Abstract
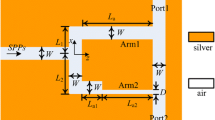
An ultra-short and broadband polarization splitter based on PCF and metal surface plasmons resonance is proposed by designing a new structure and filling gold wire into certain air holes. The introducing of gold wire aims to couple with the basic modes. Then high birefringence is obtained to improve the splitter’s performances including length, bandwidth and maximal extinction ratio. The numerical results demonstrate that the splitter can be the shortest length of 100 μm (to our knowledge) and the broad bandwidth is 470 nm simultaneously. And when the splitter’s length is set as 104 μm, the widest bandwidth reaches the maximum 575 nm (to our knowledge) which covers almost all the E, S, C, L, and U communication band. In addition, the structure is relatively simple, so it is easy to fabricate using available methods. These properties will help designing splitter in the optical communication and sensing system.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beltrán-Mejía, F., Chesini, G., Silvestre, E., George, A.K., Knight, J.C., Cordeiro, C.M.: Ultrahigh-birefringent squeezed lattice photonic crystal fiber with rotated elliptical air holes. Opt. Lett. 35, 544–546 (2010)
Birks, T., Knight, J., Russell, P.: Endlessly single mode photonic crystal fiber. Opt. Lett. 22, 961–963 (1997)
Chao, D., Jing, X.L., Li, S.G., Wu, J.J., Wang, Q.B.: A compact and low-loss polarization splitter based on dual-core photonic crystal fiber. Opt. Quant. Electron. 50(1–10), 255 (2018)
Florous, N., Saitoh, K., Koshiba, M.: A novel approach for designing photonic crystal fiber splitters with polarization-independent propagation characteristics. Opt. Express 13, 7365–7373 (2005)
Hameed, M.F.O., Obayya, S.S.A.: Polarization splitter based on soft glass nematic liquid crystal photonic crystal fiber. IEEE Photon. J. 1, 265–276 (2009)
Issa, N.A., van Eijkelenborg, M.A., Fellew, M., Cox, F., Henry, G., Large, M.C.J.: Fabrication and study of microstructured optical fibers with elliptical holes. Opt. Lett. 29, 1336–1338 (2004)
Jiang, H., Wang, E., Zhang, J., Hu, L., Mao, Q., Li, Q., Xie, K.: Polarization splitter based on dual-core photonic crystal fiber. Opt. Express 22, 30461–30466 (2014)
Knight, J.C., Russell, P.S.J.: Photonic crystal fibers: new ways to guide light. Science 296, 276–277 (2002)
Knight, J.C., Birks, T.A., Cregan, R.F., Russell, P.S.J., Sandro, J.P.: Large mode area photonic crystal fiber. Electron. Lett. 34, 1347–1348 (1998)
Li, J.H., Wang, J.Y., Wang, R., Liu, Y.: A novel polarization splitter based on dual-core hybrid photonic crystal fibers. Opt. Laser Technol. 43, 795–800 (2011)
Li, X.Y., Xu, Z.L., Ling, W.W., Liu, P.: Design of highly nonlinear photonic crystal fibers with attended chromatic dispersion. Appl. Opt. 53, 6682–6687 (2014)
Liu, Q., Li, S.-G., Fan, Z., Zhang, W., Zi, J., Li, H.: Numerical analysis of high extinction ratio photonic crystal fiber polarization splitter based on ZnTe glass. Opt. Fiber Technol. 21, 193–197 (2015)
Liu, Q., Li, S.-G., Wang, X.Y., Shi, M.: Theoretical simulation of a polarization splitter based on dual-core soft glass PCF with micron-scale gold wire. Chin. Phys. B. 25(1–8), 124210 (2016)
Lu, S., Li, W., Guo, H., Lu, M.: Analysis of birefringent and dispersive properties of photonic crystal fibers. Appl. Opt. 50, 5798–5802 (2011)
Malitson, I.H.: Interspecimen comparison of the refractive index of fused silica. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 55, 1205–1209 (1965)
Peng, G., Tjugiarto, T., Chu, P.: Polarisation beam splitting using twin-elliptic-core optical fibers. Electron. Lett. 26, 682–683 (1990)
Podoliak, N., Horak, P.: Dual-core optical fiber as beam splitter with arbitrary, tunable polarization-dependent transfer function. Opt. Commun. 35, 4040–4046 (2017)
Rajeswari, D., Sivanantha Raja, A., Selvendran, S.: Design and analysis of polarization splitter based on dual-core photonic crystal fiber. Optik 144, 15–21 (2017)
Reeves, W.H., Knight, J.C., Russell, P.S.J., Roberts, P.J.: Demonstration of ultra-attended dispersion in photonic crystal fibers. Opt. Express 10, 609–613 (2002)
Rosa, L., Poli, F., Foroni, M., Cucinotta, A., Selleri, S.: Polarization splitter based on a square-lattice photonic crystal fiber. Opt. Lett. 31, 441–443 (2006)
Saitoh, K., Sato, Y., Koshiba, M.: Coupling characteristics of dual-core photonic crystal fiber couplers. Opt. Express 11, 3188–3195 (2003)
Saitoh, K., Sato, Y., Koshiba, M.: Polarization splitter in three-core photonic crystal fibers”. Opt. Express 12, 3940–3946 (2004)
Sun, B., Chen, M.-Y., Zhou, J., Zhang, Y.-K.: Surface plasmon induced polarization splitting based on dual-core photonic crystal fiber with metal wire. Plasmonics 8, 1253–1258 (2013)
Suzuki, K., Kubota, H., Kawanishi, S., Tanaka, M., Fujita, M.: Optical properties of a low-loss polarization-maintaining photonic crystal fiber. Opt. Express 9, 676–680 (2001)
Tian, F., Yuan, L., Dai, Q., et al.: Fabrication technology of embedded multi-elliptical-cores hollow fiber. Sensor Lett. 10, 1391–1394 (2012)
Vial, A., Grimault, A., Macłas, D., Barchiesi, D., Chapelle, M.: Improved nalytical fit of gold dispersion: application to the modeling of extinction spectra with a finite-difference time-domain method. Phys. Rev. B 71(8), 085416 (2005)
Xu, Z., Li, X., Ling, W., Liu, P., Zhang, Z.: Design of short polarization splitter based on dual-core photonic crystal fiber with ultra-high extinction ratio. Opt. Common. 354, 314–320 (2015)
Younis, B.M., Heikal, A.M., Hameed, M.F.O., Obayya, S.S.A.: Highly wavelength-selective asymmetric dual-core liquid photonic crystal fiber polarization splitter. Opt. Soc. B. 35, 1020–1029 (2018)
Zhao, T., Lou, S.: Ultra-broadband polarization splitter based on three-core photonic crystal fiber with a modulation core. Appl. Opt. 55, 6428–6434 (2016)
Funding
The National Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61405172 and 61640408) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province, China (Grant No. F2018203346).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, XT., Hua, L., Xiong, Q. et al. Ultra-short and broadband polarization splitter based on PCF and metal surface plasmons resonance. Opt Quant Electron 51, 162 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-019-1884-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-019-1884-y