Abstract
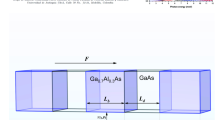
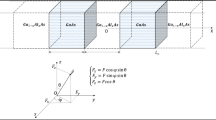
We have investigated simultaneous effects of pressure, temperature, impurity location, Rashba and Dresselhaus spin–orbit interaction and magnetic field on THG of realized GaAs/Al0.5Ga0.5As pyramid quantum dot with considering the wet layer. For this purpose, we have calculated the energy levels and wave function of one electron that is confined in constant potential, in presence of impurity, magnetic field, Rashba and Dresselhous SOI in various temperatures, pressure and impurity location in effective mass approximation by FEM. In the following, we have presented the effect of magnetic field, Rashba and Dresselhous SOI, temperature, pressure and impurity location on THG in various conditions. Results show that: (1) THG increases by increasing the magnetic field and the distance between the peaks decrease. Also, the peak corresponding to the E21 transition has a blue shift and the peaks corresponding to the E31/2 and E41/3 transitions have a red shift. (2) THG decreases and shifts to higher energies and has a small blue shift by augment of temperature. (3) THG enhances and all of peaks have a red shift by increment of pressure. (4) THG has a minimum around z0 = 4 nm in all magnetic field, temperature and pressure cases. Also, all of peaks have a blue shift by augment of z0 until z0 = 4 nm and then have a red shit by increasing the z0.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahramiyan, H., Servatkhah, M.: Second and third harmonic generation of a hexagonal pyramid quantum dot: impurity position effect. Opt. Quant. Electron. 47, 2747–2758 (2015)
Baskoutas, S., Paspalakis, E., Terzis, A.F.: Electronic structure and nonlinear optical rectification in a quantum dot: effects of impurities and external electric field. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 19, 395024–395036 (2007)
Boyd, R.W.: Nonlinear Optics, 2nd edn. Academic Press (2003)
Bychkov, Y.A., Rashba, E.I.: Oscillatory effects and the magnetic susceptibility of carriers in inversion layers. J. Phys. C 17, 6039–6045 (1984)
Davies, J.H.: The Physics of Low-Dimensional Semiconductors: An Introduction. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1998)
Dresselhaus, G.: Spin–orbit coupling effects in zinc blende structures. Phys. Rev. 100, 580–586 (1955)
Dyakonov, M.I., Kachorovskii, V.Y.: Relaxation de spin d’électrons bidimensionnels dans les semiconducteurs sans centre d’inversion. Fiz. Tekh. Poluprovodn. (S-Peterburg) 20, 178–181 (1986)
Gharaati, A.: Lande g-factor in semiconductor cylinder quantum dots under magnetic fields and spin-orbit interaction. Solid State Commun. 258, 17–20 (2017)
Hassanabadi, H., Rahimov, H., Lu, L., Wang, C.: Nonlinear optical properties of a three-electron quantum dot with account of the Rashba spin–orbit interaction. J. Lumin. 132, 1095–1100 (2012)
Hirsch, J.E.: Spin hall effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 1834–1837 (1999)
Karaaslan, Y., Gisi, B., Sakiroglu, S., Kasapoglu, E., Sari, H., Sokmen, I.: Rashba spin-orbit coupling effects on the optical properties of double quantum wire under magnetic field. Superlattices Microstruct. 93, 32–39 (2016)
Karabulut, I., Safak, H., Tomak, M.: Excitonic effects on the nonlinear optical properties of small quantum dots. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 41, 155104–155111 (2008)
Karimi, M.J., Rezaei, G., Nazari, M.: Linear and nonlinear optical properties of multilayered spherical quantum dots: effects of geometrical size, hydrogenic impurity, hydrostatic pressure and temperature. J. Lumin. 145, 555–560 (2014)
Khordad, R.: Spin-orbit interaction in a quantum pseudodot: pressure effect. J. Comput. Electron. 13, 383–393 (2014)
Khordad, R.: Bound polaron in a quantum pseudodot under Rashba effect. Physica E 69, 249–252 (2015)
Khordad, R.: Optical properties of wedge-shaped quantum dots under Rashba spin–orbit interaction. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 31, 1750055–1750065 (2017)
Khordad, R., Bahramiyan, H.: Electron-phonon interaction effect on the energy levels and diamagnetic susceptibility of quantum wires: parallelogram and triangle cross section. J. Appl. Phys. 115, 124314–124321 (2014a)
Khordad, R., Bahramiyan, H.: Electronic and optical properties of a lens shaped quantum dot under magnetic field: second and third-harmonic generation. Commun. Theor. Phys. 62, 283–289 (2014b)
Khordad, R., Bahramiyan, H.: Effect of cross sectional-shape on electronic states in quantum wires with and without impurity: Arnoldi algorithm. Superlattices Microstruct. 88, 651–661 (2015)
Khordad, R., Mirhosseini, B., Bahramiyan, H.: Effect of electron–phonon interaction on the thirdharmonic generation in a quantum pseudodot. Opt. Quant. Electron. 48, 122–133 (2016)
Knap, W., Skierbiszewski, C., Zduniak, A., Litwin-Staszewska, E., Bertho, D., Kobbi, F., Robert, J.L., Pikus, G.E., Pikus, F.G., Iordanskii, S.V., Mosser, V., Zekentes, K., Lyanda-Geller, YuB: Weak antilocalization and spin precession in quantum wells. Phys. Rev. B 53, 3912–3924 (1996)
Li, B., Guo, K.X., Liu, Z.L., Zheng, Y.B.: Nonlinear optical rectification in parabolic quantum dots in the presence of electric and magnetic fields. Phys. Lett. A 372, 1337–1340 (2008)
Miller, J.B., Zumbuhl, D.M., Marcus, C.M., Lyanda-Geller, Y.B., Goldhaber-Gordon, D., Campman, K., Gossard, A.C.: Gate-controlled spin–orbit quantum interference effects in lateral transport. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 76807–76810 (2003)
Mokhtari, P., Rezaei, G., Zamani, A.: Rashba and Dresselhaus spin–orbit interactions effects on electronic features of a two dimensional elliptic quantum dot. Superlattices Microstruct. 106, 1–7 (2017)
Okada, K.: A theory of dielectric fluid films between nanostructures. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 112, 32–41 (2017)
Rashba, E.I.: Properties of semiconductors with an extremum loop.1. Cyclotron and combinational resonance in a magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the loop. 2. Sov. Phys. Solid State Phys. 2, 1109–1122 (1960a)
Rashba, E.I.: Properties of semiconductors with an extremum loop.1. Cyclotron and combinational resonance in a magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the loop. Fiz. Tverd. Tela (Leningrad) 2, 1224–1238 (1960b)
Rezaei, G., Vaseghi, B., Khordad, R., Azadi Kenary, H.: Optical rectification coefficient of a two-dimensional quantum pseudodot system. Physica E 43, 1853–1856 (2011)
Shakouri, Kh, Szafran, B., Esmaeilzadeh, M., Peeters, F.M.: Effective spin-orbit interaction Hamiltonian for quasi-one-dimensional quantum rings. Phys. Rev. B 85, 165314–165321 (2012)
Sheng, F.J., Zheng, L.: Spin–orbit splitting in semiconductor quantum dots with a two-dimensional ring model. Chin. Phys. Lett. 26, 080305–080308 (2009)
Sousa, R.D., Das Sarma, S.: Theory of nuclear-induced spectral diffusion: spin decoherence of phosphorus donors in Si and GaAs quantum dots. Phys. Rev B 68, 155330–155342 (2003)
Wierzbicki, M.: Thermoelectric properties of magnetic configurations of graphene-like nanoribbons in the presence of Rashba and spin–orbit interactions. Physica E 87, 220–227 (2017)
Wolf, S.A., Chtchelkanova, A.Y., Treger, D.M.: Spintronics—a retrospective and perspective. IBM J. Res. Dev. 50, 101–110 (2006)
Zamani, A., Azargoshasb, T., Niknam, E.: Second and third harmonic generations of a quantum ring with Rashba and Dresselhaus spin-orbit couplings: temperature and Zeeman effects. Physica B 523, 85–91 (2017)
Acknowledgement
This work is partially supported by the AI University Research Centre (AI-URC) through XJTLU Key Programme Special Fund (KSF-P-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Avazzadeh, Z., Bahramiyan, H. Simultaneous effects of pressure, temperature, impurity location, SOI and magnetic field on THG of a pyramid quantum dot. Opt Quant Electron 52, 179 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-020-2230-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-020-2230-0