Abstract
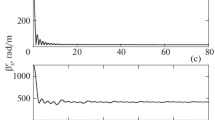
Although fiber spinning is known to reduce polarization mode dispersion (PMD) effects in optical fibers, relatively few studies have been performed of the dependence of the reduction factor on the strength of random birefringence fluctuations. In this paper, we apply a general mathematical model of random fiber birefringence to sinusoidally spun fibers. We find that while even in the presence of random birefringence perturbations the maximum reduction of PMD is still obtained when the phase matching condition is satisfied, the degree of PMD reduction and the probability distribution function of the DGD both vary with the random birefringence profiles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Galtarossa A., Palmieri L., Schiano M., Tambosso T. (2000) Statistical characterization of fiber random birefringence. Opt. Lett. 18, 1322–1324
Galtarossa A., Palmieri L., Pizzinat A. (2001) Optimized spinning design for low PMD fibers: An analytical approach. J. Lightwave Technol. 19, 1502–1512
Galtarossa A., Griggio P., Palmieri L., Pizzinat A. (2004) First- and second-order PMD statistical properties of constantly spun randomly birefringent fibers. J. Lightwave Technol. 22, 1127–1136
Huang W., Yevick D. (2006a) Polarization mode dispersion in short fiber lengths. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 23, 1509–1512
Huang, W., Yevick, D.: Improved models of optical fiber birefringence - Part I. Opt. Quant. Electron. (2007a), doi: 10.1007/s11082-007-9063-y
Huang, W., Yevick, D.: Improved models of optical fiber birefringence - Part II. Quant. Electron. (2007b, accepted), doi: 10.1007/s11082-006-9032-x
Kaminow I.P. (1981) Polarization in optical fibers. J. Quantum. Electron. QE-17, 15–22
Nolan D.A., Chen X., Li M. (2004) Fibers with low polarization-mode dispersion. J. Lightwave Technol. 22, 1066–1077
Poole C.D., Nagel J.A. (1997) Polarization effects in lightwave systems. In: Kaminow I.P., Koch T.L. (eds) Optical Fiber Telecommunications. vol. IIIA. Academic, San Diego, p. 114–161
Poole C.D., Wagner R.E. (1986) Phenomenological approach to polarization dispersion in long single-mode fibers. Elec. Lett. 22, 1029–1030
Pizzinat A., Marks B.S., Palmieri L., Menyuk C.R., Galtarossa A. (2003a) Influence of the model for ramdom birefringence on the differential group delay of periodically spun fibers. J. Lightwave Technol. 15, 819–821
Pizzinat A., Palmieri L., Marks B.S., Menyuk C.R., Galtarossa A. (2003b) Analytical treatment of randomly birefringent periodically spun fibers. J. Lightwave Technol. 21, 3355–3363
Wai P.K., Menyuk C.R. (1996) Polarization mode dispersion, decorrelation, and diffusion in optical fibers with randomly varying birefringence. J. Lightwave Technol. 14, 148–157
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, W., Yevick, D. The PMD of sinusoidally spun fibers in the presence of random birefringence perturbations. Opt Quant Electron 39, 119–129 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-007-9067-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-007-9067-7