Abstract
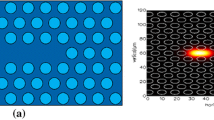
In this paper we study the characteristics of hollow waveguides that are used as polarization converting elements. In particular, numerical simulations are compared with experiments where a good agreement is found. The numerical simulations are performed with the Method of Lines—an eigenmode propagation algorithm where the eigenmodes are computed after a discretization in the cross-section. Due to the vectorial 3D-problem, extensions of the standard algorithm were required to keep the numerical effort low. Particularly, only a reduced set of eigenmodes is used in the computations and inverting rectangular matrices is done with the help of left eigenvectors. Further, it is shown how these left eigenvectors can be determined with simple matrix vector products, i.e., at very low numerical cost. The fabrication of the device is very demanding because of a very high ratio between the metal width and its height. Here, direct electron-beam lithography is used for this task.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bacher, W., Menz, J.M.W.: The liga technique and its potential for microsystems—a survey. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 42, 431–441 (1995)
Bomzon, Z., Biener, G., Kleiner, V., Hasman, E.: Radially and azimuthally polarized beams generated by space-variant dielectric sub wavelength gratings. Opt. Lett. 27, 285–287 (2002)
Born, M., Wolf, E.: Principles of Optics, 7th edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1986)
Chen, H., Wang, J., Ma, H., Zhuo, X., Zhang, A., Yan, M., Li, Y.: Ultra-wideband polarization conversion metasurfaces based on multiple plasmon resonances. J. Appl. Phys. 115, 154504 (2014)
Collin, R.E.: Field Theory of Guided Waves. Series of Electromagnetic Waves, 2nd edn. IEEE Press, New York (1991)
Cong, L., Cao, W., Zhang, X., Tian, Z., Gu, L., Singh, R., Han, J., Zhang, W.: A perfect metamaterial polarization rotator. Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 171107 (2013)
Cucinotta, A., Pelosi, G., Selleri, S., Vincetti, L., Zoboli, M.: Perfectly matched anisotropic layers for optical waveguide analysis through the finite element beam propagation method. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 23, 67–69 (1999)
Gerdes, J.: Bidirectional eigenmode propagation analysis of optical waveguides based on method of lines. Electron. Lett. 30, 550–551 (1994)
Ghadyani, Z., Dmitriev, S., Lindlein, N., Leuchs, G., Rusina, O., Harder, I.: Discontinuous space variant sub-wavelength structures for generating radially polarized light in visible region. J. Eur. Opt. Soc. Rapid Publ. 6, 11041 (2011)
Golub, G.H., van Loan, C.F.: Matrix Computations. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore (1989)
Helfert, S.F.: Efficient determination of the left-eigenvectors for the method of lines. Adv. Radio Sci. 13, 19–29 (2015)
Helfert, S.F., Pregla, R.: The method of lines: a versatile tool for the analysis of waveguide structures. Electromagnetics 22, 615–637 (2002)
Helfert, S.F., Jahns, J.: Structured illumination of hollow waveguide arrays using the Talbot self-imaging. In: EOS Topical Meeting on Diffractive Optics 2017 (DO2017), Oensuu, Finland (2017)
Helfert, S.F., Barcz, A., Pregla, R.: Three-dimensional vectorial analysis of waveguide structures with the method of lines. Opt. Quantum Electron. 35, 381–394 (2003)
Helfert, S.F., Edelmann, A., Jahns, J.: Hollow waveguides as polarization converting elements: a theoretical study. J. Eur. Opt. Soc. Rapid Publ. 10, 15006 (2015)
Jahns, J., Helfert, S.: Introduction to Micro- and Nanooptics. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim (2012)
Kämpfe, T., Parriaux, O.: Depth-minimized, large period half-wave corrugation for linear to radial and azimuthal polarization transformation by grating-mode phase management. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 28, 2235–2242 (2011)
Kaveev, A.K., Kropotov, G.I., Tsygankova, E.V., Tzibizov, I.A., Ganichev, S.D., Danilov, S.N., Olbrich, P., Zoth, C., Kaveeva, E.G., Zhdanov, A.I., Ivanov, A.A., Deyanov, R.Z., Redlich, B.: Terahertz polarization conversion with quartz waveplate sets. Appl. Opt. 52, B60–B69 (2013)
Khanikaev, A.B., Mousavi, S.H., Wu, C., Dabidian, N., Alici, K.B., Shvets, G.: Electromagnetically induced polarization conversion. Opt Commun. 285, 3423–3427 (2012)
Lalanne, P., Lemercier-Lalanne, D.: On the effective medium theory of subwavelength periodic structures. J. Mod. Opt. 43, 2063–2085 (1996)
Li, P.: A review of proximity effect correction in electron-beam lithography. Condens. Matter. arXiv:1509.05169v1 (2015)
Phua, P.B., Lai, W.J., Lim, Y.L., Tiaw, K.S., Lim, B.C., Teo, H.H., Hong, M.H.: Mimicking optical activity for generating radially polarized light. Opt. Lett. 32, 376–378 (2007)
Pregla, R.: MoL-BPM method of lines based beam propagation method. In: Huang, W.P. (ed.) Methods for Modeling and Simulation of Guided-Wave Optoelectronic Devices (PIER 11), Progress in Electromagnetic Research, pp. 65–69. EMW Publishing, Cambridge (1995)
Pregla, R.: Novel FD-BPM for optical waveguide structures with isotropic or anisotropic material. In: European Conference on Integrated Optics (ECIO), Italy, Torino, pp. 55–58 (1999)
Pregla, R.: Analysis of Electromagnetic Fields and Waves—The Method of Lines. Wiley, Chichester (2008)
Sacks, Z.S., Kingsland, D.M., Lee, R., Lee, J.F.: A perfectly matched anisotropic absorber for use as an absorbing boundary. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 43, 1460–1463 (1995)
Schneider, V.M.: Analysis of passive optical structures with an adaptive set of radiation modes. Opt. Commun. 160, 230–234 (1999)
Stork, W., Streibl, N., Haidner, H., Kipfer, P.: Artificial distributed-index media fabricated by zero-order gratings. Opt. Lett. 16, 1921–1923 (1991)
Tremain, B., Rance, H.J., Hibbins, A.P., Sambles, J.R.: Polarization conversion from a thin cavity array in the microwave regime. Sci. Rep. 5, 9366 (2015)
Werner, D.H., Mittra, R.: A new field scaling interpretation of Berenger’s PML and its comparison to other PML formulations. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 16, 103–106 (1997)
Yang, Y., Wang, W., Moitra, P., Kravchenko, I.I., Briggs, D.P., Valentine, J.: Dielectric meta-reflectarray for broadband linear polarization conversion and optical vortex generation. Nano Lett. 14, 1394–1399 (2014)
Zhao, Y., Alù, A.: Manipulating light polarization with ultrathin plasmonic metasurfaces. Phys. Rev. B 84, 205428 (2011)
Zhu, H.L., Cheung, S.W., Chung, K., Yuk, T.I.: Linear-to-circular polarization conversion using metasurface. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 61, 4615–4623 (2013)
Zurmühl, R., Falk, S.: Matrizen und ihre Anwendungen, Teil 1, 5th edn. Springer, Berlin (1984)
Acknowledgements
This work was partially carried out with support of the Karlsruhe Nano Micro Facility (KNMF, www.knmf.kit.edu), a Helmholtz research infrastructure at Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT, www.kit.edu).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Helfert, S.F., Seiler, T., Jahns, J. et al. Numerical simulation of hollow waveguide arrays as polarization converting elements and experimental verification. Opt Quant Electron 49, 313 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-017-1153-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-017-1153-x