wells: a comparative study. Solid State Commun. 147(3), 98–102 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssc.2008.05.006
Zhang, L.M., Li, C.X., Zhao, J.T., Yang, K.J., Zhang, G.F., Wang, T.S., Zhang, C.H.: Study of radiation damage in InGaN and AlGaN films induced by 8.9 MeV Bi33+ ions. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 305, 1–4 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2013.04.042
Acknowledgements
This project was funded by the Muş Alparslan University Research Council (MUSBAP) (with Project No: BAP-20-VMYO-4901-01)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The author (Asim Mantarcı) did all processes: conception or design of the work, data collection, data analysis, and interpretation, drafting the article, critical revision of the article, final approval of the version to be published.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mantarcı, A. Comparison of optical, electrical, and surface characteristics of InGaN thin films at non-flow and small nitrogen flow cases. Opt Quant Electron 53, 544 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-021-03203-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-021-03203-4