Abstract
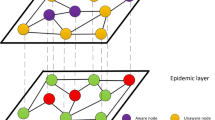
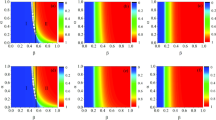
The impact of social influence on the dynamic of awareness diffusion and epidemic spreading has been researched adequately, while the feedback effect of individuals on social influence does not receive enough attention. In this study, we sought to propose a model composed of a two-layer network with complex awareness. Initially, we design expert nodes based on regret theory to characterize social influence and symmetrical interaction, including the impact of experts and the feedback of individuals. Then, we describe the social structure in the form of the simple contagion model and consider the superposition effect. According to the microscopic Markov chain approach (MMCA) derivation, a clear association emerges between epidemic threshold and complex awareness diffusion. Extensive numerical simulations reveal two implications: (1) Widening the channels of information dissemination could contribute to epidemic prevention; (2) Intensifying the recurrent diffusion of complex social awareness is beneficial to epidemic control.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analysed in this study.
References
Dezső, Z., Barabási, A.-L.: Halting viruses in scale-free networks. Phys. Rev. E 65(5), 055103 (2002)
Newman, M.E.J.: Spread of epidemic disease on networks. Phys. Rev. E 66(1), 016128 (2002)
Boguñá, M., Pastor-Satorras, R.: Epidemic spreading in correlated complex networks. Phys. Rev. E 66(4), 047104 (2002)
Tran, V.T., Nguyen, T.K., Nguyen-Xuan, H., Wahab, M.A.: Vibration and buckling optimization of functionally graded porous microplates using BCMO-ANN algorithm. Thin-Walled Struct. 182, 110267 (2023)
Dang, B.L., Nguyen-Xuan, H., Wahab, M.A.: An effective approach for VARANS-VOF modelling interactions of wave and perforated breakwater using gradient boosting decision tree algorithm. Ocean Eng. 268, 113398 (2023)
Wang, S., Wang, H., Zhou, Y., Liu, J., Dai, P., Du, X., Wahab, M.A.: Automatic laser profile recognition and fast tracking for structured light measurement using deep learning and template matching. Measurement 169, 108362 (2021)
Zhang, L., Jin, Q., Fan, S., Liu, D.: A novel dual-center based intuitionistic Fuzzy twin bounded large margin distribution machines. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 31(9), 3121–3134 (2023)
Zhang, L.B., Yu, Z.H., Wu, S.Y., Zhu, H.B., Sheng, Y.: Adaptive collaboration with training plan considering role correlation. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSS.2022.3204052
Pastor-Satorras, R., Castellano, C., Van Mieghem, P., Vespignani, A.: Epidemic processes in complex networks. Rev. Mod. Phys. 87(3), 925 (2015)
Pastor-Satorras, R., Vespignani, A.: Epidemic dynamics and endemic states in complex networks. Phys. Rev. E. 63(6), 066117 (2001)
Kaye, P.M.: Infectious diseases of humans: dynamics and control. Immunol. Today 14(12), 616 (1993)
Gómez, S., Arenas, A., Borge-Holthoefer, J., Meloni, S., Moreno, Y.: Discrete-time Markov chain approach to contact-based disease spreading in complex networks. Europhys. Lett. 89(3), 38009 (2010)
Li, C., Wang, H., Van Mieghem, P.: Epidemic threshold in directed networks. Phys. Rev. E 88(6), 062802 (2013)
Karrer, B., Newman, M.E.J.: Message passing approach for general epidemic models. Phys. Rev. E 82(1), 016101 (2010)
Shrestha, M., Scarpino, S.V., Moore, C.: Message-passing approach for recurrent-state epidemic models on networks. Phys. Rev. E 92(2), 022821 (2015)
Wang, W., Liu, Q.-H., Zhong, L.-F., Tang, M., Gao, H., Stanley, H.E.: Predicting the epidemic threshold of the susceptible-infected-recovered model. Sci. Rep. 6(1), 24676 (2016)
Wang, J., Li, C., Xia, C.: Improved centrality indicators to characterize the nodal spreading capability in complex networks. Appl. Math. Comput. 334, 388–400 (2018)
Li, C., Wang, L., Sun, S., Xia, C.: Identification of influential spreaders based on classified neighbors in real-world complex networks. Appl. Math. Comput. 320, 512–523 (2018)
Funk, S., Gilad, E., Watkins, C., Jansen, V.A.: The spread of awareness and its impact on epidemic outbreaks. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 106(16), 6872–6877 (2009)
Ruan, Z., Tang, M., Liu, Z.: Epidemic spreading with information-driven vaccination. Phys. Rev. E 86(3), 036117 (2012)
Granell, C., Gómez, S., Arenas, A.: Dynamical Interplay between awareness and epidemic spreading in multiplex networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111(12), 128701 (2013)
Zhang, L., Guo, C., Feng, M.: Effect of local and global information on the dynamical interplay between awareness and epidemic transmission in multiplex networks. Chaos: An Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 32(8), 083138 (2022)
Zhan, X.-X., Liu, C., Zhou, G., Zhang, Z.-K., Sun, G.-Q., Zhu, J.J.H., Jin, Z.: Coupling dynamics of epidemic spreading and information diffusion on complex networks. Appl. Math. Comput. 332, 437–448 (2018)
Balcan, D., Colizza, V., Gonçalves, B., Hu, H., Ramasco, J.J., Vespignani, A.: Multiscale mobility networks and the spatial spreading of infectious diseases. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 106(51), 21484–21489 (2009)
Ruan, Z., Hui, P., Lin, H., Liu, Z.: Risks of an epidemic in a two-layered railway-local area traveling network. The Eur. Phys. J. B. 86, 1–8 (2013)
Ruan, Z., Wang, C., Ming Hui, P., Liu, Z.: Integrated travel network model for studying epidemics: interplay between journeys and epidemic. Sci. Rep. 5(1), 11401 (2015)
Li, Y., Zeng, Z., Feng, M., Kurths, J.: Protection degree and migration in the stochastic SIRS model: a queueing system perspective. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. I Regul. Pap. 69(2), 771–783 (2021)
Li, Q., Chen, H., Li, Y., Feng, M., Kurths, J.: Network spreading among areas: a dynamical complex network modeling approach. Chaos: An Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 32(10), 103102 (2022)
Sun, C., Yang, W., Arino, J., Khan, K.: Effect of media-induced social distancing on disease transmission in a two patch setting. Math. Biosci. 230(2), 87–95 (2011)
Cai, Y., Kang, Y., Banerjee, M., Wang, W.: A stochastic epidemic model incorporating media coverage. Commun. Math. Sci. 14(4), 893–910 (2016)
Granell, C., Gómez, S., Arenas, A.: Competing spreading processes on multiplex networks: awareness and epidemics. Phys. Rev. E 90(1), 012808 (2014)
Wu, Q., Fu, X., Small, M., Xu, X.J.: The impact of awareness on epidemic spreading in networks. Chaos: An Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 22(1), 013101 (2012)
Wang, Z., Guo, Q., Sun, S., Xia, C.: The impact of awareness diffusion on SIR-like epidemics in multiplex networks. Appl. Math. Comput. 349, 134–147 (2019)
Liu, Q.H., Wang, W., Tang, M., Zhang, H.F.: Impacts of complex behavioral responses on asymmetric interacting spreading dynamics in multiplex networks. Sci. Rep. 6(1), 25617 (2016)
Huang, H., Chen, Y., Yan, Z.: Impacts of social distancing on the spread of infectious diseases with asymptomatic infection: A mathematical model. Appl. Math. Comput. 398, 125983 (2021)
Iacopini, I., Petri, G., Barrat, A., Latora, V.: Simplicial models of social contagion. Nat. Commun. 10(1), 2485 (2019)
Wang, Y., Wang, L.: Interplay between complex contagion of awareness and epidemic spreading in two-layer network. In: 2020 39th Chinese Control Conference (CCC) (pp. 765-770). IEEE (2020)
Wang, T., Li, H., Qian, Y., Huang, B., Zhou, X.: A regret-based three-way decision model under interval type-2 fuzzy environment. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 30(1), 175–189 (2020)
Bleichrodt, H., Cillo, A., Diecidue, E.: A quantitative measurement of regret theory. Manage. Sci. 56(1), 161–175 (2010)
Wang, J., Ma, X., Xu, Z., Zhan, J.: Regret theory-based three-way decision model in hesitant fuzzy environments and its application to medical decision. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 30(12), 5361–5375 (2022)
Liew, K.M., Akbar, A.: The recent progress of recycled steel fiber reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 232, 117232 (2020)
Gale, C.M., Eikeseth, S., Klintwall, L.: Children with autism show atypical preference for non-social stimuli. Sci. Rep. 9(1), 10355 (2019)
Hébert-Dufresne, L., Scarpino, S.V., Young, J.G.: Macroscopic patterns of interacting contagions are indistinguishable from social reinforcement. Nat. Phys. 16(4), 426–431 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62106205), Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing (Nos. cstc2021jcyj-msxmX0824 and cstc2021jcyj-msxmX0565), the Humanities and Social Science Fund Ministry of Education of the People’s Republic of China under Grant (No. 21YJCZH028), and the project of science and technology research program of Cho-ngqing Education Commission of China (Nos. KJQN202100207 and KJZD-K202100203).
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, S., Wang, Y., Guo, C. et al. Effects of experts on the coupling dynamics of complex contagion of awareness and epidemic spreading. Nonlinear Dyn 112, 2367–2380 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-09146-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-09146-7