Abstract
We explore the topological behavior of a two-dimensional honeycomb photonic crystal (2D HPC) based on the presence of double Dirac-cone connected the orbitals \(p\) and \(d\), due to the \(C_{6}\) point group symmetry. Removing the four-fold degeneracy between the bands at the Dirac point can be achieved by introducing three small dielectric rods near the bigger ones to realize the perturbed PCs with the \(C_{3}\) point group symmetry with different topological features. By proposing the unique structure involving two PCs with different topological effects, one may study the one-way light distribution along the local boundary in spite of the defects, cavities, and disorders. Moreover, we investigate the variation of the transmitted intensity values under different defect conditions and realize that the size, location and material type affect the transmitted light. In the other words, tunable intensity of the edge states can be achieved through adjusting the defects such that by decreasing the radius of rods, the intensity of the edge states can be decreased or by increasing their distance from the unit cell center, the intensity will be decreased too. Finally, topological rhombic resonator enables unidirectional filtering of guided mode. The fact that different light manipulation scenarios can be realized provides a unique aspect for topological photonic insulators.





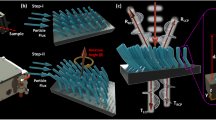
source along the interface of two types of HPCs; b–e helical edge state distributions at the interface, Z shape, against the cavity, Ag rod and Al blocks, respectively. Yellow star indicates the point-like source at the interface; f the intensity of the edge states versus frequency for different cases: without defect, cavity, Al and Ag defects



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandres, M.A., Rechtsman, M.C., Segev, M.: Topological photonic quasicrystals: fractal topological spectrum and protected transport. Phys. Rev. X 6, 011016 (2016)
Bansil, A., Lin, H., Das, T.: Colloquium: topological band theory. Rev. Mod. Phys. 88(2), 1–16 (2016)
Barik, S., Miyake, H., DeGottardi, W., Waks, E., Hafezi, M.: Two-dimensionally confined topological edge states in photonic crystals. New J. Phys. 18, 113013 (2016)
Barik, S., et al.: A topological quantum optics interface. Science 359, 666–668 (2018)
Chen, W.J., Jiang, S.J., Chen, X.D., Zhu, B., Zhou, L., Dong, J.W., Chan, C.T.: Experimental realization of photonic topological insulator in a uniaxial metacrystal waveguide. Nat. Commun. 5, 1–7 (2014)
Estep, N.A., Sounas, D.L., Soric, J., Alù, A.: Nonreciprocity and magnetic-free isolation based on optomechanical interactions. Nat. Phys. 10, 923–927 (2014)
Fan, H., Xia, B., Tong, L., Zheng, S., Yu, D.: Elastic higher-order topological insulator with topologically protected corner states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 122, 204301 (2019)
Fang, K., Yu, Z., Fan, S.: Realizing effective magnetic field for photons by controlling the phase of dynamic modulation. Nat. Photonics 6, 782–787 (2012)
Hafezi, M., Demler, E.A., Lukin, M.D., Taylor, J.M.: Robust optical delay lines with topological protection. Nat. Phys. 7, 907–912 (2011)
Hafezi, M., Mittal, S., Fan, J., Migdall, A., Taylor, J.M.: Imaging topological edge states in silicon photonics. Nat. Photonics 7, 1001–1005 (2013)
Hajivandi, J., Kurt, H.: Topological photonic states and directional emission of the light exiting from the photonic topological structure composed of two dimensional Honeycomb photonic crystals with different point group symmetries, submitted in JOURNAL OF OPTICS, OPTI-D-20-00101 (2020)
Hajivandi, J., Kurt, H.: Robust transport of the edge modes along the photonic topological interfaces of different configurations. Phys. B Condens. Matter. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2020.412550(2020)
Hajivandi, J., Kurt, H.: Topological phase transition of the centered rectangular photonic lattice, arXiv:2005.11916 [physics.app-ph] (2020)
Hajivandi, J., Kaya, E., Edwards G., Kurt, H.: Simulating topological robustness of Fano resonance in rotated Honeycomb photonic crystals, submitted in PNFA, PNFA-D-20-00069 (2020)
Haldane, F.D., Raghu, S.: Possible realization of directional optical waveguides in photonic crystals with broken Time-Reversal symmetry. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 013904 (2008)
Hasan, M.Z., Kane, C.L.: Topological insulators. Rev. Mod. Phys. 82(4), 3045 (2010)
He, C., Sun, X.C., Liu, X.P., Lu, M.H., Chen, Y., Feng, L., Chen, Y.F.: Photonic topological insulator with broken time-reversal symmetry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 113, 4924–4928 (2016)
Huo, S.Y., Chen, J.J., Feng, L.Y., Huang, H.B.: Pseudospins and topological edge states for fundamental antisymmetric Lamb modes in snowflake like phononic crystal slabs. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 146, 729–735 (2019)
Lumerical Inc. https://www.lumerical.com/tcad-pucts/fdtd/
Johnson, P.B., Christy, R.W.: Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys. Rev. B 6, 4370–4379 (1972)
Johnson, S.G., Joannopoulos, J.D.: Block-iterative frequency-domain methods for Maxwell’s equations in a planewave, basis. Opt. Express 8, 173–190 (2001)
Kane, C.L., Mele, E.J.: Quantum spin Hall effect in graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95(22), 226801 (2005)
Kapit, E., Hafezi, M., Simon, S.H.: Induced self-stabilization in fractional quantum Hall states of light. Phys. Rev. X 4(3), 031039 (2014)
Khanikaev, A.B., Mousavi, S.H., Tse, W.K., Kargarian, M., MacDonald, A.H., Shvets, G.: Photonic topological insulators. Nat. Mater. 12, 233–239 (2013)
Leykam, D., Chong, Y.D.: Edge solitons in nonlinear-photonic topological insulators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 143901 (2016)
Leykam, D., Rechtsman, M.C., Chong, Y.D.: Anomalous topological phases and unpaired Dirac cones in photonic floquet topological insulators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 013902 (2016)
Liu, C.X., Zhang, S.C., Qi, X.L.: The quantum anomalous Hall effect. Annu. Rev. Condens. Matter Phys. 7, 301–321 (2016)
Lu, L., Joannopoulos, J.D., Soljačić, M.: Topological photonics. Nat. Photon 8, 821–829 (2014)
Ma, T., Shvets, G.: All-Si valley-Hall photonic topological insulator. New J. Phys. 18, 025012 (2016)
Noh, J., Benalcazar, W.A., Huang, S., Collins, M.J., Chen, K., Hughes, T.L., Rechtsman, M.C.: Topological protection of photonic mid-gap defect modes. Nat. Photonics 12, 408–415 (2018)
Palik, E.D.: Handbook of optical constants of solids. Academic Press, Orlando (1985)
Qi, X.L., Zhang, S.C.: Topological insulators and superconductors. Rev. Mod. Phys. 83(4), 1057 (2011)
Raghu, S., Haldane, F.D.M.: Analogs of quantum Hall effect edge states in photonic crystals. Phys. Rev. A 78, 033834 (2018)
Rechtsman, M.C., Plotnik, Y., Zeuner, J.M., Song, D., Chen, Z., Szameit, A., Segev, M.: Topological creation and destruction of edge states in photonic graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 103901 (2013)
Rechtsman, M.C., Zeuner, J.M., Plotnik, Y., Lumer, Y., Podolsky, D., Dreisow, F., Nolte, S., Segev, M., Szameit, A.: Photonic floquet topological insulators. Nature (London) 496, 196–200 (2013)
Sakoda, K.: Dirac cone in two and three-dimensional metamaterials. Opt. Express 20, 3898–3917 (2012)
Song, Z., Liu, H.J., Huang, N., Wang, Z.: Prediction of two-dimensional organic topological insulator in metal-DCB lattices. Appl. Opt 57, 29 (2018)
Sounas, D.L., Caloz, C., Alu, A.: Magnetic-free non-reciprocity based on staggered commutation. Nat. Commun. 4, 2407 (2013)
Sun, X.C., He, C., Liu, X.P., Lu, M.H., Zhu, S.N., Chen, Y.F.: Photonics meets topology. Prog. Quantum Electron 55, 52–73 (2017)
Umucalilar, R.O., Carusotto, I.: Artificial gauge field for photons in coupled cavity arrays. Phys. Rev. A 84, 043804 (2011)
Wang, Z., Chong, Y.D., Joannopoulos, J.D., Soljacic, M.: Reflection-free one-way edge modes in a gyromagnetic photonic crystal. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 013905 (2008)
Wang, Z., Chong, Y., Joannopoulos, J.D., Soljacic, M.: Observation of unidirectional backscattering-immune topological electromagnetic states. Nature (London) 461, 772–775 (2009)
Wang, H.X., Xu, L., Chen, H.Y., Jiang, J.H.: Three-dimensional photonic Dirac points stabilized by point group symmetry. Phys. Rev. B 93, 235155 (2016)
Wang, H.X., Chen, Y., Hang, Z.H., Kee, H.Y., Jiang, J.H.: Type-II. Dirac photons. NPJ Quantum Mater 2, 54 (2017)
Wu, L.H., Hu, X.: Scheme for achieving a topological photonic crystal by using dielectric material. Phys. Rev. Lett. 114, 223901 (2015)
Xia, B., Fan, H., Liu, T.: Topologically protected edge states of phoxonic crystals. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 155, 197–205 (2019)
Xie, B.Y., Wang, H.F., Zhu, X.Y., Lu, M.H., Wang, Z.D., Chen, Y.F.: Feature issue introduction: topological photonics and materials. Opt. Express 26, 19 (2018)
Xu, L., Wang, H.X., Xu, Y.D., Chen, H.Y., Jiang, J.H.: Accidental degeneracy in photonic bands and topological phase transitions in two-dimensional core-shell dielectric photonic crystals. Opt. Express 24, 18059 (2016)
Yang, Y., Xu, Y.F., Xu, T., Wang, H.X., Jiang, J.H., Hu, X., Hang, Z.H.: Visualization of unidirectional optical waveguide using topological photonic crystals made of dielectric material, arXiv:1610.07780
Zhu, X., Wang, H.X., Xu, C., Lai, Y., Jiang, J.H., John, S.: Topological transitions in continuously deformed photonic crystals. J. Phys. Rev. B 97, 085148 (2018)
Acknowledgements
H. Kurt acknowledges partial support of the Turkish Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hajivandi, J., Pakarzadeh, H. & Kurt, H. Intensity tuning of the edge states in the imperfect topological waveguides based on the photonic crystals with the \(C_{3}\) point group symmetry. Opt Quant Electron 53, 102 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-021-02745-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-021-02745-x