Abstract
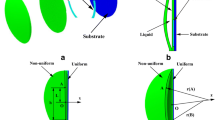
For a liquid progressive multifocal lens with an elastic membrane deformed by liquid pressure, to realize a reasonably power distribution, an asymmetric deformation characteristics of membrane surface is needed. Based on the asymmetric freeform surface structure, this paper proposed liquid progressive multifocal lenses focused by liquid with non-uniform thickness membranes and different boundary constraints. The structure and mathematical model of power distribution for the lens are introduced. The membrane deformation and the corresponding power distribution of the lenses with asymmetric freeform surface are predicted and compared under uniform pressure load and different boundary constraints. A membrane deformation testing system is constructed to analyze the power distribution of fabricated lenses through measuring the surface sag using laser displacement sensor and corresponding optical power distribution can be calculated. Experimental results show that the liquid lenses can realize as liquid progressive multifocal lenses after liquid accommodation, meanwhile, the trends of power distribution of the lenses generally agree well with simulations.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi, S.T., Son, B.S., Seo, G.W., et al.: Opto-mechanical analysis of nonlinear elastomer membrane deformation under hydraulic pressure for variable-focus liquid-filled microlenses. Opt. Express 22, 6133–6146 (2014)
Ding, Z., Wang, C., Zhixiong, H., et al.: Surface profiling of an aspherical liquid lens with a varied thickness membrane. Opt. Express 25, 3122–3132 (2017)
Fang, C., Dai, B., Zhuo, R., et al.: Focal-length-tunable elastomer-based liquid-filled plano-convex mini lens. Opt. Lett. 41, 404–407 (2016)
Flores-Bustamante, M.C., Rosete-Aguilar, M., Calixto, S.: Mechanical and optical behavior of a tunable liquid lens using a variable cross section membrane. Modeling results. Proc. SPIE 9699, 969908 (2016)
Hasan, N., Kim, H., Mastrangelo, C.H.: Large aperture tunable-focus liquid lens using shape memory alloy spring. Opt. Express 24, 13334–13342 (2016)
Huang, H., Wei, K., Wang, Q., et al.: Improved optical resolution for elastomer-liquid lens at high dioptre using varied thickness membrane. Proc. SPIE 9705, 970504 (2016)
Iimura, Y., Onoe, H., Teshima, T., et al.: Liquid-filled tunable lenticular lens. J. Micromech. Microeng. 25, 035030 (2015)
Lan, G., Mauger, T.F., Li, G.: Design of high-performance adaptive objective lens with large optical depth scanning range for ultrabroad near infrared microscopic imaging. Biomed. Opt. Express 6, 3362–3377 (2015)
Li, Z., Li, D.: Surface analysis and evaluation of progressive addition lens. Proc. SPIE 10154, 101540M (2016)
Liang, D., Liang, D.T., Wang, X.Y., et al.: Flexible fludic lens with polymer membrane and multi-flow structure. Opt. Commun. 421, 7–13 (2018)
Lin, W.-C., Chenb, C.-C.A., Huang, K.-C.: Design and fabrication of soft zoom lens. Proc. SPIE 7061, 70610W (2008)
Malyuk, AYu., Ivanova, N.A.: Varifocal liquid lens actuated by laser-induced thermal Marangoni forces. Appl. Phys. Lett. 112, 103701 (2018)
Pokorný, P., Šmejkal, F., Kulmon, P., et al.: Calculation of nonlinearly deformed membrane shape of liquid lens caused by uniform pressure. Appl. Opt. 56, 5939–5947 (2017)
Santiago-Alvarado, A., González-García, J., Itubide-Jiménez, F., et al.: Simulating the functioning of variable focus length liquid-filled lenses using the finite element method (FEM). Optik 124, 1003–1010 (2013)
Shaw, D., Cuo, S.P.: A study of the sensor shape of a hemispherical electronic eye variable focus camera lens. Opt. Rev. 17, 541–548 (2010)
Shaw, D., Lin, C.-W.: Design and analysis of an asymmetrical liquid-filled lens. Opt. Eng. 46, 123002 (2007)
Shimoda, M., Yamane, K.: A numerical form-finding method for the minimal surface of membrane structures. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 51, 333–345 (2015)
Son, H.-M., Kim, M.Y., Lee, Y.-J.: Tunable-focus liquid lens system controlled by antagonistic winding-type SMA actuator. Opt. Express 17, 14350–14399 (2009)
Steele, T., McLoughlin, H., Payne, D.: Progressive addition power lenses. U.S. Patent, 6776486 B2 (2004)
Strasky, J., Juchelková, P., Kaláb, P., et al.: Roofs of prestressed concrete membranes. Struct. Concr. 18, 5–18 (2017)
Wang, L., Zhang, Q., Yang, B.: Free form design for single layer shell structures. In: PIC-2010, pp. 1062–1066. IEEE (2010)
Wang, L., Oku, H., Ishikawa, M.: Variable-focus lens with 30 mm optical aperture based on liquid-membrane-liquid structure. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 131111 (2013)
Wang, L., Oku, H., Ishikawa, M.: An improved low-optical-power variable focus lens with a large aperture. Opt. Express 22, 19448–19456 (2014)
Wei, K., Huang, H., Wang, Q., et al.: Focus-tunable liquid lens with an aspherical membrane for improved central and peripheral resolutions at high diopters. Opt. Express 24, 3929–3939 (2016)
Zhao, P., Ataman, Ç., Zappe, H.: An endoscopic microscope with liquid-tunable aspheric lenses for continuous zoom capability. Proc. SPIE 9130, 913004 (2014)
Zhao, P., Ataman, Ç., Zappe, H.: Spherical aberration free liquid-filled tunable lens with variable thickness membrane. Opt. Express 23, 21264–21278 (2015)
Zhao, P., Ataman, Ç., Zappe, H.: Gravity-immune liquid-filled tunable lens with reduced spherical aberration. Appl. Opt. 55, 7816–7823 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Grant No. 51175101).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, W., Li, S. Liquid progressive multifocal lenses based on asymmetrical freeform surface structure using non-uniform thickness membranes. Opt Quant Electron 52, 143 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-020-02269-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-020-02269-w