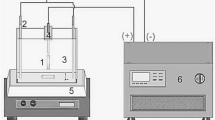
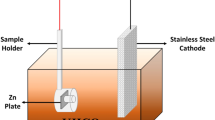
Abstract
A comparison of photocatalytic properties of ZnO nanostructures fabricated by different methods was carried out. The photocatalytic properties of as grown and Ar-ion-treated ZnO materials were tested using photocatalytic degradation of an aqueous solution of methyl orange dye serving as a model water contaminant. The reaction rate constants of methyl orange photodegradation for untreated ZnO nanorods grown by the method of gas-transport reactions and hydrothermal method were equal to 5.3 × 10−5 and 3.7 × 10−4 s−1, respectively, whereas for the case of the Ar-ion-treated samples they reached 1.85 × 10−4 and 5.9 × 10−4 s−1, respectively. Based on the analysis of the photoluminescence spectra, it is assumed that the difference in photocatalytic activity is connected with different type of defects predominant on the surfaces of ZnO nanorods grown by the hydrothermal and gas-transport reactions methods. The experimental results show that ZnO nanostructures grown by the hydrothermal method would be promising for producing efficient catalysts.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abed, S., Aida, M.S., Bouchouit, K., Arbaoui, A., Iliopoulos, K., Sahraoui, B.: Non-linear optical and electrical properties of ZnO doped Ni thin films obtained using spray ultrasonic technique. Opt. Mater. 33(6), 968–972 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2011.01.018
Ban, K.: Foreword. In: R. Connor (ed.) The United Nations World Water Development Report 2015: Water for a Sustainable World. UNESCO Publishing, Paris (2015)
Baruah, S., Khan, M.N., Dutta, J.: Perspectives and applications of nanotechnology in water treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 14(1), 1–14 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-015-0542-2
Chen, C.-C., Hu, S.-H., Fu, Y.-P.: Effects of surface hydroxyl group density on the photocatalytic activity of Fe3+-doped TiO2. J. Alloys Compd. 632, 326–334 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.01.206
Ge, M., Guo, C., Zhu, X., Ma, L., Han, Z., Hu, W., Wang, Y.: Photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange using ZnO/TiO2 composites. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 3, 271–280 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-009-0035-2
Harun, K., Yaakob, M.K., Taib, M.F.M., Sahraoui, B., Ahmad, Z.A., Mohamad, A.A.: Efficient diagnostics of the electronic and optical properties of defective ZnO nanoparticles synthesized using the sol–gel method: experimental and theoretical studies. Mater. Res. Express 4(8), 085908-1–085908-15 (2017)
Hatch, S.M., Briscoe, J., Sapelkin, A., Gillin, W.P., Gilchrist, J.B., Ryan, M.P., Heutz, S., Dunn, S.: Influence of anneal atmosphere on ZnO-nanorod photoluminescent and morphological properties with self-powered photodetector performance. J. Appl. Phys. 113, 204501-1–204501-9 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4805349
Janotti, A., Van de Walle, C.G.: Fundamentals of zinc oxide as a semiconductor. Rep. Prog. Phys. 72, 126501-1–126501-29 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1088/0034-4885/72/12/126501
Janotti, A., Van de Walle, C.G.: Native Point Defects and Doping in ZnO. In: Litton, C.W., Reynolds, D.C., Collins, T.C. (eds.) Zinc Oxide Materials for Electronic and Optoelectronic Device Applications, Chap. 5, vol. 1. Wiley, Chichester (2011)
Kapustianyk, V., Turko, B., Kostruba, A., Sahraoui, B., Sofiani, Z., Dabos-Seignon, S., Barwinski, B., Eliyashevskyi, Yu.: Influence of size effect and sputtering conditions on the crystallinity and optical properties of ZnO thin films. Opt. Commun. 269, 346–350 (2007)
Kapustianyk, V., Turko, B., Rudyk, V., Rudyk, Y., Rudko, M., Panasiuk, M., Serkiz, R.: Effect of vacuumization on the photoluminescence and photoresponse decay of the zinc oxide nanostructures grown by different methods. Opt. Mater. 56, 71–74 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2016.01.057
Kostruba, A., Kulyk, B., Turko, B.: Ellipsometric studies of optical properties of copper doped zinc oxide films on glass substrates. J. Alloys Compd. 518, 96–100 (2012)
Kulyk, B., Essaidi, Z., Kapustianyk, V., Turko, B., Rudyk, V., Partyka, M., Addou, M., Sahraoui, B.: Second and third order nonlinear optical properties of nanostructured ZnO thin films deposited on α-BBO and LiNbO3. Opt. Commun. 281, 6107–6111 (2008)
Kulyk, B., Essaidi, Z., Luc, J., Sofiani, Z., Boudebs, G., Sahraoui, B., Kapustianyk, V., Turko, B.: Second and third order nonlinear optical properties of microrods ZnO films deposited on sapphire substrates by thermal oxidation of metallic zinc. J. Appl. Phys. 102, 113113-1–113113-6 (2007)
Kulyk, B., Sahraoui, B., Figa, V., Turko, B., Rudyk, V., Kapustianyk, V.: Influence of Ag, Cu dopants on the second and third harmonic response of ZnO films. J. Alloys Compd. 481, 819–825 (2009)
Kumar, S., Sahare, P.D.: Effect of surface defects on green luminescence from ZnO nanoparticles. AIP Conf. Proc. 1393, 159–160 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3653658
Kumar, S., Sahare, P.D.: Effects of annealing on the surface defects of zinc oxide nanoparticles. NANO 7, 1250022-1–1250022-9 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1142/S1793292012500221
Lee, J.-M., Kim, K.-K., Park, S.-J., Choi, W.-K.: Low-resistance and nonalloyed ohmic contacts to plasma treated ZnO. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 3842–3844 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1379061
Lee, K.M., Lai, C.W., Ngai, K.S., Juan, J.C.: Recent developments of zinc oxide based photocatalyst in water treatment technology: a review. Water Res. 88, 428–448 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.09.045
Lv, J., Gong, W., Huang, K., Zhu, J., Meng, F., Song, X., Sun, Z.: Effect of annealing temperature on photocatalytic activity of ZnO thin films prepared by sol–gel method. Superlattices Microstruct. 50, 98–106 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2011.05.003
Mishra, R., Yadav, R.S., Pandey, A.C., Sanjay, S.S., Dar, C.: Formation of ZnO@ Cd (OH) 2 core–shell nanoparticles by sol–gel method: an approach to modify surface chemistry for stable and enhanced green emission. J. Lumin. 130, 365–373 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2009.09.022
Moafi, H.F., Hafezi, M., Khorram, S., Zanjanchi, M.A.: The effects of non-thermal plasma on the morphology of Ce-doped ZnO: synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity of hierarchical nanostructures. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 37, 159–176 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-016-9748-8
Moore, J.C., Louder, R., Thompson, C.V.: Photocatalytic activity and stability of porous polycrystalline ZnO thin-films grown via a two-step thermal oxidation process. Coatings 4, 651–669 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings4030651
Palma, P., Fialho, S., Alvarenga, P., Santos, C., Brás, T., Palma, G., Cavaco, C., Gomes, R., Neves, L.A.: Membranes technology used in water treatment: chemical, microbiological and ecotoxicological analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 568, 998–1009 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.04.208
Panasiuk, M.R., Turko, B.I., Kapustianyk, V.B., Stanko, O.P., Mandryka, A.V., Serkiz, R.Y., Dubov, Y.H.: Photo-and thermostimulated luminescence of ZnO nanowires. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 80, 240–243 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-013-9752-1
Park, J.S., Jeong, J.K., Mo, Y.G., Kim, H.D., Kim, S.I.: Improvements in the device characteristics of amorphous indium gallium zinc oxide thin-film transistors by Ar plasma treatment. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 262106-1–262106-3 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2753107
Ra, H.W., Choi, K.S., Ok, C.W., Jo, S.Y., Bai, K.H., Im, Y.H.: Ion bombardment effects on ZnO nanowires during plasma treatment. Appl. Phys. 93, 033112-1–033112-3 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2965109
Santhosh, C., Velmurugan, V., Jacob, G., Jeong, S.K., Grace, A.N., Bhatnagar, A.: Role of nanomaterials in water treatment applications: a review. Chem. Eng. J. 306, 1116–1137 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.08.053
Savastenko, N.A., Filatova, I.I., Lyushkevich, V.A., Chubrik, N.I., Gabdullin, M.T., Ramazanov, T.S., Abdullin, H.A., Kalkozova, V.A.: Enhancement of ZnO-based photocatalyst activity by RF discharge-plasma treatment. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 83, 757–763 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-016-0359-1
Schmidt-Mende, L., MacManus-Driscoll, J.L.: ZnO—nanostructures, defects, and devices. Mater. Today 10, 40–48 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-7021(07)70078-0
Sharma, A., Singh, B.P., Dhar, S., Gondorf, A., Spasova, M.: Effect of surface groups on the luminescence property of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by sol–gel route. Surf. Sci. 606, L13–L17 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susc.2011.09.006
Simonsen, M.E., Li, Z., Søgaard, E.G.: Influence of the OH groups on the photocatalytic activity and photoinduced hydrophilicity of microwave assisted sol–gel TiO2 film. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 8054–8062 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.05.013
Sulyok, A., Menyhard, M., Malherbe, J.B.: Stability of ZnO {0 0 0 1} against low energy ion bombardment. Surf. Sci. 601, 1857–1861 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susc.2007.02.011
Sun, R., Nakajima, A., Fujishima, A., Watanabe, T., Hashimoto, K.: Photoinduced surface wettability conversion of ZnO and TiO2 thin films. J. Phys. Chem. 105, 1984–1990 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp002525j
Wang, C.-C., Lee, C.-K., Lyu, M.-D., Juang, L.-C.: Photocatalytic degradation of CI Basic Violet 10 using TiO2 catalysts supported by Y zeolite: an investigation of the effects of operational parameters. Dyes Pigments 76, 817–824 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2007.02.004
Willander, M., Nur, O., Sadaf, J.R., Qadir, M.I., Zaman, S., Zainelabdin, A., Bano, N., Hussain, I.: Luminescence from zinc oxide nanostructures and polymers and their hybrid devices. Materials 3, 2643–2667 (2010). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3042643
Yadav, R.S., Pandey, A.C.: Small angle X-ray scattering and photoluminescence study of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by hydrothermal process. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2, 177–182 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1080/17458080701474242
Yamada, T., Kuroda, Y., Fukuoka, A., Ichikawa, M., Tanaka, K.J.: Reactivity of surface hydroxyl groups with metal complex compounds. J. Electron. Spectrosc. 54, 845–854 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1016/0368-2048(90)80277-H
Zha, R., Nadimicherla, R., Guo, X.J.: Ultraviolet photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange by nanostructured TiO2/ZnO heterojunctions. Mater. Chem. A 3, 6565–6574 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TA00764J
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toporovska, L.R., Hryzak, A.M., Turko, B.I. et al. Photocatalytic properties of zinc oxide nanorods grown by different methods. Opt Quant Electron 49, 408 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-017-1254-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-017-1254-6