Abstract
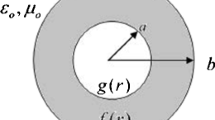
When performing optical simulations for rotationally symmetric geometries using the eigenmode expansion technique, it is necessary to place the geometry under investigation inside a cylinder with perfectly conducting walls. The parasitic reflections at the boundary of the computational domain can be suppressed by introducing a perfectly matched layer (PML) using e.g. complex coordinate stretching of the cylinder radius. However, the traditional PML suffers from an artificial field divergence limiting its usefulness. We show that the choice of a constant cylinder radius leads to mode profiles with exponentially increasing field amplitudes resulting in numerical instability. As a remedy we propose an improved PML based on a mode-dependent cylinder radius and mode profiles with stable field amplitudes. The new PML formulation eliminates the artificial field divergence and ensures numerical stability.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PML:
-
Perfectly Matched Layer
- EET:
-
Eigenmode Expansion Technique
References
Balanis C.A.: Auxiliary vector potentials, construction of solutions, and radiation and scattering equations. In: Balanis, C.A. (eds) Advanced Engineering Electromagnetics, pp. 254–309. Wiley, New York (1989)
Bérenger J.-P.: A perfectly matched layer for the absorption of electromagnetic waves. J. Comput. Phys. 114, 185–200 (1994). doi:10.1006/jcph.1994.1159
Bienstman P., Baets R.: Optical modelling of photonic crystals and VCSELs using eigenmode expansion and perfectly matched layers. Opt. Quantum Electron. 33, 327–341 (2001). doi:10.1023/A:1010882531238
Bienstman P., Derudder H., Baets R., Olyslager F., De Zutter D.: Analysis of cylindrical waveguide discontinuities using vectorial eigenmodes and perfectly matched layers. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theor. Tech. 49, 349–354 (2001). doi:10.1109/22.903096
Bienstman P., Baets R.: Advanced boundary conditions for eigenmode expansion models. Opt. Quantum Electron. 34, 523–540 (2002)
Chen L., Towe E.: Nanowire lasers with distributed-Bragg-reflector mirrors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 053125 (2006). doi:10.1063/1.2245219
Chew W.C., Weedon W.H.: A 3D perfectly matched medium from modified Maxwell’s equations with stretched coordinates. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 7, 599–604 (1994). doi:10.1002/mop.4650071304
Gregersen N., Tromborg B., Bozhevolnyi S.I.: Vectorial modeling of near-field imaging with uncoated fiber probes: transfer function and resolving power. Appl. Opt. 45, 8739–8747 (2006). doi:10.1364/AO.45.008739
Gregersen N., Nielsen T.R., Tromborg B., Mørk J.: Quality factors of nonideal micro pillars. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 011116 (2007). doi:10.1063/1.2751586
Gregersen N., Nielsen T.R., Claudon J., Gérard J.-M., Mørk J.: Controlling the emission profile of a nanowire with a conical taper. Opt. Lett. 33, 1693–1695 (2008). doi:10.1364/OL.33.001693
Li L.: Formulation and comparison of two recursive matrix algorithms for modeling layered diffraction gratings. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 13, 1024–1035 (1996). doi:10.1364/JOSAA.13.001024
Maslov A.V., Ning C.Z.: Far-field emission of a semiconductor nanowire laser. Opt. Lett. 29, 572–574 (2004). doi:10.1364/OL.29.000572
Sacks Z., Kingland D., Lee R., Lee J.: A perfectly matched anisotropic absorber for use as an absorbing boundary condition. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 43, 1460–1463 (1995). doi:10.1109/8.477075
Sagan H.: Boundary and eigenvalue problems in mathematical physics. Dover Publications Inc., New York (1989)
Shyroki D.M., Lavrinenko A.V.: Perfectly matched layer method in the finite-difference time-domain and frequency-domain calculations.. Phys. Stat. Sol. (b) 244, 3506–3514 (2007)
Watanabe Y., Yamamoto N., Komori K.: Numerical analysis of waveguides in three-Dimensional photonic crystal with finite thickness. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 43, 2015–2018 (2004). doi:10.1143/JJAP.43.2015
Yariv A.: Propagation of optical beams in fibers. In: Yariv, A. (eds) Optical Electronics in Modern Communications, pp. 76–120. Oxford University Press, New York (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gregersen, N., Mørk, J. An improved perfectly matched layer for the eigenmode expansion technique. Opt Quant Electron 40, 957–966 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-009-9275-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-009-9275-4