Abstract
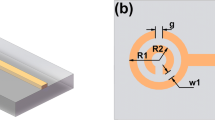
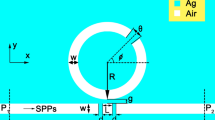
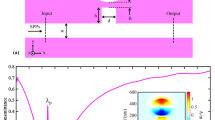
In this work, a configuration of nano plasmonic switch is proposed and investigated. The structure is comprised of the combination of split square ring and straight waveguides. Simulations are done based on Finite-Difference-Time Domain method. The structure is based on metal-insulator-metal configuration. Split square ring and straight waveguides are consisted of air, which are situated in a silver background. The proposed switch can confine light to sub-wavelength dimensions (on the order of nano meter); therefore it can be used in highly integrated optical circuits. The split square ring structure can operate both directly or reversely based on the split position. The transmitted powers in different cases of split square switch are acceptable and higher than 0.6. Therefore, the proposed switch is an appropriate candidate for highly integrated optical communication systems.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahador, M., et al.: A circuit model for analysis of metal–insulator–metal plasmonic complementary split-ring resonators. J. Light. Technol. 32, 2659–2665 (2014)
Cai, W., et al.: Elements for plasmonic nanocircuits with three-dimensional slot waveguides. Adv. Mater. 22, 5120–5124 (2010)
Chen, J., et al.: Tunable resonances in the plasmonic split-ring resonator. IEEE Photonics J. 6, 1–6 (2014)
Chen, J., et al.: High-quality temperature sensor based on the plasmonic resonant absorber. Plasmonics 14, 1–5 (2018)
Choo, H., et al.: Nanofocusing in a metalinsulator- metal gap plasmon waveguide with a three-dimensional linear taper. Nat. Photon. 6, 838–844 (2012)
Eftekharinia, B., et al.: Design of a slit-groove coupler for unidirectional excitation of the guided surface plasmon polaritons through a plasmonic slot waveguide. Plasmonics 12, 131–138 (2017)
Eshaghian, A., et al.: Transmission enhancement of sharply bent nanoplasmonic slot waveguides. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 31, 458–463 (2014)
Farmani, A., et al.: Design of a tunable graphene plasmonic-on-white graphene switch at infrared range. Superlattice Microstruct. 112, 404–414 (2017)
Farmani, A., et al.: Broadly tunable and bidirectional terahertz graphene plasmonic switch based on enhanced Goos–Hänchen effect. Appl. Surf. Sci. 453, 358–364 (2018)
Foroutana, S., et al.: All-optical switching in metal nanoparticles plasmonic waveguide using EIT phenomenon. Optik 132, 291–298 (2017)
Ghadrdan, M., et al.: Design and implementation of optical switches based on nonlinear plasmonic ring resonators: circular, square and octagon. Photonics Nanostruct. Fundam. Appl. 29, 15–21 (2018)
Giannini, V., et al.: Plasmonic nanoantennas: fundamentals and their use in controlling the radiative properties of nanoemitters. Chem. Rev. 111, 3888–3912 (2011)
Gramotnev, D.K., et al.: Plasmonics beyond the diffraction limit. Nat. Photonics 4, 83–91 (2010)
Halpern, R., et al.: Lithographically patterned electrodeposition of gold, silver, and nickel nanoring arrays with widely tunable near-infrared plasmonic resonances. ACS Nano 7, 1755–1762 (2013)
Han, Z., et al.: Surface plasmon Bragg gratings formed in metal-insulator-metal waveguides. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 19, 91–93 (2007)
Janipour, M., et al.: A novel adjustable plasmonic filter realization by split mode ring resonators. JEMAA 5, 405–414 (2013)
Lehr, D., et al.: Plasmonic properties of aluminum nanorings generated by double patterning. Opt. Lett. 37, 157–159 (2012)
Liu, D.: High sensitivity and large field enhancement of symmetry broken Au nanorings: effect of multipolar plasmon resonance and propagation. Opt. Express 17, 2906–2917 (2009)
Luo, X., et al.: Plasmonic filter using metal-insulator-metal waveguide with phase shifts and its transmission characteristics. Plasmonics 9, 887–892 (2014)
Maier, S.A.: Plasmonics Fundamentals and Applications. Springer, Bath (2007)
Mei, X., et al.: A sub-wavelength electro-optic switch based on plasmonic T-shaped waveguide. Plasmonics 6, 613–618 (2011)
Nurmohammadi, T., et al.: Ultra-fast all-optical plasmonic switching in near infra-red spectrum using a Kerr nonlinear ring resonator. Opt. Commun. 410, 142–147 (2018)
Pandesh, S., et al.: The sub-wavelength plasmonic nano-antenna based on cross structure. Optik 127, 3770–3774 (2016)
Rafiee, E., et al.: Coupling coefficient increment and free spectral range decrement by proper design of microring resonator parameters. Opt. Eng. 53, 123108 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1117/1.OE.53.12.123108
Rafiee, E., et al.: Investigating the effects of structural parameters on the optical characteristics of add-drop filters. Optik 127, 1690–1694 (2016)
Rafiee, E., et al.: Design and simulation of a novel nano-plasmonic split-ring resonator filter. J. Electromagn. Wave 32, 1925–1938 (2018)
Shahamat, Y., et al.: Designing ultra-compact high efficiency electro-optical plasmonic switches by using of nanocavity reflectors. Opt. Commun. 410, 25–29 (2018)
Vlădescu, E., et al.: Reconfigurable plasmonic logic gates. Plasmonics 13, 1–7 (2018)
Wang, T.B., et al.: The transmission characteristics of surface plasmon polaritons in ring resonator. Opt. Express 17, 24096–24101 (2009)
Zarrabi, F.B., et al.: Cross-slot nano-antenna with graphene coat for bio-sensing application. Opt. Commun. 371, 34–39 (2016)
Zarrabi, F.B., et al.: Investigated the Fano resonance in the nano ring arrangement. Optik 138, 80–86 (2017)
Zentgraf, T., et al.: Babinet’s principle for optical frequency metamaterials and nanoantennas. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 76, 033407-1–033407-4 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Negahdari, R., Rafiee, E. & Emami, F. Realization of all-optical plasmonic MIM split square ring resonator switch. Opt Quant Electron 51, 235 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-019-1924-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-019-1924-7