Abstract
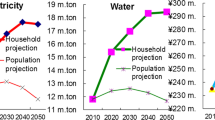
This study employs threshold models to investigate the nonlinear relationship between household composition and residential electricity consumption. Household size and level of electricity use are employed as the threshold variables. Household data are obtained from Taiwan’s 2020 Family Income and Expenditure Survey. The results verify that the effects of household composition and household size on household electricity use differ depending on the specific household size and level of electricity use. The economic scale effect on electricity use per capita due to an additional member only appears for households with three or more members. Among households with one or two members, an increase in the number of members aged 25–44 years results in more electricity use than an increase in the number of members of other age groups, reflecting the inefficient electricity use among those aged 25–44 years. Moreover, the economic scale effect of an increasing number of members is weaker for households using more electricity. For households with the highest level of electricity use, an elderly member would contribute to more electricity use than a member of another age group. Given the trends of demographic change and global warming, electricity demand can be expected to increase in the future due to population aging, declining family size, and higher dependency on electricity. Policy makers should improve residential electricity efficiency and adopt strategies specifically for small households.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberini A, Gans W, Velez-Lopez D (2011) Residential consumption of gas and electricity in the U.S.: the role of prices and income. Energy Econ 33:870–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2011.01.015
Bedir M, Hasselaar E, Itard L (2013) Determinants of electricity consumption in Dutch dwellings. Energy Build 58:194–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2012.10.016
Brounen D, Kok N, Quigley JM (2012) Residential energy use and conservation: economics and demographics. Eur Econ Rev 56(5):931–945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroecorev.2012.02.007
Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) (2021) The CIA World Factbook 2020-2021, Skyhorse. https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/field/total-fertility-rate/country-comparison
Directorate-General of Budget, Accounting and Statistics (DGBAS), Executive Yuan (2021) The survey of family income and expenditure, 2020 (AA170045) [data file]. Available from Survey Research Data Archive, Academia Sinica. https://doi.org/10.6141/TW-SRDA-AA170045-1
Druckman A, Jackson T (2008) Household energy consumption in the UK: a highly geographically and socio-economically disaggregated model. Energy Policy 36(8):3177–3192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2008.03.021
Enders W, Siklos PL (2001) Cointegration and threshold adjustment. J Bus Econ Stat 19(2):166–176
Farrell N (2017) What factors drive inequalities in carbon tax incidence? Decomposing socioeconomic inequalities in carbon tax incidence in Ireland. Ecol Econ 142:31–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2017.04.004
Frondel M, Sommer S, Vance C (2019) Heterogeneity in German residential electricity consumption: a quantile regression approach. Energy Policy 131:370–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2019.03.045
Fu C, Wang W, Tang J (2014) Exploring the sensitivity of residential energy consumption in China: implications from a micro-demographic analysis. Energy Res Soc Sci 2:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.erss.2014.04.010
Gannon B, Harris D, Harris M (2014) Threshold effects in nonlinear with an application to the social capital-retirement-health relationship. Health Econ 23(9):1072–1083. https://doi.org/10.1002/hec.3088
Grynkiv G, Stentoft L (2018) Stationary threshold vector autoregressive models. J Risk Financ Manage 11:45. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm11030045
Gonzalo J, Pitarakis JY (2002) Estimation and model selection based inference in single and multiple threshold models. J Econom 110(2):319–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4076(02)00098-2
Hansen BE (2011) Threshold autoregression in economics. Stat Interface 4:123–127
Hansen AR (2018) Heating homes: understanding the impact of prices. Energy Policy 21:138–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2018.06.021
Hansen BE, Seo B (2002) Testing for two-regime threshold cointegration in vector error correction models. J Econom 110(2):293–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4076(02)00097-0
Huang WH (2015) The determinants of household electricity consumption in Taiwan: evidence from quantile regression. Energy 87(1):120–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2015.04.101
Huebner G, Shipworth D, Hamilton I, Chalabi Z, Oreszczyn T (2016) Understanding electricity consumption: a comparative contribution of building factors, socio-demographics, appliances, behaviours and attitudes. Appl Energy 177:692–702
Hung MF, Huang TH (2015) Dynamic demand for residential electricity in Taiwan under seasonality and increasing-block pricing. Energy Econ 48:168–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2015.01.010
Jones RV, Fuertes A, Lomas KJ (2015) The socio-economic, dwelling and appliance related factors affecting electricity consumption in domestic buildings. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 43:901–917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.11.084
Kim MJ (2018) Characteristics and determinants by electricity consumption level of households in Korea. Energy Rep 4:70–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2017.12.001
Kim MJ (2020) Understanding the determinants on household electricity consumption in Korea: OLS regression and quantile regression. Electr J 33(7):106802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tej.2020.106802
Kostakis I (2020) Socio-demographic determinants of household electricity consumption: evidence from Greece using quantile regression analysis. Curr Res Environ Sustain 1:23–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crsust.2020.04.001
Kotsila D, Polychronidou P (2021) Determinants of household electricity consumption in Greece: a statistical analysis. J Innov Entrep 10:19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13731-021-00161-9
Krug R, Mehrmann V, Schmidt M (2021) Nonlinear optimization of district heating networks. Optim Eng 22:783–819. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11081-020-09549-0
Leahy E, Lyons S (2010) Energy use and appliance ownership in Ireland. Energy Policy 38(8):4265–4279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2010.03.056
McKenna R, Hofmann L, Merkel E, Fichtner W, Strachan N (2016) Analysing socioeconomic diversity and scaling effects on residential electricity load profiles in the context of low carbon technology uptake. Energy Policy 97:13–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2016.06.042
McKerracher C, Torriti J (2013) Energy consumption feedback in perspective: integrating Australian data to meta-analyses on in home displays. Energy Eff 6(2):387–405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12053-012-9169-3
McLoughlin F, Duffy A, Conlon M (2012) Characterising domestic electricity consumption patterns by dwelling and occupant socio-economic variables: an Irish case study. Energy Build 48:240–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2012.01.037
Mouassa S, Bouktir T, Jurado F (2021) Scheduling of smart home appliances for optimal energy management in smart grid using Harris-hawks optimization algorithm. Optim Eng 22(3):1625–1652. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11081-020-09572-1
Nelson JA (1988) Household economies of scale in consumption: theory and evidence. Econometrica 56(6):1301–1314. https://doi.org/10.2307/1913099
O’Neill BC, Chen BS (2002) Demographic determinants of household energy use in the United States. Popul Dev Rev 28:53–88
Pirani E (2014) Household composition. In: Michalos AC (ed) Encyclopedia of quality of life and well-being research. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-0753-5_1319
Ramsey JB (1969) Tests for specification errors in classical linear least-squares analysis. J R Stat Assoc Ser B 71:350–371
Romero-Jordan D, de Rio P, Penasco C (2016) An analysis of the welfare and distributive implications of factors influencing household electricity consumption. Energy Policy 88:361–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2015.09.037
Ryu JY, Kim DW, Kim MK (2021) Household differentiation and residential electricity demand in Korea. Energy Econ 95:105090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2020.105090
Su YW (2019) Residential electricity demand in Taiwan: consumption behavior and rebound effect. Energy Policy 124:36–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2018.09.009
Tong H (2011) Threshold models in time-series analysis–30 years on. Stat Its Interfaces 4:107–118
Tsay RS (1998) Testing and modeling multivariate threshold models. J Am Stat Assoc 93:1188–1202. https://doi.org/10.2307/2669861
United Nations (2019) World Population Ageing 2019 Highlights, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division, United Nations (ST/ESA/SER.A/451).
United Nations (2020) World population ageing 2020 highlights: living arrangements of older persons, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division, United Nations (ST/ESA/SER.A/451).
Valor C, Escudero C, Labajo V, Cossent R (2019) Effective design of domestic energy efficiency displays: a proposed architecture based on empirical evidence. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 114:109301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.109301
Verardi V, Croux C (2009) Robust regression in Stata. Stand Genomic Sci 9(3):439–453
Wooldridge JM (2012) Introductory econometrics: a modern approach, 5th edn. Cengage Learning, South-Western
Yamasaki E, Tominaga N (1997) Evolution of an aging society and effect on residential energy demand. Energy Policy 25(11):903–912
Ye Y, Kocha SF, Zhang J (2018) Determinants of household electricity consumption in South Africa. Energy Econ 75:120–133
Yohai VJ (1987) High breakdown-point and high efficiency robust estimates for regression. Ann Stat 15:642–656
Yu P, Phillips PCB (2018) Threshold regression with endogeneity. J Econom 203:50–68
Zhang Z, Cai W, Feng X (2017) How do urban households in China respond to increasing block pricing in electricity? Evidence from a fuzzy regression discontinuity approach. Energy Policy 105:161–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2017.02.025
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, for providing funding support (MOST 108-2410-H-275-002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, WH. Nonlinear relationship between household composition and electricity consumption: optimal threshold models. Optim Eng 23, 2261–2292 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11081-022-09732-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11081-022-09732-5