Abstract
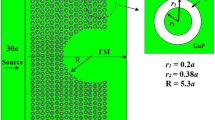
In this paper, an active 2D plasmonic lens has been carefully designed to achieve intensity beam modulation. The design has been thoroughly studied by using rigorous finite element method (FEM). Combination of silicon oxide (SiO2), nematic liquid crystal (NLC) layer and array of non-uniform nano-scale golden (Au) rods along with finely optimized geometry paved the way to achieve good modulation intensity in terms of extinction ratio of about 3.5 dB. Further, the tolerance analysis reveals that the performance of the suggested intensity-modulation lens is almost unchangeable with ± 15 nm variation in the nano-scale golden rods dimensions. Additionally, the proposed lens has been examined using different noble metals such as silver (Ag) and Aluminum (Al). In comparison with other reported lenses, the proposed lenses based Ag, Al and Au have relatively smaller dimensions, maximum intensity amplification factors of about 10.4, 16.6 and 12.5; respectively. The proposed lens may render itself as an efficient unit in the ultra-high nano scale integrated optical systems.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelghani, A.M., Areed, N.F.F., Hameed, M.F., el Hamid Hindy, M.A., Obayya, S.S.A.: Design of UWB antenna using reconfigurable optical router. Opt. Quant. Electron. 47(8), 2675–2688 (2015)
Areed, N.F.F., Obayya, S.S.A.: Novel all-optical liquid photonic crystal router. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 25(13), 1254–1257 (2013)
Areed, N.F.F., Obayya, S.S.A.: Multiple image encryption system based on nematic liquid photonic crystal layers. J. Lightwave Technol. 32, 1344–1350 (2014)
Areed, N.F.F., El Fakhrany, A., Hameed, M.F., Obayya, S.S.A.: Controlled optical photonic crystal AND gate using nematic liquid crystal layers. J. Opt. Quant. Electron. 49, 45–49 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-016-0852-zpp
Bahramipanah, M., Abrishamian, M.S., Mirtaheri, S.A.: Beam manipulating by metal–anisotropic–metal plasmonic lens. J. Opt. 14(10), 105001 (2012)
Bedoya, A.C., Domachuk, P., Grillet, C., Monat, C., Mägi, E.: Reconfigurable photonic crystal waveguides created by selective liquid infiltration. Opt. Express 20(10), 11046–11056 (2012)
Chen, J., Wang, W.S., Fang, J., Varahramyan, K.: Variable-focusing microlens with microfluidic chip. J. Micromech. Microeng. 14, 675–680 (2004)
Chen, J., Wang, C., Lu, G., Li, W., Xiao, J., Gong, Q.: Highly efficient nanofocusing based on a T-shape micro-slit surrounded with multi-slits. Opt. Express 20(16), 17734–17740 (2012)
El-metwally, A., Areed, N.F.F., Hameed, M.F.O.: Obayya SSA Reconfigurable unidirectional photonic crystal using liquid crystal layer. IEEE Photonics J. 9(1), 1–9 (2017)
Elrabiaey, M.A., Areed, N.F.F., Obayya, S.S.: Novel plasmonic data storage based on nematic liquid crystal layers. J. IEEE Light Wave Technol 34(16), 3726–3732 (2016)
Eskalen, H., Özgan, S., Alver, Ü., Kerl, S.: Electro-Optical properties of liquid crystals composite with Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle. J. Acta Phys. Polonica A 127(3), 756–760 (2015)
Gibbs, H.M.: Optical Bistability: Controlling Light with Light. Academic Press, New York (1995)
Goh, X.M., Lin, L., Roberts, A.: Planar focusing elements using spatially varying near-resonant aperture arrays. Opt. Express 18(11), 11683–11688 (2010)
Harm, W., Roider, C., Jesacher, A., Bernet, S., Ritsch-Marte, M.: Dispersion tuning with a varifocal diffractive-refractive hybrid lens. Opt. Express 22(5), 5260–5269 (2014)
Hranilovic, S., Kschischang, F.R.: Optical intensity-modulated direct detection channels, signal space and lattice codes. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 49(6), 1385–1399 (2003)
Jeong, Y., Bae, S., Oh, K.: All fiber N × N fused tapered plastic optical fiber (POF) power splitters for photodynamic therapy applications. Curr. Appl. Phys. 9(4), e273–e275 (2009)
Jia, S., Wu, Y., Wang, X., Wang, N.: A subwavelength focusing structure composite of nanoscale metallic slits array with patterned dielectric substrate. IEEE Photonics 6(1), 1–8 (2014)
Lin, H.C., Chen, M.S., Chen, Y.H.: A review of electrically tunable focusing liquid crystal lenses. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 12(6), 234–240 (2011)
Ma, C., Aguinaldo, R., Liu, Z.: Advances in the hyperlens. Chin. Sci. Bull. 55(24), 2618–2624 (2010)
Matoba, O., Javidi, B.: Encrypted optical memory system using three-dimensional keys in the Fresnel domain. Opt. Lett. 24(11), 762–764 (1999)
Maurer, C., Jesacher, A., Bernet, S., Ritsch-Marte, M.: What spatial light modulators can do for optical microscopy. Laser Photonics Rev. 5(1), 81–101 (2011)
Obayya, S.S.A., Hameed, M.F.O., Areed, N.F.F.: Computational liquid crystal photonics: fundamentals, modelling and applications. Wiley, Chichester (2016)
Papaioannou, M., Plum, E., Rogers, E.T., Zheludev, N.I.: All-optical dynamic focusing of light via coherent absorption in a plasmonic metasurface. Light Sci. Appl. 7(3), 17157 (2018)
Ray, S.: Applied Photographic Optics: Lenses and Optical Systems for Photography, Film, Video and Electronic Imaging, 3rd edn. Focal Press, Oxford (2002)
Salian, P.P., Prabhu, S., Amin, P., Naik, S.K., Parashuram M.K.: Visible Light Communication. India Educators’ Conference (TIIEC), https://doi.org/10.1109/tiiec.2013.74, 4–6 April (2013)
Steinmanna, P., Weaver, J.M.R.: Fabrication of sub-5 nm gaps between metallic electrodes using conventional lithographic techniques. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 22(6), 3178–3181 (2004)
Sun, H., Zhu, Y., Gao, B., Wang, P., Yu, Y.: Polarization-dependent quasi-far-field superfocusing strategy of nanoring-based plasmonic lenses. Nanoscale Res. Lett. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-017-2154-1
Takeda, M., Tanimoto, T., Inoue, T., Aizawa, K.: Plasmonic lens for ultraviolet wavelength. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. (2016). https://doi.org/10.7567/JJAP.55.09SD03
Takeda, M., Tsuchiyama, A., Okada, M., Matsui, S., Inoue, T., Aizawa, K.: Improvement of focusing characteristics of a surface plasmonic lens for UV wavelength. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. (2017). https://doi.org/10.7567/JJAP.56.09NC02
Towghi, N., Javidi, B., Luo, Z.: Fully phase encrypted image processor. J. OSA A 16(8), 1915–1927 (1999)
Van de Nes, A.S., Braat, J.J., Pereira, S.F.: High-density optical data storage. Rep. Prog. Phys. 69(8), 2323 (2006)
Verslegers, L., Catrysse, P.B., Yu, Z., White, J.S., Barnard, E.S., Brongersma, M.L., Fan, S.: Planar lenses based on nanoscale slit arrays in a metallic film. Nano Lett. 9(1), 235–238 (2008)
Wang, H., Deng, Y., He, J., Gao, P., Yao, N., Wang, C., Zhao, Z., Wang, J., Jiang, B., Luo, X.: Subwavelength light focusing of plasmonic lens with dielectric filled nanoslits structures. J. Nanophotonics (2014). https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JNP.8.083079
Yu, Y., Zappe, H.: Effect of lens size on the focusing performance of plasmonic lenses and suggestion for the design. Opt. Express 19(10), 9439–9444 (2011)
Zhao, Y., Lin, S.S., Nawaz, A.A., Kiraly, B., Hao, Q., Liu, Y., Huang, T.J.: Beam bending via plasmonic lenses. Opt. Express 18(22), 23458–23465 (2010)
Zhu, Y., Yuan, W., Yu, Y., Wang, P.: Robustly efficient superfocusing of immersion plasmonic lenses based on coupled nanoslits. Plasmonics 11(6), 1543–1548 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors would like to clarify that there is no sources of funding, and no potential conflicts of interest (financial or non-financial).
Ethical standard
The authors would like to ensure the objectivity and transparency in the submitted research paper. Additionally, the authors would like to ensure that accepted principles of ethical and professional conduct have been followed through the preparation of the proposed paper.
Human and animal rights statement
Moreover, the submitter research does not involve human participants, or animals.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Optical Wave and Waveguide Theory and Numerical Modelling, OQTNM 2017.
Guest Edited by Bastiaan Pieter de Hon, Sander Johannes Floris, Manfred Hammer, Dirk Schulz, Anne-Laure Fehrembach.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Areed, N.F.F., El-Baz, M., Heikal, A.M. et al. Intensity modulation lens on the basis of nano-scale golden rods and liquid crystal layer. Opt Quant Electron 50, 240 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-018-1501-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-018-1501-5