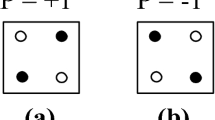
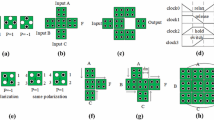
Abstract
Quantum-dot cellular automata (QCA) technology is believed to be a good alternative to CMOS technology. This nanoscale technology can provide a platform for design and implementation of high performance and power efficient logic circuits. However, the fabrication of QCA circuits is susceptible to faults appearing in this form of missing cells, additional cells, rotated cells and displaced cells. Over the years, several solutions have been proposed to address these problems. This paper presents a new solution for improving the fault tolerance of three input majority gate. The proposed majority gate is then used to design 2-1 multiplexer and 4-1 multiplexer. The proposed designs are implemented in QCA Designer. Simulation results demonstrate significant improvements in terms of fault tolerance and area requirement. The proposed gate consists of 11 cells and requires an area of 0.0096 μm2. The proposed design has 100% tolerance to the fault of a single missing cell and 71.43% tolerance to the rotation of one cell. The proposed 2-1 multiplexer consists of 41 cells and requires an area of 0.066 μm2. This multiplexer has 95.24% tolerance to the fault of a single missing cell.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afrooz, S., Navimipour, N.J.: Memory designing using quantum-dot cellular automata: systematic literature review classification and current trends. J Circuits Syst Comput 26(12), 1730004 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218126617300045
Ahmadpour, S.S., Mosleh, M.: A novel fault-tolerant multiplexer in quantum-dot cellular automata technology. J. Supercomput. 74(9), 4696–4716 (2018)
Ahmed, S., Naz, S.F.: Design of quantum dot cellular automata based fault tolerant convolution encoders for secure nanocomputing. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 18(6), 2050032 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1142/S021974992050032X
Babaie, S., Sadoghifar, A., Bahar, A.N.: Design of an Efficient Multilayer Arithmetic Logic Unit in Quantum-Dot Cellular Automata (QCA). IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II: Express Br. 66(6), 963–967 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSII.2018.2873797
Beard MJ. Design and simulation of fault-tolerant quantum-dot cellular automata (QCA) NOT gates. Dissertation, Wichita State University, 2006.
Bilal, B., Ahmed, S., Kakkar, V.: Modular adder designs using optimal reversible and fault tolerant gates in field-coupled QCA nanocomputing. Int. J. Theor. Physics 57(5), 1356–1375 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-018-3664-z
Chandra, Jangam Siva, Suresh, Kandula, Ghosh, Bahniman: Clocking Scheme Implementation for Multi-Layered Quantum Dot Cellular Automata Design. Journal of Low Power Electronics. 10(2), 272–278 (2014)
Compano R,Molenkamp L, Paul D. Roadmap for nanoelectronics. In: Future and Emerging Technologies: European Commission IST Programme; 2000.
Das, K., De, D.: QCA defect and fault analysis of diverse nanostructure for implementing logic gate. International journal of recent trends in Eng Technol 3(1), 84–97 (2010)
Du, H., et al.: Design and analysis of new fault-tolerant majority gate for quantum-dot cellular automata. J Comput Electron 15(4), 1484–1497 (2016)
Dysart TJ, M Kogge P, S Lent C. An analysis of missing cell defects in quantum-dot cellular automata, 2017.
Fam, S.R., Navimipour, N.J.: Design of a loop-based random access memory based on the nanoscale quantum dot cellular automata. Photonic Netw. Commun. 37(1), 120–130 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11107-018-0801-9
Hasani, B., Navimipour, N.J.: A new design of a carry-save adder based on quantum-dot cellular automata. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Electr. Eng. 45(3), 993–999 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40998-020-00395-5
Hashemi, S., Tehrani, M., Navi, K.: An efficient quantum-dot cellular automata full-adder. Sci. Res. Essays 7(2), 177–189 (2012)
Heikalabad, S.R.: Non-coplanar counter in quantum-dot cellular automata. European Phys. J. Plus 136(2) (2021). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01198-1
Heikalabad, R.S., Gadim, M.R.: Design of improved arithmetic logic unit in quantum-dot cellular automata. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57(6), 1733–1747 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-018-3699-1
Heikalabad, S.R., Salimzadeh, F., Barughi, Y.Z.: A unique three-layer full adder in quantum-dot cellular automata. Comput. Electr. Eng. 86, 106735 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2020.106735
Hosseinzadeh, H.: Saeed Rasouli Heikalabad. A Novel Fault Tolerant Majority Gate in Quantum-Dot Cellular Automata to Create a Revolution in Design of Fault Tolerant Nanostructures, with Physical Verification, Microelectronic Engineering 192, 52–60 (2018)
Huakun Du, Hongjun Lv, Yongqiang Zhang, Fei Peng, Guangjun Xie. "Design and analysis of new fault-tolerant majority gate for quantum-dot cellular automata," J Comput Electron, 2016.
Huang, J., Momenzadeh, M., Lombardi, F.: On the tolerance to manufacturing defects in molecular QCA tiles for processing-by-wire. J. Electron. Test. 23(2–3), 163–174 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10836-006-0548-6
Karim, F., Walus, K.: Efficient simulation of correlated dynamics in quantum-dot cellular automata (QCA). IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 13(2), 294–307 (2014)
Kumar, D., Mitra, D.: Design of a practical fault-tolerant adder in quantumdot cellular automata. Microelectron. J. 53, 90–104 (2016)
Lent, C.S., Tougaw, P.D.: A device architecture for computing with quantum dots. Proc IEEE 85(4), 541–557 (1997)
Lent, C.S., Tougaw, P.D., Porod, W., Bernstein, G.H.: Quantum cellular automata. Nanotechnology 4, 49–57 (1993)
Meirav, U., Kastner, M.A., Wind, S.J.: Singleelectron charging and periodic conductance resonances in GaAs nanostructures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 65(6), 771–774 (1990)
Moghimizadeh T., Mosleh M., A novel design of fault tolerant RAM cell in quantum‑dot cellular automata with physical verification, The Journal of Supercomputing, 2019.
Mohammadi, M., Gorigin, S.: An efficient design of full adder in quantum-dot cellular automata technology. Microelectron. J. 50, 38–43 (2016)
Momenzadeh M, Ottavi M, Lombardi F. Modeling QCA defects at molecular-level in combinational circuits. In: 20th IEEE International Symposium on Defect and Fault Tolerance in VLSI Systems, 2005. DFT 2005.
Norouzi, A., Heikalabad, S.R.: Design of reversible parity generator and checker for the implementation of nano-communication systems in quantum-dot cellular automata. Photonic Netw. Commun. 38(2):231–243 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11107-019-00850-2
Norouzi, M., Heikalabad, S.R., Salimzadeh F.: A reversible ALU using HNG and Ferdkin gates in QCA nanotechnology. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 48(8), 1291–1303 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/cta.2799
Nuriddin S., Jun-C. j., A novel controllable inverter and adder/subtractor in quantum-dot cellular automata using cell interaction based XOR gate, Microelectronic Engineering, Vol. 222, 2020, 111197.
Rahimpour Gadim, M., Jafari Navimipour, N.: A new three-level fault tolerance arithmetic and logic unit based on quantum dot cellular automata. Microsyst. Technol. 24(2), 1295–1305 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-017-3502-x
Rahmani, Y., Heikalabad, S.R., Mosleh, M.: Efficient structures for fault-tolerant majority gate in quantum-dot cellular automata. Opt. Quant. Electron. 53, 45 (2021)
Raj, M., Ahmed, S., Gopalakrishnan, L.: Subtractor circuits using different wire crossing techniques in quantum-dot cellular automata. J Nanophotonics 14(2), 1 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JNP.14.026007
Rasouli Heikalabad, S., Ahmadi, R., Salimzadeh, F.: Introducing a full-adder structure for finite field in QCA. ECS J. Solid State. Sci. Technol. 10(6), 063006 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1149/2162-8777/ac08d9
Reed, M.A., Randall, J.N., Aggarwal, R.J., Matyi, R.J., Moore, T.M., Wetsel, A.E.: Observation of discrete electronic states in a zero-dimensional semiconductor nanostructure. Phys. Rev. Lett. 60, 535–539 (1988)
Roohi, A., Sayedsalehi, S., Khademolhosseini, H., Navi, K.: Design and evaluation of a reconfigurable fault tolerant quantum-dot cellular automata gate. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 10, 380–388 (2013)
Roohi, A., DeMara, R.F., Khoshavi, N.: Design and evaluation of an ultra-area-efficient faulttolerant QCA full adder. Microelectron. J. 46(6), 531–542 (2015)
Safoev, N., Ahmed, S., Tashev, K., Naz, S.F.: Design of fault tolerant bifunctional parity generator and scalable code converters based on QCA technology. Int. J. Inf. Tecnol. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-021-00730-x
Salimzadeh, F., Heikalabad, S.R.: Design of a novel reversible structure for full adder/subtractor in quantum-dot cellular automata. Phys. B: Condens. Matter 556, 163–169 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2018.12.028
Salimzadeh, F., Heikalabad, S.R.: A full adder structure with a unique XNOR gate based on Coulomb interaction in QCA nanotechnology. Opt. Quantum Electron. 53(8) (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-021-03127-z
Salimzadeh, F., Safarpoor, E., Rasouli Heikalabad, S.: Designing and implementing a fault-tolerant priority encoder in QCA nanotechnology. ECS J. Solid. State Sci. Technol. 10(6), 063004 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1149/2162-8777/ac0118
Sen, B., Rajoria, A., Sikdar, B.K.: Design of Efficient full adder in quantum-dot cellular automata. Sci. World J. 2013, 10–25 (2013)
Sen, B., et al.: Modular Design of testable reversible ALU by QCA multiplexer with increase in programmability. Microelectron. J (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mejo.2014.08.012i
Sen, B., Sahu, Y., Mukherjee, R., Nath, R.K., Sikdar, B.K.: On the reliability of majority logic structure in quantum-dot cellular automata. Microelectron. J. 47, 7–18 (2016a)
Sen, B., Dutta, M., Mukherjee, R., et al.: Towards the design of hybrid QCA tiles targeting high fault tolerance. J. Comput. Electron. 15(2), 429–445 (2016b)
Sun, M., Lv, H., Zhang, Y., Xie, G.: The Fundamental Primitives with Fault-Tolerance in Quantum-Dot Cellular Automata. J. Electron. Test. 34(2), 109–122 (2018)
Toth, G., Lent, C.S.: Quasiadiabatic switching for metal-island quantum-dot cellular automata. J Appl Phys. 85(5), 2977–2984 (1999)
Tougaw, P.D., Lent, C.S.: Logical devices implemented using quantum cellular automata. J Appl Phys 75(3), 1818–1825 (1994)
Walus, K., et al.: QCADesigner: a rapid design and simulation tool for quantum-dot cellular automata. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol 3(1), 26–31 (2004)
Wilson, M, Kannangara, K, Smith, G, Simmons, M, Raquse, “B: Nanotechnology: basic science and emerging technologies. Chapman and Hall, London”, 2002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahmani, Y., Heikalabad, S.R. & Mosleh, M. Design of a new multiplexer structure based on a new fault-tolerant majority gate in quantum-dot cellular automata. Opt Quant Electron 53, 539 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-021-03179-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-021-03179-1