Abstract
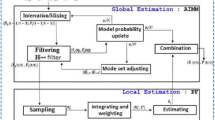
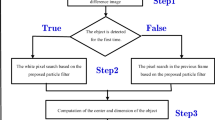
Faced with problems of low contrast, poor SNR, and relatively complicated tracking environment, stable infrared target tracking is worth researching for its many potential applications. In this paper, instead of traditional target tracking in the pixel domain, we propose a sampling importance resampling (SIR) particle filter method with indirect velocity measurements to track infrared targets in the modulation domain. The dominant amplitude modulation (AM) features used for tracking is extracted by decomposing the input image using an 18-channel Gabor filter bank followed by the application of the dominant component analysis approach. The dominant AM modulation features provide a significant partial texture characteristic of the target which can be separated from background with better discrimination. To take advantage of observed kinematics, we utilize the augmented state vector with indirect velocity information via combining the measurements of velocity in adjacent frames to the SIR particle filter framework, which weakens weights of particles with bad velocity estimates but still having association with the cluttered background or other moving objects. A dynamic template update strategy is also provided to prevent the tracker from appearance model drift. Experiments indicate that the proposed method is effective for raising the tracking accuracy compared with other tracking methods.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arulampalam, M., Maskell, S., Gordon, N., Clapp, T.: A tutorial on particle filters for online nonlinear/non-Gaussian Bayesian tracking. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 50(2), 174–188 (2002)
Asha, C.S., Narasimhadhan, A.V.: Robust infrared target tracking using discriminative and generative approaches. Infrared Phys. Technol. 85, 114–127 (2017)
Bello, J.C.F., Havlicek, J.P.: A state vector augmentation technique for incorporating indirect velocity information into the likelihood function of the sir video target tracking filter. IEEE Southwest Symposium on Image Analysis and Interpretation (SSIAI). IEEE (2016)
Comaniciu, D., Ramesh, V., Meer, P.: Kernel-based object tracking. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 25(5), 564–575 (2003)
Cui, Z., Yang, J., Jiang, S., et al.: Robust spatio-temporal context for infrared target tracking. Infrared Phys. Technol. 91, 263–277 (2018)
Gong, J.L., Xin, H.E., Wei, Z.H., et al.: Multiple infrared target tracking using improved auxiliary particle filter. Opt. Precis. Eng. 20(2), 413–421 (2012)
Han, T.X., Ming, L., Thomas, S.H.: A drifting-proof framework for tracking and online appearance learning. IEEE Workshop on Applications of Computer Vision, WACV’07. IEEE (2007)
Havlicek, J.P., Bovik, A., Chen, D.: AM–FM image modeling and Gabor analysis. Opt. Eng. N. Y. Marcel Dekker Inc. 64, 343–386 (1999)
Havlicek, J.P., Tay, P.C., Bovik, A.C.: AM–FM image models: fundamental techniques and emerging trends. In: Handbook of Image and Video Processing, 2nd edn (2005)
Huang, Q., Yang, J.: A multistage target tracker in IR image sequences. Infrared Phys. Technol. 65(7), 122–128 (2014)
Jenkins, M.D., et al.: Selective sampling importance resampling particle filter tracking with multibag subspace restoration. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 48, 264–276 (2016)
King, F.: Hilbert Transforms. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2009)
Kyriakides, I.: Target tracking using adaptive compressive sensing and processing. Signal Proc. 127(C), 44–55 (2016)
Li, X.R., Jilkov, V.P.: Survey of maneuvering target tracking: part I. Dynamic models. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 39(4), 1333–1364 (2003)
Liu, W., et al.: Leveraging long-term predictions and online learning in agent-based multiple person tracking. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 25(3), 399–410 (2015)
Matthews, L., Ishikawa, T., Baker, S.: The template update problem. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 26(6), 810–815 (2004)
Mei, X., Ling, H.: Robust visual tracking using L1 minimization. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, DBLP, pp. 1436–1443 (2009)
Nguyen, C.T., Havlicek, J.P.: Modulation domain features for discriminating infrared targets and backgrounds. In: IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. IEEE (2006)
Nguyen, C.T., Havlicek, J.P., Yeary, M.: Modulation domain template tracking. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR’07. IEEE (2007)
Nguyen, C.T., Havlicek, J.P., Fan, G., et al.: Robust dual-band MWIR/LWIR infrared target tracking. In: Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, pp. 78–83. IEEE (2015)
Pan, J., Bo, H.: Robust object tracking against template drift. In: IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, ICIP 2007, vol. 3. IEEE (2007)
Ponsa, D., López, A.M.: Variance reduction techniques in particle-based visual contour tracking. Pattern Recogn. 42(11), 2372–2391 (2009)
Prakash, R.S., Aravind, R.: Modulation-domain particle filter for template tracking. In: 19th International Conference on Pattern Recognition. ICPR 2008. IEEE, 2008
Ross, D.A., Lim, J., Lin, R.S., et al.: Incremental learning for robust visual tracking. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 77(1–3), 125–141 (2008)
Venkataraman, V., Fan, G., Havlicek, J.P., et al.: Adaptive kalman filtering for histogram-based appearance learning in infrared imagery. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 21(11), 4622–4635 (2012)
Wang, Z., Zhang, K.D., Wu, Y., et al.: Tracking dim target in infrared imagery using the trust region embedded particle filter. In: International Conference on Signal Processing. IEEE (2006)
Wang, Q., Chen, F., Xu, W., et al.: Online discriminative object tracking with local sparse representation. IEEE Workshop on the Applications of Computer Vision. IEEE Computer Society (2012)
Wang, F., Zhen, Y., Zhong, B., et al.: Robust infrared target tracking based on particle filter with embedded saliency detection. Inf. Sci. Int. J. 301(C), 215–226 (2015)
Wu, Y., Lim, J., Yang, M.H.: Online object tracking: a benchmark. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2411–2418. IEEE Computer Society (2013)
Yilmaz, A., Javed, O., Shah, M.: Object tracking: a survey. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 38(4), 1–45 (2006)
Zhang, T., Liu, S., Ahuja, N., et al.: Robust visual tracking via consistent low-rank sparse learning. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 111(2), 171–190 (2015)
Zhang, X., Ren, K., Wan, M., et al.: Infrared small target tracking based on sample constrained particle filtering and sparse representation. Infrared Phys. Technol. 87, 72–82 (2017)
Zhou, S.K., Chellappa, R., Moghaddam, B.: Visual tracking and recognition using appearance-adaptive models in particle filters. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 13(11), 1491–1506 (2004)
Zhou, T., Yao, L., Di, H.: Locality-constrained collaborative model for robust visual tracking. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 27(2), 313–325 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61701233), and China Scholarship. The author would also like to thank Professor Joseph Havlicek and Doctor Jonathan Williams of the University of Oklahoma for the great help of the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest concerning the content of this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, X., Chen, Q., Gu, G. et al. Particle filter-based modulation domain infrared targets tracking. Opt Quant Electron 51, 13 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-018-1723-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-018-1723-6