Abstract
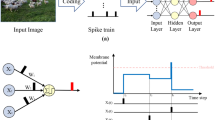
Spiking neural network (SNN) is a biologically-plausible model and exhibits advantages of high computational capability and low power consumption. While the training of deep SNN is still an open problem, which limits the real-world applications of deep SNN. Here we propose a deep SNN architecture named Spiking SiamFC++ for object tracking with end-to-end direct training. Specifically, the AlexNet network is extended in the time domain to extract the feature, and the surrogate gradient function is adopted to realize direct supervised training of the deep SNN. To examine the performance of the Spiking SiamFC++, several tracking benchmarks including OTB2013, OTB2015, VOT2015, VOT2016, and UAV123 are considered. It is found that, the precision loss is small compared with the original SiamFC++. Compared with the existing SNN-based target tracker, e.g., the SiamSNN, the precision (success) of the proposed Spiking SiamFC++ reaches 0.861 (0.644), which is much higher than that of 0.528 (0.443) achieved by the SiamSNN. To our best knowledge, the performance of the Spiking SiamFC++ outperforms the existing state-of-the-art approaches in SNN-based object tracking, which provides a novel path for SNN application in the field of target tracking. This work may further promote the development of SNN algorithms and neuromorphic chips.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
Roy, K., Jaiswal, A., Panda, P.: Towards spike-based machine intelligence with neuromorphic computing. Nature 575(7784), 607–617 (2019)
Maass, W.: Networks of spiking neurons: the third generation of neural network models. Neural Netw. 10(9), 1659–1667 (1997)
Gerstner, W., Kistler, W.: Spiking neuron models: single neurons, populations, plasticity. CUP 32(7/8), 25–34 (2002)
Merolla, P., et al.: A million spiking-neuron integrated circuit with a scalable communication network and interface. Science 345(6197), 668–673 (2014)
Shen, J., et al.: Darwin: a neuromorphic hardware co-processor based on spiking neural networks. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 59(2), 1–5 (2016)
Schuman, C., et al.: A survey of neuromorphic computing and neural networks in hardware, arXiv preprint arXiv:1705.06963 (2017)
Davies, M., et al.: Loihi: a neuromorphic manycore processor with on-chip learning. IEEE Micro 38(1), 82–99 (2018)
Marković, D., Mizrahi, A., Querlioz, D., Grollier, J.: Physics for neuromorphic computing. Nat. Rev. Phys 2, 499–510 (2020)
Wetzstein, G., et al.: Inference in artificial intelligence with deep optics and photonics. Nature 588, 39–47 (2020)
Shastri, B., et al.: Photonics for artificial intelligence and neuromorphic computing. Nat Photon. 15, 102–114 (2021)
Huynh, P., et al.: Implementing spiking neural networks on neuromorphic architectures: a review. arXiv preprint arXiv:2202.08897 (2022)
Bi, G., Poo, M.: Synaptic modifications in cultured hippocampal neurons: dependence on spike timing, synaptic strength, and postsynaptic cell type. J. Neurosci. 18(24), 10464–10472 (1998)
Bi, G., Poo, M.: Synaptic modification by correlated activity: Hebb’s postulate revisited. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24, 139–166 (2001)
Masquelier, T., Thorpe, S.: Unsupervised learning of visual features through spike timing dependent plasticity. PLoS Comput. Biol. 3(2), e31 (2007)
Diehl, P., Cook, M.: Unsupervised learning of digit recognition using spike-timing-dependent plasticity. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 9(99) (2015)
Xiang, S., et al.: STDP-based unsupervised spike pattern learning in a photonic spiking neural network with VCSELs and VCSOAs. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 25(6), 1–9 (2019)
Bohte, S., Kok, J., Poutre, H.: Error-backpropagation in temporally encoded networks of spiking neurons. Neurocomputing 48(1), 17–37 (2002)
Gütig, R., Sompolinsky, H.: The tempotron: a neuron that learns spike timing-based decisions. Nat. Neurosci. 9(3), 420–428 (2006)
Ponulak, F., Kasiński, A.: Supervised learning in spiking neural networks with ReSuMe: sequence learning, classification, and spike shifting. Neural Comput. 22(2), 467–510 (2010)
Xiang, S., et al.: Computing primitive of fully VCSEL-based all-optical spiking neural network for supervised learning and pattern classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 32(6), 2494–2505 (2021)
Sporea, I., Grüning, A.: Supervised learning in multilayer spiking neural networks. Neural Comput. 25(2), 473–509 (2013)
Lee, J., Delbruck, T., Pfeiffer, M.: Training deep spiking neural networks using backpropagation. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 10(508), 1–13 (2016)
Kheradpisheh, S., Ganjtabesh, M., Thorpe, S., Masquelier, T.: STDP-based spiking deep convolutional neural networks for object recognition. Neural Netw. 99, 56–67 (2018)
Tavanaei, A., et al.: Deep learning in spiking neural networks. Neural Netw. 111, 47–63 (2019)
Rueckauer, B., Lungu, I., Hu, Y.: Conversion of continuous-valued deep networks to efficient event-driven networks for image classification. Front. Neurosci. 11(682) (2017)
Sengupta, A., Ye, Y., Wang, R., Liu, C., Roy, K.: Going deeper in spiking neural networks: Vgg and residual architectures. Front. Neurosci. 13(95) (2019)
Ding, J., Shi, Y., Tian, Y., Huang, T.: Optimal ANN-SNN conversion for fast and accurate inference in deep spiking neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.11654 (2021)
Wu, Y., Deng, L., Li, G., Zhu, J., Shi, L.: Spatio-temporal backpropagation for training high-performance spiking neural networks. Front. Neurosci. 12(331) (2018)
Neftci, E., Mostafa, H., Zenke, F.: Surrogate gradient learning in spiking neural networks: bringing the power of gradient-based optimization to spiking neural networks. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 36(6), 51–63 (2019)
Wu, Y. et al.. Direct training for spiking neural networks: faster, larger, better. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 33(1) (2019)
Guo, Y., Huang, X., Ma, Z.: Direct learning-based deep spiking neural networks: a review. Front. Neurosci. 17, 1209795 (2023)
Chen, Y., Zhang, S. et al.: Gradual surrogate gradient learning in deep spiking neural networks. ICASSP, pp. 8927–8931 (2022)
Zhang, T., Xiang, S., Liu., W.: Hybrid spiking fully convolutional neural network for semantic segmentation. ELEC, 12, 3565 (2023)
Han, B., Roy, K.: Deep spiking neural network: energy efficiency through time based coding. Comput. Vis. 12355, 388–404 (2020)
Sengupta, A., Ye, Y., Wang, R., et al.: Going deeper in spiking neural networks: VGG and residual architectures. Front. Neurosci. 13, 95 (2019)
Xiang, S., et al.: Spiking VGG7: deep convolutional spiking neural network with direct training for object recognition. Electronics 11(13), 2097 (2022)
Kim, S., Park, S., Na, B., Sungroh, Y.: Spiking-yolo: spiking neural network for energy-efficient object detection. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 34(7) (2020)
Yamazaki, K., Vo-Ho, V., Bulsara, D., Ngan, L.: Spiking neural networks and their applications: a Review. Brain Sci. 12(7), 863 (2022)
Yilmaz, A., Javed, O., Shah, M.: Object tracking: a survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 38(4), 1–45 (2006)
Chen, F., et al.: Visual object tracking: a survey. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 222, 1–42 (2022)
Bertinetto, L., Valmadre, J., Henriques, J.: Fully-convolutional siamese networks for object tracking. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, Cham, pp 850–865 (2016)
Li, B. et al.: High performance visual tracking with siamese region proposal network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8971–8980 (2018)
Li, B. et al.: Siamrpn++: evolution of siamese visual tracking with very deep networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4282–4291 (2019)
Xu, Y., et al.: Siamfc++: towards robust and accurate visual tracking with target estimation guidelines. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 34(7), 12549–12556 (2020)
Yang, Z., et al.: DashNet: a hybrid artificial and spiking neural network for high-speed object tracking, arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.12942 (2019)
Luo, Y., et al.: SiamSNN: siamese spiking neural networks for energy-efficient object tracking. Neural Netw. 12895, 182–194 (2021)
Luo, Y., et al.: Conversion of Siamese networks to spiking neural networks for energy-efficient object tracking. Neural Comput. Appl. 34(12), 9967–9982 (2022)
Zhang, J., et al.: Spiking transformers for event-based single object tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition., pp. 8801–8810 (2022)
Wu, Y., Lim, J., Yang, M.: Online object tracking: a benchmark. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 2411–2418 (2013)
Wu, Y., Lim, J., Yang, M.: Object tracking benchmark. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 37(9), 1834–1848 (2015)
Kristan, M.: The visual object tracking VOT2016 challenge results. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Lecture Notes in Computer Science vol. 9914, pp. 777–823 (2016)
Kristan, M., et al.: The sixth visual object tracking vot2018 challenge results. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), vol. 11129, pp. 3–53 (2018)
Huang, L., Zhao, X., Huang, K.: Got-10k: a large high-diversity benchmark for generic object tracking in the wild. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 43(5), 1562–1577 (2021)
Xiang, S. et al.: Spiking SiamFC++: deep spiking neural network for object tracking, arXiv preprint arXiv:2209.12010 (2022)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.: Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Proc. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 60(6), 84–90 (2012)
Paszke, A., Gross, S., Massa, F.: Pytorch: an imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. Proc. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 32(721), 8026–8037 (2019)
Fang, W., et al.: SpikingJelly: an open-source machine learning infrastructure platform for spike-based intelligence[J]. Sci. Adv. 9(40), eadi1480 (2023)
Guo, Z., et al.: Online object tracking by sparse and structural model. Cluster Comput 22(2), 2801–2808 (2019)
Mueller, M., Smith, N., Ghanem, B.: A benchmark and simulator for UAV tracking. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 9905, pp. 445–461 (2016)
Kristan, M. et al.: The visual object tracking vot2015 challenge results. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops. pp. 1–23 (2015)
Merolla, P.A., Arthur, J.V., Alvarez-Icaza, R., et al.: A million spiking-neuron integrated circuit with a scalable communication network and interface. Science 345(6197), 668–673 (2014)
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No.2021YFB2801900, 2021YFB2801901, 2021YFB2801902, 2021YFB2801903, 2021YFB2801904), in part by the National Outstanding Youth Science Fund Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62022062), in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61974177), in part by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. QTZX23041).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no Conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiang, S., Zhang, T., Jiang, S. et al. Spiking SiamFC++: deep spiking neural network for object tracking. Nonlinear Dyn 112, 8417–8429 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-024-09525-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-024-09525-8