Abstract
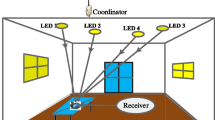
An indoor wireless communication using LED as both transmitter and receiver is presented in this paper. Ambient light noise from natural and artificial sources, would easily saturate the LED acting as sensor and decrease the indoor VLC system performance. Hence the receiver structure is designed using RC high pass filter to mitigate the ambient light noise. The measurement results shows that it could effectively reduce noise and improve the VLC system’s stability and reliability.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheong, Y.K., Weing, X., Youn, Chung W.: Hazardless biomedical sensing data transmission using VLC. IEEE Sens. J. 13, 3347–3348 (2013)
Dhatchayeny, D., Sewaiwar, A., Tiwari, S., Chung, Y.: Experimental biomedical EEG signal transmission using VLC. IEEE Sens. J. 15(10), 5386–5387 (2015)
IEEE Standards Association, IEEE Standard for Local and metropolitan area networks—Part 15.7: Short-Range Wireless Optical Communication Using Visible Light (IEEE std 802.15.7) (2011)
Kim, S., Lee, H.: Half-duplex visible light communication using LED as both a transmitter and a receiver. Int. J. Commun Syst 29(12), 1889–1895 (2015)
Komine, T., Nakagawa, M.: Integrated system of white LED visible-light communication and power-line communication. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 49(1), 71–79 (2003)
Pathak, P.H., Feng, X., Hu, P., Mohapatra, P.: Visible light communication, networking and sensing: a survey, potential and challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 17(4), 2047–2077 (2015)
Varanva, D.J., Prasad, K.: LED to LED communication with WDM concept for flashlight of mobile phones. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 4(7), 28–31 (2013a)
Varanva, D.J., Prasad, K.: LED to LED communication using WDM. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 72(19), 36–38 (2013b)
Visible Light Communications Consortium. http://www.vlcc.net (2008). Accessed 02 July 2016
Wireless World Research Forum. http://www.wireless-world-research.org (2008). Accessed 02 July 2016
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kadirvelu, S., Baba, V. Visible light communication using LED as receiver with the effect of ambient light. Opt Quant Electron 50, 15 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-017-1280-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-017-1280-4