Abstract
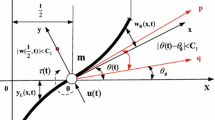
Satellite borne flexible structure is a multi-degree-of-freedom system, which contains complex dynamic characteristics such as time-varying parameters, geometric nonlinearity, gap nonlinearity, and so on. Flexible structure suspension typically results in geometric nonlinearity. The oscillation equation with nonlinear term is established according to the law of motion of a nonlinear pendulum and considering the influence of medium swing angle and lateral force. The perturbation approach is used to get the relationship between vibration frequency and the nonlinear term, and the impact of factors on vibration characteristics is investigated. The satellite borne flexible structure’s active vibration control (AVC) system is then established. Considering proportional differential (PD) or fuzzy control adjustment, variable step size least mean square (VSS-LMS) adaptive filtering algorithm is used to calculate the control signal, and considering the influence of geometric nonlinearity, the actuator is used to suppress the vibration of the satellite borne flexible structure. Finally, the vibration response’s amplitude under steady-state excitation significantly decreases as an outcome of the vibration control simulation.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data underlying this article will be shared on reasonable request to the corresponding author.
References
Liu, J.Y., Sun, Y., Yao, M.H., Ma, J.G.: Stability analysis and nonlinear vibrations of the ring truss antenna with the six-dimensional system. J. Vib. Eng. Technol. 1–22 (2022)
Cao, S.L., Huo, M.Y., Qi, N.M., Zhao, C., Zhu, D.F., Sun, L.J.: Extended continuum model for dyamic analysis of beam-like truss structures with geometrical nonlinearity. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 103, 105927 (2020)
Zhang, W., Zheng, Y., Liu, T., Guo, X.Y.: Multi-pulse jumping double-parameter chaotic dynamics of eccentric rotating ring truss antenna under combined parametric and external excitations. Nonlinear Dyn. 98(1), 761–800 (2019)
Siriguleng, B., Zhang, W., Liu, T., Liu, Y.Z.: Vibration modal experiments and modal interactions of a large space deployable antenna with carbon fiber material and ring-truss structure. Eng. Struct. 207, 109932 (2019)
Hu, H.Y., Tian, Q., Zhang, W., Jin, D.P., Hu, G.K., Song, Y.P.: Nonlinear dynamics and control of large deployable space structures composed of trusses and meshes. Adv. Mech. 43(4), 390–414 (2013)
Wang, P.P., Wang, B., Shi, T., Zheng, S.K., Ma, X.F.: Gravity influence on thermal distortion of a large deployable antenna. J. Mech. Eng. 57(3), 69–76 (2021)
Tian, D., Fan, X.D., Zheng, X.J., Liu, R.Q., Guo, H.W., Deng, Z.Q.: Research status and prospect of micro-gravity environment simulation for space deployable antenna. J. Mech. Eng. 57(3), 11–25 (2021)
Ma, G.L., Xu, M.L., Dong, L.L., Zhang, Z.: Multi-point suspension design and stability analysis of a scaled loop truss antenna structure. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 21(6), 2150077 (2021)
Zhang, W., Chen, J., Sun, Y.: Nonlinear breathing vibrations and chaos of a circular truss antenna with 1:2 internal resonance. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 26(5), 1650077 (2016)
Wu, R.Q., Zhang, W., Behdinan, K.: Vibration frequency analysis of beam-ring structure for circular deployable truss antenna. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 19(2), 1950012 (2018)
Zhang, W., Wu, R.Q., Behdinan, K.: Nonlinear dynamic analysis near resonance of a beam-ring structure for modeling circular truss antenna under time-dependent thermal excitation. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 86, 296–311 (2019)
Siriguleng, B., Zhang, W., Liu, T.: Vibration modal experiments and modal interactions of a large space deployable antenna with carbon fiber material and ring-truss structure. Eng. Struct. 207, 109932 (2020)
Greschik, G., Belvin, W.K.: High-fidelity gravity offloading system for free-free vibration testing. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 44(1), 132–142 (2007)
Sato, Y., Ejiri, A., Iida, Y., Kanda, S.: Micro-G emulation system using constant tension suspension for a space manipulator. In: Proceedings of the 1991 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Sacramento, CA, USA, vol. 3, pp. 1893–1900. (1991)
Liu, Z., Gao, H.B., Deng, Z.Q.: Design of the low gravity simulation system for planetary rovers. Robot 35(6), 750–756 (2013)
Fischer, A., Pellegrino, S.: Interaction between gravity compensation suspension system and deployable structure. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 37(1), 93–99 (2000)
Yang, Q.L., Yan, Z., Ren, S.Z., Song, X.D., He, P.P.: Study on gravity compensation in ground deployment tests of large retractable flexible solar array driven by telescopic boom. Manned Spacefl. 23(4), 536–545 (2017)
Luo, Y.J., Xu, M.L., Yan, B., Zhang, X.N.: PD control for vibration attenuation in Loop truss structure based on a novel piezoelectric bending actuator. J. Sound Vib. 339, 11–24 (2015)
An, Z.Y., Xu, M.L., Luo, Y.J., Wu, C.S.: Active vibration control for a large annular flexible structure via a macro-fiber composite strain sensor and voice coil actuator. Int. J. Appl. Mech. 7(4), 1550066 (2015)
Ma, G.L., Gao, B., Xu, M.L., Feng, B.: Active suspension method and active vibration control of a loop truss structure. AIAA J. 56(4), 1689–1695 (2018)
Ding, H., Wang, S., Zhang, Y.W.: Free and forced nonlinear vibration of a transporting belt with pulley support ends. Nonlinear Dyn. 92(4), 2037–2048 (2018)
Taha, E.S., Bauomy, H.S.: A beam–ring circular truss antenna restrained by means of the negative speed feedback procedure. J. Vib. Control 28(15–16), 2032–2051 (2022)
Ma, G.L., Xu, M.L., Chen, L.Q.: The response analysis and vibration control of flexible arms with two nonlinear factors. Int. J. Appl. Mech. 13(1), 2150005 (2021)
Luo, Y.J., Zhang, Y.H., Xu, M.L., Fu, K.K., Ye, L., Xie, S.L., Zhang, X.N.: Improved vibration attenuation performance of large loop truss structures via a hybrid control algorithm. Smart Mater. Struct. 28(6), 065007 (2019)
Li, F.M., Song, Z.G.: Vibration analysis and active control of nearly periodic two-span beams with piezoelectric actuator/sensor pairs. Appl. Math. Mech. (English Edition) 36(3), 279–292 (2015)
Guo, X.Y., Zhu, Y., Qu, Y.G., Cao, D.X.: Design and experiment of an adaptive dynamic vibration absorber with smart leaf springs. Appl. Math. Mech. (English Edition) 43(10), 1485–1502 (2022)
Wang, C.S., Liang, S., Wei, L.M.: Investigation on the dynamic characteristics of the new smart vibration isolation composite structure. J. Vib. Shock 34(8), 61–65 (2015)
Wang, X.B., Zhu, C.S.: Multi-frequency compensation for active magnetic bearing-flexible rotor system based on adaptive least mean square algorithm with a phase shift. J. Mech. Eng. 57(17), 110–119 (2021)
Shi B., Ji H.L., Qiu J.H., Wu Y.P.: An ultra-low frequency vibration semi-active controller based on adaptive filter and synchronized switch damping techniques. In: Proceedings of the 12th National Conference on Vibration Theory and Application, Nanning, vol. 10, pp. 21–23. (2017)
Yang, D.P., Song, D.F., Zeng, X.H., Wang, X.L., Zhang, X.M.: Adaptive nonlinear ANC system based on time-domain signal reconstruction technology. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 162(22), 108056 (2022)
Li, W.G., Yang, Z.C., Li, K., Wang, W.: Hybrid feedback PID-FxLMS algorithm for active vibration control of cantilever beam with piezoelectric stack actuator. J. Sound Vib. 509(4), 116243 (2021)
Zhu, X.J.: Analysis and validation of the active vibration control of flexible piezoelectric beam with Fx-VSSLMS algorithms. Vib. Test Diagn. 2, 215–221 (2020)
Tang, X., Du, H.P., Sun, S.S., Ning, D.H., Xing, Z.W., Li, W.H.: Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy control for a semi-active vehicle suspension system with an magneto-rheological damper and experimental validation. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2(1), 291–300 (2017)
Wang, Y.W., Sun, H.B., Hou, L.L.: Event-triggered anti-disturbance attitude and vibration control for T-S fuzzy flexible spacecraft model with multiple disturbances. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 117, 106973 (2021)
Zhang, M.H., Jing, X.J.: A bioinspired dynamics-based adaptive fuzzy smc method for half-car active suspension systems with input dead zones and saturations. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 51(4), 1743–1755 (2021)
Wang, Y.N., Liu, K.: Vibration suppression of magnetic levitation flywheel based on variable step size LMS method. J. Dyn. Control 20(3), 77–82 (2022)
Ma, X.F., Yang, J.G., Hu, J.F., Zhang, X., Xiao, Y., Zhao, Z.H.: Deployment dynamical numerical simulation on large elliptical truss antenna. Chin. Sci. Phys. Mech. Astron. 49(2), 143–151 (2019)
Funding
This work is supported by the Ministry of Education Chunhui Program Cooperative Research Project of China (No. HZKY20220517) and Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China (No. 2022JQ-021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research and publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, G., Wang, P., Chen, L. et al. Suspension nonlinear analysis and VSS-LMS adaptive filtering control of satellite borne flexible structure. Nonlinear Dyn 112, 3679–3693 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-09222-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-09222-y