Abstract
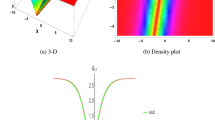
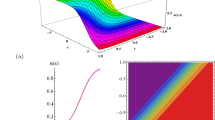
This current work examines the 2-dimensional Sharma–Tasso–Olver system (\(\textrm{STOS}\)). This system is crucial for precise wave motion in real-world applications such as wireless networks, systems for control, and digital signal processing. There are three major goals for this investigation. Firstly, the Lie symmetries are constructed and the corresponding transformation is used to reduce the model to an ordinary differential equation. Invariant solutions are established and illustrated via plots. Secondly, we employ the unified Riccati equation expansion (\(\textrm{UREE}\)) approach to obtain several unique soliton solutions, including single, dark periodic, and rational wave solutions across several physical domains for the \(\textrm{STOS}\). Thirdly, we explore the chaotic structure with and without perturbation to the governing model with time series analysis by using chaos theory. The investigations, which concentrate on the nonlinear dynamic behaviors of the solutions, are new and unexplored. These behaviors are shown in 3-D plots, contour plots, 2-D curves, and descriptions of the related physical properties. Our findings demonstrate that the \(\textrm{UREE}\) approach can potentially be used for producing soliton solutions and analyzing them in nonlinear models and dynamic data. This method offers useful mathematical tools and can be applied to the study of wave motion in a dispersive medium.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Tang, S., Feng, X., Wu, W., Xu, H.: Physics-informed neural networks combined with polynomial interpolation to solve nonlinear partial differential equations. Comput. Math. Appl. 132, 48–62 (2023)
Liu, C.S., Qiu, L.: Solving the 2D and 3D nonlinear inverse source problems of elliptic type partial differential equations by a homogenization function method. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 39(2), 1287–98 (2023)
Malik, S., Hashemi, M.S., Kumar, S., Rezazadeh, H., Mahmoud, W., Osman, M.S.: Application of new Kudryashov method to various nonlinear partial differential equations. Opt. Quantum Electron. 55(1), 8 (2023)
Alquran, M.: New symmetric bidirectional progressive surface-wave solutions to a generalized fourth-order nonlinear partial differential equation involving second-order time-derivative. J. Ocean. Eng. Sci. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joes.2022.06.021
Wazwaz, A.M.: New (3+ 1)-dimensional integrable fourth-order nonlinear equation: lumps and multiple soliton solutions. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 32(5), 1664–73 (2022)
Fronk, M.D., Fang, L., Packo, P., Michael, J.L.: Elastic wave propagation in weakly nonlinear media and metamaterials: a review of recent developments. Nonlinear Dyn. 111, 10709–10741 (2023)
Tawfiq, L.N., Kareem, Z.H.: New modification of decomposition method for solving high order strongly nonlinear partial differential equations. AIP Conf. Proc. 2398, 060036 (2022)
Khater, M.M., Muhammad, S., Al-Ghamdi, A., Higazy, M.: Abundant wave structures of the fractional Benjamin–Ono equation through two computational techniques. J. Ocean. Eng. Sci. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joes.2022.01.009
Yin, Y.H., Lü, X., Ma, W.X.: Bäcklund transformation, exact solutions, and diverse interaction phenomena to a (3+1)-dimensional nonlinear evolution equation. Nonlinear Dyn. 108, 4181–4194 (2022)
Javed, S., Ali, A., Ahmad, J., Hussain, R.: Study the dynamic behavior of bifurcation, chaos, time series analysis and soliton solutions to a Hirota model. Opt. Quantum Electron. 55(12), 1114 (2023)
Rehman, H.U., Akber, R., Wazwaz, A.M., Alshehri, H.M., Osman, M.S.: Analysis of Brownian motion in stochastic Schrödinger wave equation using Sardar sub-equation method. Optik 289, 171305 (2023)
Zhang, R.F., Bilige, S., Liu, J.G., Li, M.: Bright–dark solitons and interaction phenomenon for p-gBKP equation by using bilinear neural network method. Phys. Scr. 96(2), 025224 (2020)
Zhang, R.F., Li, M.C., Gan, J.Y., Li, Q., Lan, Z.Z.: Novel trial functions and rogue waves of generalized breaking soliton equation via bilinear neural network method. Chaos Solit. Fractals 154, 111692 (2022)
Zhang, R.F., Li, M.C.: Bilinear residual network method for solving the exactly explicit solutions of nonlinear evolution equations. Nonlinear Dyn. 108(1), 521–531 (2022)
Ibrahim, S., Ashir, A.M., Sabawi, Y.A., Baleanu, D.: Realization of optical solitons from nonlinear Schrödinger equation using modified Sardar sub-equation technique. Opt. Quantum Electron. 55(7), 617 (2023)
Murad, M.A., Ismael, H.F., Hamasalh, F.K., Shah, N.A., Eldin, S.M.: Optical soliton solutions for time-fractional Ginzburg–Landau equation by a modified sub-equation method. Res. Phys. 53, 106950 (2023)
Ali, A., Ahmad, J., Javed, S.: Exact soliton solutions and stability analysis to (3+1)-dimensional nonlinear Schrödinger model. Alex. Eng. J. 76, 747–56 (2023)
Ozisik, M., Secer, A., Bayram, M.: On solitary wave solutions for the extended nonlinear Schrödinger equation via the modified F-expansion method. Opt. Quantum Electron. 55(3), 215 (2023)
Wazwaz, A.M.: New (3+1)-dimensional Painlevé integrable fifth-order equation with third-order temporal dispersion. Nonlinear Dyn. 106(1), 891–897 (2021)
Wilson, M., Moroni, S., Holzmann, M., Gao, N., Wudarski, F., Vegge, T., Bhowmik, A.: Neural network ansatz for periodic wave functions and the homogeneous electron gas. Phys. Rev. B. 107(23), 235139 (2023)
Chernyak, D., Gainutdinov, A.M., Jacobsen, J.L., Saleur, H.: Algebraic Bethe Ansatz for the open XXZ spin chain with non-diagonal boundary terms via Uqsl2 symmetry. Symmetry Integrab. Geom. Methods Appl. 19, 046 (2023)
Yadav, N., Das, A., Singh, M., Singh, S., Kumar, J.: Homotopy perturbation method and its convergence analysis for nonlinear collisional fragmentation equations. Proc. R. Soc. A. 479(2279), 20230567 (2023)
Alim, M.A., Kawser, M.A.: Illustration of the homotopy perturbation method to the modified nonlinear single degree of freedom system. Chaos Solit. Fractals 171, 113481 (2023)
Salah, M., Ragb, O., Wazwaz, A.M.: Efficient discrete singular convolution differential quadrature algorithm for solitary wave solutions for higher dimensions in shallow water waves. Waves Random Complex (2023). https://doi.org/10.1080/17455030.2022.2136420
Zhang, R., Shah, N.A., El-Zahar, E.R., Akgül, A., Chung, J.D.: Numerical analysis of fractional-order Emden–Fowler equations using modified variational iteration method. Fractals 31(2), 2340028 (2023)
Ain, Q.T., Nadeem, M., Karim, S., Akgül, A., Jarad, F.: Optimal variational iteration method for parametric boundary value problem. AIMS Math. 7(9), 16649–16656 (2022)
Akram, S., Ahmad, J., Alkarni, S., Shah, N.A.: Exploration of solitary wave solutions of highly nonlinear KDV-KP equation arise in water wave and stability analysis. Res. Phys. 54, 107054 (2023)
Yamgoué, S.B., Deffo, G.R., Pelap, F.B.: A new rational sine-Gordon expansion method and its application to nonlinear wave equations arising in mathematical physics. Eur. Phys. J. Plus. 134, 1–15 (2019)
Ali, M.H., El-Owaidy, H.M., Ahmed, H.M., El-Deeb, A.A., Samir, I.: Optical solitons and complexitons for generalized Schrödinger–Hirota model by the modified extended direct algebraic method. Opt. Quantum Electron. 55(8), 675 (2023)
Ali, A., Javed, S., Nadeem, M., Iambor, L.F., Mureşan, S.: A soliton solution for the Kadomtsev–Petviashvili model using two novel schemes. Symmetry 15(7), 1364 (2023)
Wazwaz, A.M., El-Tantawy, S.A.: New (3+1)-dimensional equations of Burgers type and Sharma–Tasso–Olver type: multiple-soliton solutions. Nonlinear Dyn. 87, 2457–2461 (2017)
Zhang, R.F., Li, M.C., Cherraf, A., Vadyala, S.R.: The interference wave and the bright and dark soliton for two integro-differential equation by using BNNM. Nonlinear Dyn. 111(9), 8637–8646 (2023)
Ali, A., Ahmad, J., Javed, S.: Solitary wave solutions for the originating waves that propagate of the fractional Wazwaz–Benjamin–Bona–Mahony system. Alex. Eng. J. 69, 121–33 (2023)
Ali, A., Javed, S., Hussain, R., Muhammad, T.: Secure information transmission using the fractional coupled Schrödinger model: a dynamical perspective. Opt. Quantum Electron. 55(14), 1267 (2023)
Wazwaz, A.M., El-Tantawy, S.A.: Bright and dark optical solitons for (3+1)-dimensional hyperbolic nonlinear Schrödinger equation using a variety of distinct schemes. Optik 270, 170043 (2022)
Kaur, L., Wazwaz, A.M.: Optical soliton solutions of variable coefficient Biswas–Milovic (BM) model comprising Kerr law and damping effect. Optik 266, 169617 (2022)
Adytia, D., Tarwidi, D., Kifli, S.A., Pudjaprasetya, S.R.: Staggered grid implementation of 1D Boussinesq model for simulating dispersive wave. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 971(1), 012020 (2018)
He, J.H., Wu, X.H.: Exp-function method for nonlinear wave equations. Chaos Solitons Fractals 30(3), 700–8 (2006)
Sharma, A.S., Tasso, H.: Connection between wave envelope and explicit solution of a nonlinear dispersive wave equation. Muenchen Germany (1977)
Wang, S., Tang, X.Y., Lou, S.Y.: Soliton fission and fusion: Burgers equation and Sharma–Tasso–Olver equation. Chaos Solitons Fractals 21(1), 231–9 (2004)
Chen, A.: Multi-kink solutions and soliton fission and fusion of Sharma–Tasso–Olver equation. Phys. Lett. A. 374(23), 2340–5 (2010)
Wang, C.: Dynamic behavior of traveling waves for the Sharma–Tasso–Olver equation. Nonlinear Dyn. 85, 1119–1126 (2016)
Wazwaz, A.M.: Two-mode Sharma–Tasso–Olver equation and two-mode fourth-order Burgers equation: multiple kink solutions. Alex. Eng. J. 57(3), 1971–6 (2018)
Wang, G.W., Xu, T.Z.: Invariant analysis and exact solutions of nonlinear time fractional Sharma–Tasso–Olver equation by Lie group analysis. Nonlinear Dyn. 76, 571–580 (2014)
Kuehl, H.H., Zhang, C.Y.: Effects of higher-order dispersion on envelope solitons. Phys. Fluids B Plasma Phys. 2(5), 889–900 (1990)
Chen, Y., Wang, Q.: A unified rational expansion method to construct a series of explicit exact solutions to nonlinear evolution equations. Appl. Math. Comput. 177(1), 396–409 (2006)
Youssif, M.Y., Helal, K.A., Juma, M.Y., Elhag, A.E., Elamin, A.E., Aiyashi, M.A., Abo-Dahab, S.M.: Embed-solitons in the context of functions of symmetric hyperbolic Fibonacci. Symmetry 15(8), 1473 (2023)
Chahlaoui, Y., Ali, A., Ahmad, J., Javed, S.: Dynamical behavior of chaos, bifurcation analysis and soliton solutions to a Konno–Onno model. PLoS ONE 18(9), e0291197 (2023)
Ali, A., Ahmad, J., Javed, S., Rehman, S.U.: Analysis of chaotic structures, bifurcation and soliton solutions to fractional Boussinesq model. Phys. Scr. 98, 075217 (2023)
Tariq, K.U., Bekir, A., Nisar, S.: The dynamical structures of the Sharma–Tasso–Olver model in doubly dispersive medium. Chaos Solitons Fractals 177, 114290 (2023)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Chunhui Project of the Chinese Ministry of Education (202201245).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JL developed the study design. MN wrote the manuscript and performed the simulation of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors claim to have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Nadeem, M. Analysis of the dynamical perspective of chaos, Lie symmetry, and soliton solution to the Sharma–Tasso–Olver system. Nonlinear Dyn 112, 3835–3850 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-09250-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-09250-8